Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2437–2469) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic glucocorticoid (GC) therapy is indispensable for treating active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN), while contributing significantly to comorbidities and irreversible damage. The judicious limitation of GC use while effectively managing disease activity represents a critical yet unresolved challenge. This study aimed to formulate pragmatic recommendations for GC utilization in SLE.
Methods: Adhering to established consensus guideline procedures, Taiwan College of Rheumatology (TCR) SLE Special Interest Group (SLE-SIG) formulated a set of recommendations utilizing a systematic literature review and a formalized Delphi process. The literature review group identified the topics of interest and the scope of review, and generated preliminary statements. The selected questions constitute (1) general GC usage, tapering, and targets, (2) GC dosing across organ systems, and (3) special considerations on SLE antiphospholipid syndrome, SLE pulmonary arterial hypertension, and pregnancy. Organ involvements and severities were evaluated based on BILAG-2004 and SLEDAI-2K. The GC doses were specified in weight-adjusted daily doses (prednisolone equivalent) and the GC pulses were described in daily doses (methylprednisolone equivalent.) A preliminary Delphi round by the expert panel was exercised to deduce the statements based on evidence review and group consensus, and the final statements were modified.
Results: A series of consensus statements encompassed three overarching principles regarding GC utilization in SLE, five general recommendations pertaining to GC initiation, tapering, and therapeutic goals, and eleven organ-specific recommendations. The preliminary evaluation of GC regimens for active SLE involved assessing organ involvement and severity, considering comorbidities and the potential risk of complications, and evaluating concomitant medication regimens, including immunosuppressants and biologics. The initial GC dose and GC pulse therapy were determined based on this evaluation, with the utilization of a tapering protocol to reach the target long-term GC dose at 5 mg/day by week 24 (Figure).Organ-specific statements delineated the recommended initial GC dose and GC pulses. Organ involvement was categorized as mild disease and constitutional symptoms, mucocutaneous and arthritis, lupus nephritis (LN), neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE), and internal organ SLE. The latter three categories were further stratified according to severity for LN and NPSLE, and potential life- or organ-threatening disease for internal organ SLE, respectively. Statements regarding GC use in special considerations, including SLE with anti-phospholipid syndrome (SLE-APS), SLE with pulmonary arterial hypertension (SLE-PAH), and pregnancy, were also provided (Table).This report presents preliminary consensus statements, subject to a formal Delphi process and subsequent voting by the expert panel to establish agreement levels. The final recommendations will be revised accordingly.
Conclusion: These preliminary statements provide evidence-driven, consensus-based guidance on GC dosing in SLE.
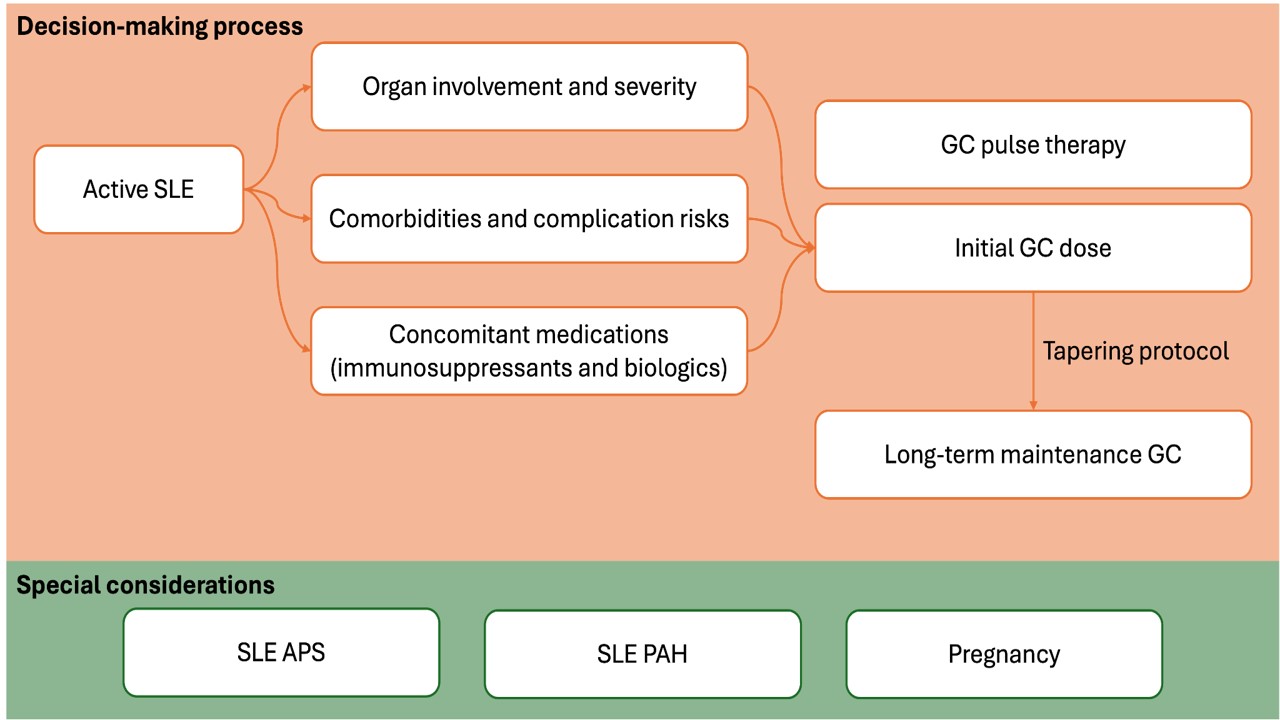 Figure Proposed decision-making process of glucocorticoid dosing in SLE
Figure Proposed decision-making process of glucocorticoid dosing in SLE
.jpg) Table Summary of preliminary recommendations of initial glucocorticoid doses
Table Summary of preliminary recommendations of initial glucocorticoid doses
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sheu H, Huang W, Fang Y, Lee T, Lu L, Chen M, Chen D, Yeh F, Liao Y, Tsai C, Hsieh T, Hsieh S, Luo S, Su Y, Wu Y, Lu C. Development of Consensus Statements on Glucocorticoid Use in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-consensus-statements-on-glucocorticoid-use-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-consensus-statements-on-glucocorticoid-use-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
