Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a group of vasculitides that consists of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss; EGPA), and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA). Large-vessel vasculitis (LVV) includes Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) and giant cell arteritis (GCA). Validated algorithms are needed to accurately identify patients with AAV and LVV in administrative databases. This study sought to evaluate and validate case-finding algorithms for AAV and LVV in 3 large health administrative databases.
Methods: To develop the algorithms, 125 patients per disease and per healthcare system (System 1 and System 2) were randomly selected using the International Classification of Diseases version 9 (ICD9) codes for GPA: 446.4, EGPA: 446.4, MPA: 446.0, TAK: 446.7, and GCA: 446.5. 16 case-finding algorithms were constructed using a combination of ICD9 code, encounter type (1 inpatient ICD9 code on 3 consecutive days or 2 outpatient ICD9 codes 3 months apart), physician specialty, use of immunosuppressive medications, ANCA pattern (for AAV), and age (< 50 and ≥ 50 years) for LVV algorithms. The diagnosis was confirmed by chart review using the modified ACR classification criteria or the Chapel Hill Consensus Conference definitions for each disease. The positive predictive value (PPV) of each algorithm was calculated. For validation, algorithms with the highest average PPV from both Systems 1 and 2 with at least sensitivity > 50% were validated in the third healthcare system (System 3).
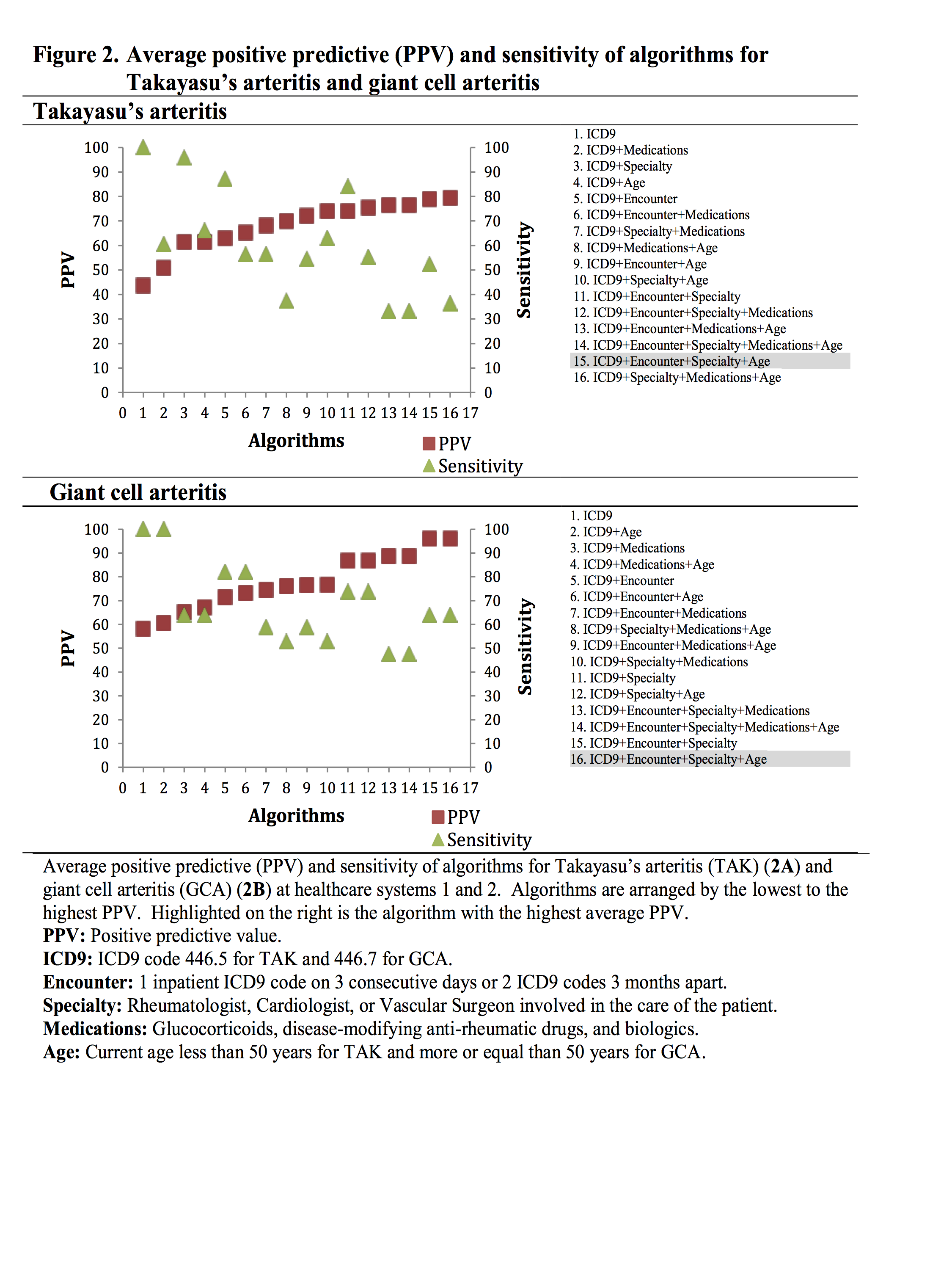
Results: A total of 1,250 patients were included in the study. Figures 1 and 2 show the average PPV and sensitivity of the 16 algorithms for AAV and LVV tested in Systems 1 and 2. The ICD9 code alone had a low PPV. Most algorithms with the highest average PPV had the encounter and/or specialty variables as part of the algorithm. Adding the ANCA pattern increased PPV in AAV algorithms. Table 1 shows the PPV of algorithms with the highest average PPV validated in System 3.
Conclusion: Case-finding algorithms can accurately identify patients with AAV and LVV. These algorithms can be used to assemble population-based cohorts of patients with AAV and LVV and facilitate future research in healthcare use, outcomes, and comparative effectiveness.
| Table 1. Positive predictive value of the algorithms with the highest average positive predictive value developed from Systems 1 and 2, and validated in System 3 | |||
| Algorithm | PPV % | 95% CI | |
