Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sensory ataxic neuropathy (SAN) is one of the neurologic complications in Sjögrenfs syndrome (SS). The underlying pathology was lymphocytic infiltration to the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), called dorsal root ganglionitis. 3-Tesla magnetic resonance neurography (3T MRN) clearly delineate DRGs and peripheral nerves, and has been used to evaluate various neurological disorders. However, there has been no reports correlating signal change in DRGs and subtypes of neuropathy. This study aimed to determine whether 3T MRN is useful for the diagnosis of SAN in SS.
Methods: On retrospective chart review from 2014 to 2016, we found that eight patients (including four patients with SS; three fulfilled American-European Consensus Group classification criteria) had been admitted for the evaluation of neuropathy and underwent 3T MRN of lumbosacral plexus. Data were collected on clinical examination including Romberg test and deep tendon reflex, electrophysiological tests, and spinal cord MRI/MRN with a 3T MRI scanner. In MRN, coronal and sagittal short-tau inversion recovery technique was used to detect abnormalities. In each patient with SAN, the signal intensity and size of DRGs were compared with those of non-SAN patients and age-matched control data (cases without systemic neuropathy)
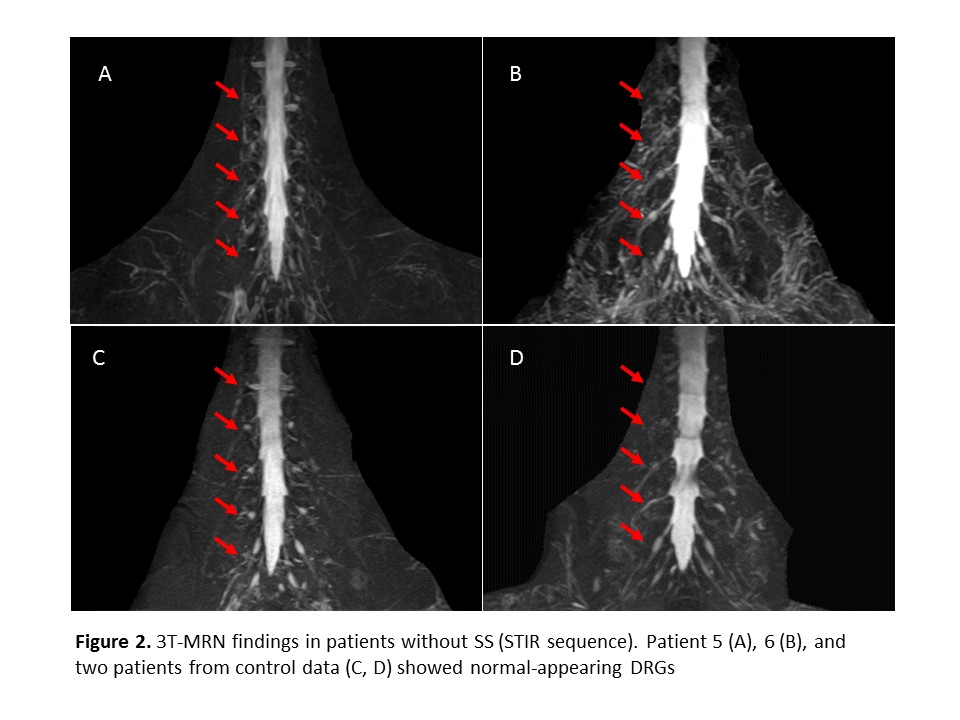
Results: Among four patients with SS, three presented with SAN and one patient showed predominant motor neuropathy. Among four patients without SS, the diagnosis was Guillain-Barré syndrome (N = 3) or idiopathic chronic neuropathy (N = 1). All three patients with SAN showed sensory ataxia with positive Romberg sign, decreased or diminished sensory nerve action potential of sural nerve on nerve conduction study. Five patients without SAN presented with predominant motor symptoms and did not accompany sensory ataxia. On 3T MRN, DRGs in SAN patients were atrophic and their signal intensity were decreased compared to non-SAN patients and control data.
Conclusion: In this study, we described the clinical utility of signal abnormality of DRGs with 3T MRN for the diagnosis of SAN in SS. Larger prospective study would be warranted to establish efficacy of MRN and to elucidate the exact nature of this radiologic finding. 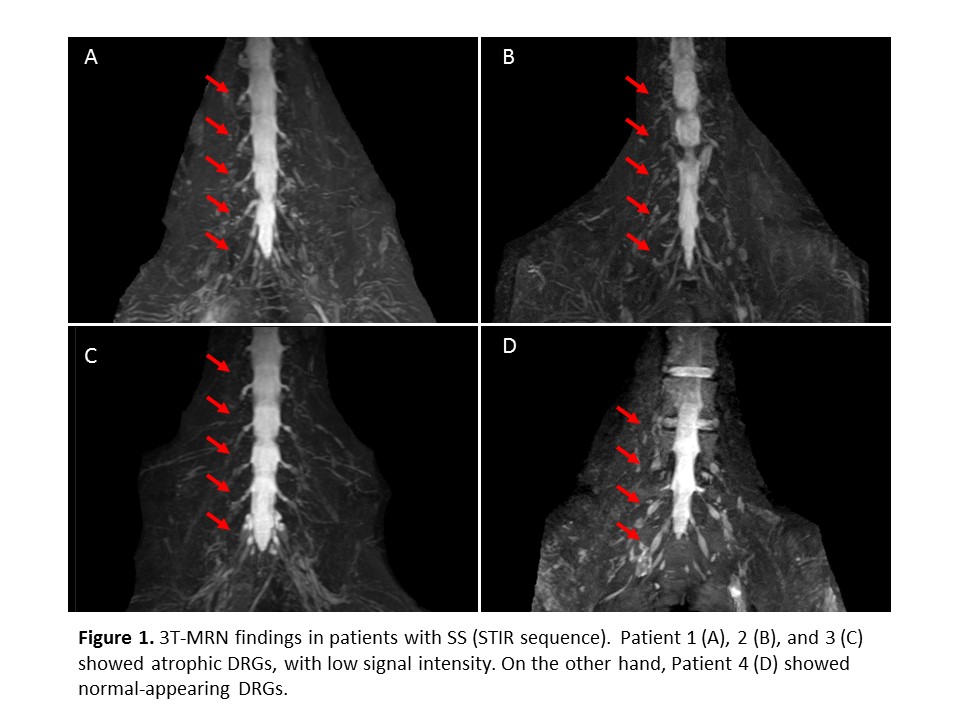
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoshida T, Sueyoshi T, Suwazono S, Kinjo M. Detection of Dorsal Root Ganglionitis with Magnetic Resonance Neurography in Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy Associated with SjöGren’s Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/detection-of-dorsal-root-ganglionitis-with-magnetic-resonance-neurography-in-sensory-ataxic-neuropathy-associated-with-sjogrens-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/detection-of-dorsal-root-ganglionitis-with-magnetic-resonance-neurography-in-sensory-ataxic-neuropathy-associated-with-sjogrens-syndrome/