Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease primarily affecting spine and sacroiliac joints (SIJ), leading to pain and disability. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has transformed axSpA diagnosis in non-radiographic cases–undetectable on X-rays–, guiding treatment and improving long term outcomes. As per the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis international Society (ASAS), “active sacroiliitis” requires bone marrow edema (BME) on T2-weighted MRI, indicating SIJ inflammation highly suggestive of axSpA. However, “positive MRI” definitions vary, with high inter-/intra-observer variability and frequent underdiagnosis, contributing to a mean 7-year delay. Thus, standardized, automated tools are needed. This study aimed to develop an artificial intelligence (AI)-based model to detect active axSpA on MRI.
Methods: This retrospective, observational study (NCT06591481) used real-world data from six international sites. The dataset included 684 SIJ MRIs, each with coronal-oblique T2 short tau inversion recovery (STIR) or T2 fat-saturated (FS) sequences acquired at diagnosis and follow-up. Imaging data were collected and processed using Quibim platform (Quibim SL, Valencia, Spain). All scans underwent quality checks by three radiographers with >5 years of experience on image interpretation. Following ASAS criteria, MRIs were double read by radiologists with >12 years of experience, with adjudication by a third reader. Scans were classified as positive active sacroiliitis on MRI (ASAS-positive MRI; BME on two consecutive slices) or negative, and structural damage (ankylosis, erosion and fat metaplasia) were noted. A deep-learning-based AI classification model was developed to identify axSpA patients with ASAS-positive MRI. Of the total 684 cases, 563 were used for training and validation, and 121 for testing. The model performs automated sacroiliac joint segmentation on T2 imaging to predict BME presence across patient slices. Detection of two consecutive positive slices yields a positive patient diagnosis. To enhance interpretability, heat maps highlight the regions that most influence the model’s predictions.
Results: Overall, 32% of patients (n = 218) fulfilled the ASAS classification criteria for axSpA. The model achieved high balanced accuracy (bal acc = 81.3%), sensitivity (se = 71.4%) and specificity (sp = 91.1%) for ASAS-positive MRI detection. Performance was higher (bal acc = 89.3%; se = 84% and spe = 94.5%) in cases with consensus readings and clearly visible lesions on at least two consecutive slices. However, performance declined (bal acc = 51.5%) in cases with poor image quality, motion artifacts, or subtle lesions, highlighting the need for expert oversight. In such cases heat maps can assist in achieving a correct diagnosis.
Conclusion: We developed an AI-based classification model with high diagnostic performance in detecting MRI-positive axSpA, especially in terms of specificity (91.1%). This tool could support radiologists by standardizing MRI interpretation. Its integration into clinical workflows may enhance diagnostic accuracy and improve patient care.
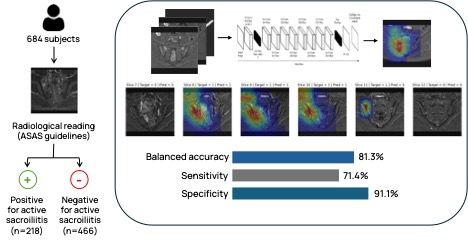 Figure 1. Development of AI-based tool for lesion detection in axSpA patients with active sacroiliitis using MRI
Figure 1. Development of AI-based tool for lesion detection in axSpA patients with active sacroiliitis using MRI
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alnaqbi K, Fragío Gil J, Khogali H, Statache G, Abouelnadar A, Almarzooqi A, AlJasmi A, Shawaqfeh J, Mashaleh M, Bani Hani M, Alshammari S, Alghamdi Y, Alfaisal F, Almosabihi A, Campos Fernández C, González Mazario R, Lozano-Montoya J, Jiménez-Pastor A, Moreno-Ruiz P, Martínez-Calle M, bellvís-Bataller F, Fuster-Matanzo A. Development of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Lesion Detection in Axial Spondyloarthritis patients with Active Sacroiliitis on Magnetic Resonance Imaging [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-an-artificial-intelligence-tool-for-lesion-detection-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-with-active-sacroiliitis-on-magnetic-resonance-imaging/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-an-artificial-intelligence-tool-for-lesion-detection-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-with-active-sacroiliitis-on-magnetic-resonance-imaging/
