Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Manifestations (0855–0896)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The spread of COVID-19 misinformation through social/news media is a health risk in SLE. We assessed the determinants of SLE patients accessing health information in social and news media, and self-reporting negative health impacts associated with accessing health information from these sources.
Methods: International patients meeting ACR or Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics Classification Criteria for SLE were recruited from 15 patient cohorts, and patients self-reporting SLE were recruited from five advocacy organizations.They completed an online survey (06/2020-04/2021) about sources of health information accessed preceding (pre 03/11/2020) and during (post 03/11/2020) the COVID-19 pandemic. Logistic regression was used to explore factors (region, sociodemographics, SLE characteristics, access to/trust in sources) associated with: 1) accessing social media, 2) news media, and 3) self-reported negative impacts from health information accessed through these sources.
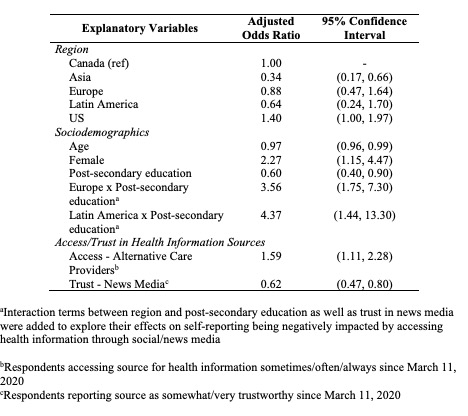
Results: 1935 patients (Asia n=201, Canada n=845, Europe n=324, Latin America (LA) n=118, US n=447) completed the survey (27.1% response rate): 92.7% female, 35.2% non-white race/ethnicity, mean age at diagnosis 32.0 years (SD 13.3), mean disease duration 16.6 years (SD 12.0), and 76.6% had post-secondary education. 21.6% and 37.0% accessed health information often/always from social and news media, respectively, and 17.0% reported being negatively impacted by health information accessed through these sources.
Respondents in Europe and LA vs Canada were more likely to access social (Europe: OR 1.46, 95% CI 1.03, 2.07; LA: OR 2.19, 95% CI 1.36, 3.56) and news media (Europe: OR 1.77, 95% CI 1.26, 2.49; LA: OR 1.71, 95% CI 1.03, 2.83), and those in the US were less likely to access social media (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.40, 0.84) (Table 1). Females were more likely (OR 2.02, 95% CI 1.17, 3.49), while older subjects were less likely to access social media (OR 0.98, 95% CI 0.97, 0.99). Patients accessing family physicians during COVID-19 were less likely to access social (OR 0.70, 95% CI 0.54, 0.92) and news (OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.50, 0.80) media, and those reporting trust in social (OR 3.18, 95% CI 2.45, 4.14) and news media (OR 4.33, 95% CI 3.40, 5.52) were more likely to access each, respectively. Those in Asia vs Canada (OR 0.34, 95% CI 0.17, 0.66) and older participants (OR 0.97, 95% CI 0.96, 0.99) were less likely to report negative impacts, and females (OR 2.27, 95% CI 1.15, 4.47) were more likely to report negative impacts (Table 2). While subjects with post-secondary education were less likely to be negatively impacted (OR 0.60, 95% CI 0.40, 0.90), those with post-secondary education in Europe (OR 3.56, 95% CI 1.75, 7.30) and LA (OR 4.37, 95% CI 1.44, 13.30) were more likely to report negative impacts.
Conclusion: Region, age, gender, accessing family physicians, and education were associated with accessing social/news media and/or self-reporting negative impacts of accessing health information from these sources. Education was inversely associated with reporting a negative impact, yet in Europe and LA the relationship is reversed, likely due to local context. This study emphasizes the need for targeted health messaging.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cardwell F, Elliott S, Chin R, Rowbottom L, St.Pierre Y, Choi M, Urowitz M, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Bernatsky S, Petri M, Manzi S, Peschken C, Ramsey-Goldman R, Fortin P, Shin J, Bae S, Cho J, Mak A, Hanly J, Askanase A, Romero-Diaz J, Nieto R, Pons-Estel B, Bruce I, Wallace D, Clarke A. Determinants of Accessing Social and News Media and Experiencing Negative Impacts During COVID-19 in an International SLE Sample [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/determinants-of-accessing-social-and-news-media-and-experiencing-negative-impacts-during-covid-19-in-an-international-sle-sample/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/determinants-of-accessing-social-and-news-media-and-experiencing-negative-impacts-during-covid-19-in-an-international-sle-sample/