Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Recent studies have highlighted the potential of composite scores such as the DAPSA for assessing peripheral arthritis in axSpA and pSpA. However, the swollen (SJC66) and tender (TJC68) joint counts required for the DAPSA calculation are often unavailable in axSpA randomized controlled trials.This study aimed to develop and evaluate the construct validity of a modified-DAPSA score using the 44-joint count in patients with SpA (axSpA, pSpA, and PsA).
Methods: In this ancillary analysis of the ASAS-PerSpA study, patients with axSpA, pSpA, or PsA were included and allocated at random by diagnosis and country into two a derivation (33%) and a validation cohort (66%). The derivation cohort was used to calculate conversion factors for SJC66/TJC68 to SJC44/TJC44, to allow the calculation of DAPSA44, using mixed-effects linear regression models. The validation cohort assessed the new score’s construct validity through: i) agreement between original-DAPSA and DAPSA44, evaluated as a continuous score with the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) and categorically with disease activity states with weighted kappa coefficients, along with Bland-Altman plots; ii) original-DAPSA and DAPSA44 correlations with external constructs, with a predefined 0.3-wide acceptable range of difference between the scores; iii) the discrimination between known groups, calculated using standardized mean differences (SMDs) after stratifying patients into active/inactive based on a combination of PGA (≥5/ < 5) and SJC (≥1/0 or ≥2/ < 2, median SJC). An SMD with higher absolute value indicates better discriminatory ability, and an SMD above 0.8 is considered as ‘good’.
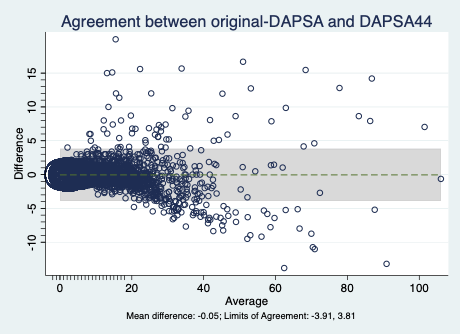
Results: A total of 4121 patients with complete data on disease activity measures were analyzed, including 2679 (65%) with axSpA, 428 (10%) with pSpA, and 1014 (25%) with PsA. A history of peripheral arthritis was reported in 2291 (56%) patients, predominantly with oligoarticular (43%) or polyarticular involvement (45%). The prevalence of peripheral arthritis varied across disease phenotypes: 36% in axSpA, 95% in pSpA and 91% in PsA. Conversion factors from the derivation cohort (n=1364) from TJC68 and SJC66 to TJC/SJC44 were 1.3 and 1.3, respectively. The mean DAPSA44 scores were similar between cohorts: 12.6 (SD 12.3) in the derivation and 12.2 (SD 12.4) in the validation cohort (p=0.33). The validation cohort (n=2757) analyses showed near-perfect agreement between DAPSA-original and DAPSA44, with a ICC 0.98, 95% CI 0.98–0.99 and kappa=0.95. The Bland–Altman plot demonstrated a mean difference of 0.25 points with a 95% limit of agreement between 0.25 and –0.02. (Figure 1)In correlation analyses, Spearman coefficients between DAPSA44 and external constructs fell within the predefined 0.3-wide range of corresponding DAPSA-original coefficients, with some coefficients even showing identical values. For discrimination between active and inactive disease, DAPSA44 demonstrated excellent discriminatory ability (SDM >0.8) across all scenarios.
Conclusion: These findings support the use of DAPSA44 as a comparable tool to DAPSA-original for assessing disease activity due to peripheral arthritis, in situations where only a reduced joint count is available.
.gif) Figure 1. Bland–Altman plot. Agreement between original-DAPSA and DAPSA44.
Figure 1. Bland–Altman plot. Agreement between original-DAPSA and DAPSA44.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
capelusnik D, López Medina C, Van Der Heijde D, Aletaha D, Smolen J, Molto A, Ramiro S. Development and validation of a Disease Activity index for PSoriatic Arthritis based on 44 joints: DAPSA44 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-a-disease-activity-index-for-psoriatic-arthritis-based-on-44-joints-dapsa44/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-a-disease-activity-index-for-psoriatic-arthritis-based-on-44-joints-dapsa44/