Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Inflammatory Arthritis – RA, SpA, & Gout (0560–0593)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Spondyloarthritis (SpA) causes pain, fatigue, stiffness, loss of physical function and impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
This study aims to: 1) to compare HRQoL in patients with SpA, chronic low back pain (CLBP) and subjects with no rheumatic disease (noRMD), and 2) to evaluate determinants of HRQoL in SpA patients, in a population-based setting.
Methods: Data from EpiReumaPt, a national health survey with 10 661 adult participants, randomly selected, that were screened for rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) was used. Subjects were asked about socio-demographic data, lifestyle habits, chronic non-communicable diseases and HRQoL. SpA diagnosis was based on a positive expert opinion (rheumatologist) combined with predefined criteria; SpA disease activity was also collected. CLBP was established by predefined criteria and noRMD by expert opinion. Univariate and multivariate linear regressions were performed to explore factors associated with QoL assessed by EuroQoL- 5 Dimensions 3L (EQ-5D).
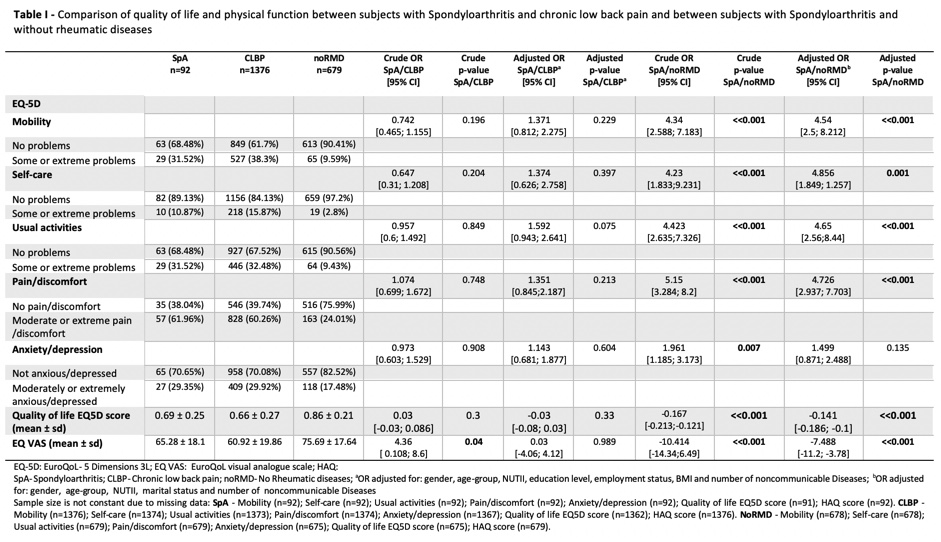
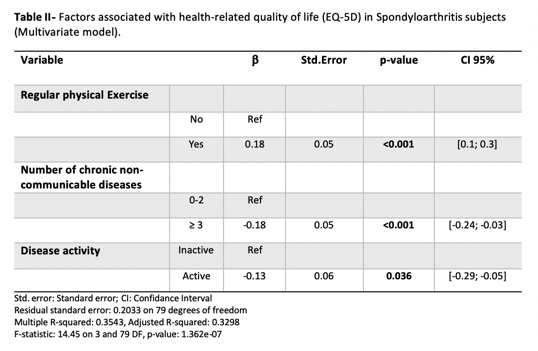
Results: We included 92 SpA, 1376 CLBP and 679 with noRMD. The mean age was 48.4 years (SD=13.7) for SpA, 58.8 years (SD=14.6) for CLBP and 45.9 years (SD=15.6) for noRMD. The 3 groups had a female predominance (64.1%, 70.3% and 53.9%, respectively). SpA and CLBP had similar HRQoL reflected by EQ5D-3L index (ß=-0.03, p-value=0.33), much lower when compared to subjects noRMD (ß=-0.14, p-value< 0.001) (table I), Patients with SpA had lower scores in all EQ-5D dimensions, similar in patients with CLBP, but much higher than in participants noRMD. Pain, was reported in almost 60% of SpA adults, followed by limitations in mobility. In our cohort, SpA adults showed similar individual perception of health than adults with CLBP by EuroQoL visual analogue scale (ß=0.03, p-value=0.989), that was much lower (higher score=better health) when compared to adults noRMD (ß=-7.49, p-value=< 0.001) (table I). Considering the factors associated with HRQoL in SpA, multimorbidity (³3 chronic non-communicable diseases) (ß=-0.18; p-value< 0.001) and an active disease (ß=-0.13; p-value=0.036), were associated with worse HRQoL; on the other hand, regular physical exercise was significantly associated with better HRQoL (ß=0.18; p-value< 0.001) (table II). Our model can explain 35.43% of the variance of HRQoL in SpA subjects.
Conclusion: In this nation-wide study, SpA showed a similar impact in HRQoL than CLBP. An active disease, multimorbidity and regular physical exercise are largely responsible for HRQoL in SpA.
 4A3B4CD6-C833_4673-992B-7C15BCDDA785.jpeg”
4A3B4CD6-C833_4673-992B-7C15BCDDA785.jpeg”
 EE955534_1E73_4673-B1A8-6C3E9A3FC223_4_5005_c.jpeg”
EE955534_1E73_4673-B1A8-6C3E9A3FC223_4_5005_c.jpeg”
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santos H, Henriques A, Rodrigues A, Branco J, Canhao H. Determinants of Health-Related Quality of Life in Spondyloarthritis and Comparison with Chronic Low Back Pain – Results from a Nation-Wide Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/determinants-of-health-related-quality-of-life-in-spondyloarthritis-and-comparison-with-chronic-low-back-pain-results-from-a-nation-wide-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/determinants-of-health-related-quality-of-life-in-spondyloarthritis-and-comparison-with-chronic-low-back-pain-results-from-a-nation-wide-study/