| GPA | ICD9+Encounter+Specialty | 92.5 | 87.0 – 97.9 |
| ICD9+Encounter+Specialty+cANCA* | 100.0 | 99.1 – 100.0 | |
| EGPA | ICD9+Specialty | 100.0 | 73.5 – 100.0 |
| ICD9+Specialty+ pANCA* | 100.0 | 47.8 – 100.0 | |
| MPA | ICD9+Encounter+Specialty+Medications | 76.2 | 60.4 – 91.9 |
| ICD9+Encounter+Specialty+Medications+pANCA* | 100.0 | 82.5 – 100.0 | |
| TAK | ICD9+Encounter+Specialty+Age | 78.8 | 68.1 – 89.4 |
| GCA | ICD9+Encounter+Specialty+Age | 95.9 | 91.7 – 100.0 |
| *Given that the anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) test is not readily searchable in many healthcare systems we sought to validate algorithms with and without the ANCA pattern. PPV: Positive predictive value; CI: Confidence interval. GPA: Granulomatosis with polyangiitis; EGPA: Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; MPA: Microscopic polyangiitis; TAK: Takayasu’s arteritis; GCA: Giant cell arteritis. ICD9: 446.4 for GPA/EGPA; 446.0 for MPA; 446.5 for TAK; 446.7 for GCA. Encounter: 1 inpatient ICD9 code on 3 consecutive days or 2 ICD9 codes 3 months apart. Specialty: Rheumatologist, Allergist/Immunologist, Nephrologist, Pulmonologist, or Otorhinolaryngologist involved in the care of the patients with GPA, EGPA, or MPA. Rheumatologist, Cardiologist, or Vascular Surgeon involved in the care of the patients with TAK or GCA. ANCA: Positive test for cytoplasmic pattern (cANCA) and perinuclear pattern (pANCA) of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody. Medications: Glucocorticoids, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, and biologics. Age: Current age less than 50 years for TAK and more or equal than 50 years for GCA. | |||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sreih AG, Annapureddy N, Springer J, Byram K, Casey G, Cruz A, Estephan M, Frangiosa V, George MD, Liu M, Maz M, Parker A, Sangani S, Sharim R, Merkel PA. Development and Validation of Case-Finding Algorithms for the Identification of Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Large-Vessel Vasculitis in Healthcare Administrative Databases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-case-finding-algorithms-for-the-identification-of-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-and-large-vessel-vasculitis-in-healthcare-administrative-databases/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-case-finding-algorithms-for-the-identification-of-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-and-large-vessel-vasculitis-in-healthcare-administrative-databases/