Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) mediates signaling of key cytokines (eg, Type 1 IFNs, IL-23, and IL-12) involved in lupus pathogenesis. Deucravacitinib (DEUC) has a unique mechanism of action distinct from Janus kinase (JAK) 1/2/3 inhibitors, being an oral, selective, allosteric TYK2 inhibitor. DEUC demonstrated a favorable safety and efficacy profile in a phase 2 trial in patients with PsA, a phase 2 trial in patients with active SLE, and 2 phase 3 trials in patients with plaque psoriasis. The phase 2 PAISLEY study in patients with active SLE assessed the effects of DEUC on levels of immunological markers of TYK2-mediated pathways, B cell pathways, and serological biomarkers.
Methods: The 48-week (wk), double-blind trial (NCT03252587) enrolled 363 SLE patients randomized 1:1:1:1 to placebo (PBO) or DEUC 3 mg twice daily (BID), 6 mg BID, or 12 mg once daily (QD).1 Whole blood transcripts, serum proteins, blood cell subsets, and antibody profiles at screening and baseline through wk 48 were measured by immunoassays and flow cytometry. In a substudy, samples were collected from 83 subjects 22 to 114 hours after the initial dose. Samples from demographically matched healthy subjects were collected and measured for comparison.
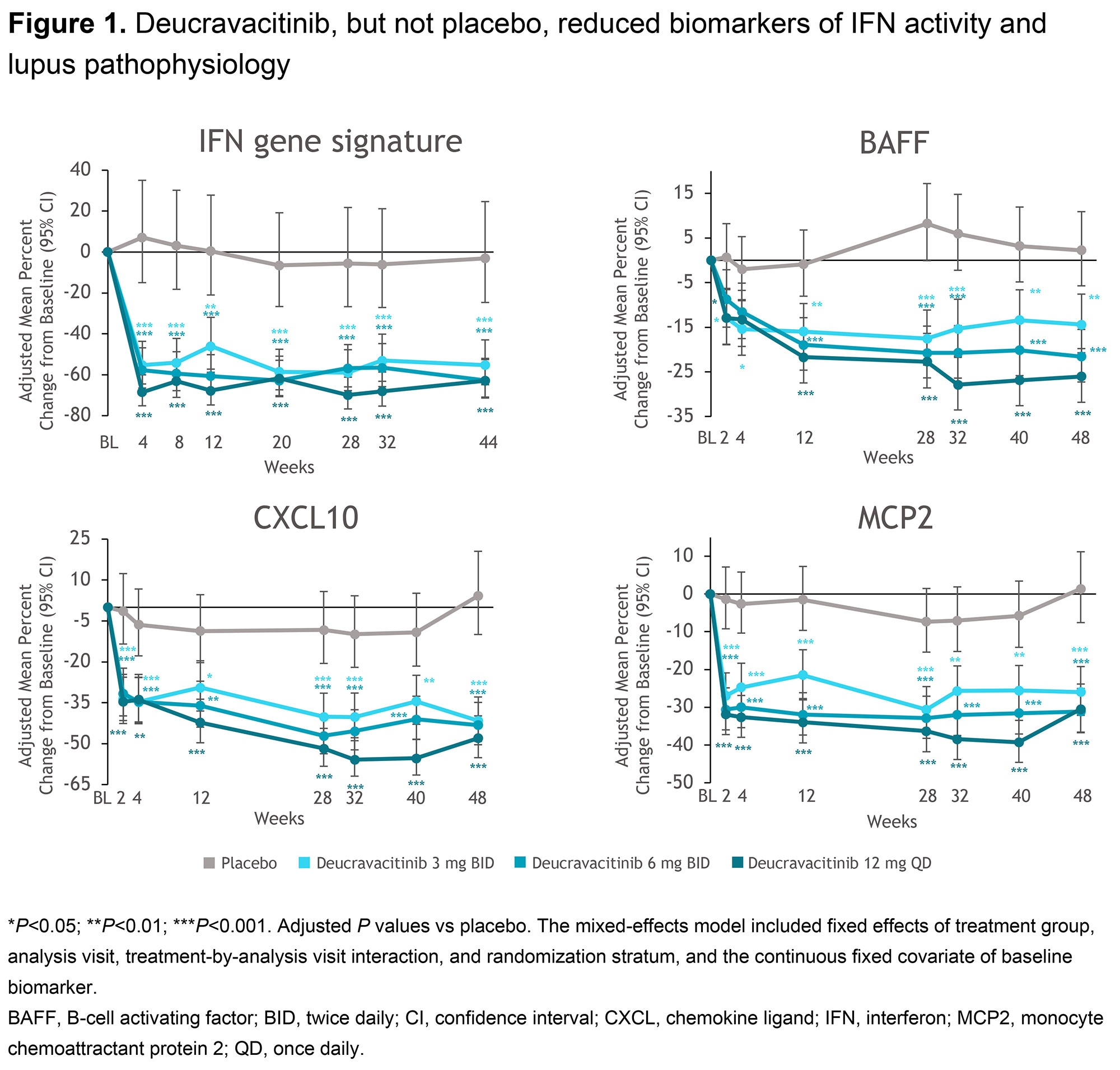
Results: At screening, 42 genes/modules and 75 proteins were differentially expressed compared to healthy subjects, with fold change >1.5 and adjusted P value < 0.05. Following treatment with DEUC, IFNa was significantly reduced at wk 48, IFNl was significantly reduced from wk 2 through wk 48, and IFNg was numerically lower after wk 12. DEUC significantly inhibited IFN-regulated gene (IRG) expression from wk 2 through wk 48. DEUC, but not PBO, reduced expression of cytokines and chemokines downstream of IFN activity, including BAFF, MCP2, and CXCL10 (Figure 1). Adjusted mean percent changes from baseline at wk 48 after treatment with DEUC 3 mg BID, 6 mg BID, or 12 mg QD were -26%, -31%, or -30% for MCP2 and -42%, -43%, or -48% for CXCL10, respectively. Selected cytokines and chemokines including IFNl, CXCL10, CCL19, and MCP2 were significantly reduced in the BID-dosed arms as early as 2 to 3 days after dose initiation. Lymphocyte and neutrophil counts and complement levels increased with DEUC treatment, while markers associated with B cell activation and differentiation including BLC (CXCL13), CD38 (gene expression), and autoantibodies were reduced after treatment with DEUC.
Conclusion: DEUC suppressed IFN production, IRG expression, IFN-inducible proteins, B cell pathway markers, and serological biomarkers, consistent with clinical symptom improvements in SLE patients treated with DEUC. Suppression of both IFN and B cell pathways suggests a broad reduction in lupus pathophysiology. These results provide a molecular framework for understanding how DEUC modifies molecular networks in SLE and support the continued investigation of DEUC as a treatment for SLE in phase 3 trials.
Reference
1. Morand et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of deucravacitinib, an oral, selective, allosteric TYK2 inhibitor, in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 81:209.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kahlenberg J, Sanz I, Wu C, Hu S, Hyang Kim J, Singhal S, Catlett I. Deucravacitinib Reduces Interferons, B Cell Pathways, and Serological Biomarkers of Systemic Lupus Disease Activity: Pharmacodynamic Analysis from the Phase 2 PAISLEY Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deucravacitinib-reduces-interferons-b-cell-pathways-and-serological-biomarkers-of-systemic-lupus-disease-activity-pharmacodynamic-analysis-from-the-phase-2-paisley-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deucravacitinib-reduces-interferons-b-cell-pathways-and-serological-biomarkers-of-systemic-lupus-disease-activity-pharmacodynamic-analysis-from-the-phase-2-paisley-study/