Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) are frequently chosen as the first biologic therapy for patients (pts) with PsA, though a sizeable proportion of pts have an inadequate response (IR), and some may also have intolerance. Guselkumab (GUS), a human mAb that targets the IL-23 p19 subunit, provides an alternative mechanism of action by which to treat PsA. In the Phase 3 (Ph3) DISCOVER-1 study of GUS in active PsA, GUS Q4W and Q8W clinical response rates were generally consistent between TNFi-naïve (263 pts) and TNFi-experienced (118 pts) cohorts. In the TNFi-experienced cohort and the limited number of DISCOVER-1 pts with IR to their prior TNFi (N=44), ACR 50% improvement (ACR50) and ACR70 response rates at W24 were numerically higher in GUS Q4W- than Q8W-treated pts.1 Seeking to further investigate whether GUS Q4W could provide incremental benefit to some TNFi-IR PsA pts, we analyzed the existing DISCOVER-1 dataset to facilitate the design of a new clinical trial.
Methods: Study feasibility assessments included comparison of key efficacy endpoints by treatment group at W24 among TNFi-experienced pts receiving GUS Q8W and Q4W in DISCOVER-1. Results from the DISCOVER-1 study also informed sample size power calculations for a primary endpoint of ACR20 response at W24 in a future trial in a TNFi-IR PsA pt population.
Results: Comparison of several efficacy endpoints (ACR70 response, minimal disease activity [MDA], Investigator’s Global Assessment [IGA] of psoriasis 0/1 response) across treatment group in the TNFi-experienced DISCOVER-1 cohort supports a potential dose response, with more frequent GUS administration eliciting numerically higher response rates (Table 1). A similar trend was observed for ACR20/50/70 responses in the smaller TNFi-IR population1, though these findings should be interpreted with caution due to limited sample size. ACR20 response rates at W24 of DISCOVER-1 were employed to estimate sample size requirements for a new study. Assuming comparable rates of GUS treatment effect seen in DISCOVER-1, a sample size of 150 randomized pts per group for PBO, GUS Q8W, and GUS Q4W would provide >90% power to detect a significant difference between each GUS group and PBO for ACR20 response at W24 (Table 2). Based on these findings, a new Ph3b, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, PBO-controlled study, SOLSTICE, was designed to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of GUS in approximately 450 pts with active PsA who had IR to one prior TNFi, and to investigate the effect of GUS dosing interval in this important cohort of pts with PsA (Fig).
Conclusion: PsA pts with TNFi-IR are typically difficult to treat. Overall data from the pivotal DISCOVER-1 trial of GUS in pts with active PsA showed consistent clinical response between doses and between TNFi-naïve and TNFi-experienced pts. Analyses based on limited numbers of TNFi-experienced pts from DISCOVER-1 demonstrated potential incremental benefit for achievement of higher response criteria with more frequent dosing in some TNFi-IR pts. SOLSTICE, a Ph3b, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, will test this hypothesis.
References
1. Deodhar A. Lancet. 2020;395:1115-1125
 Table 1. Clinical efficacy at W24 among DISCOVER_1 TNFi-experienced pts.
Table 1. Clinical efficacy at W24 among DISCOVER_1 TNFi-experienced pts.
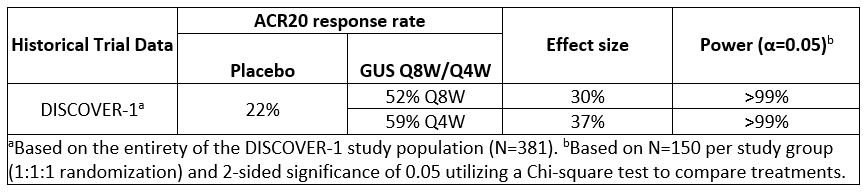 Table 2. Power calculations for SOLSTICE primary endpoint (ACR20 response rate at W24).
Table 2. Power calculations for SOLSTICE primary endpoint (ACR20 response rate at W24).
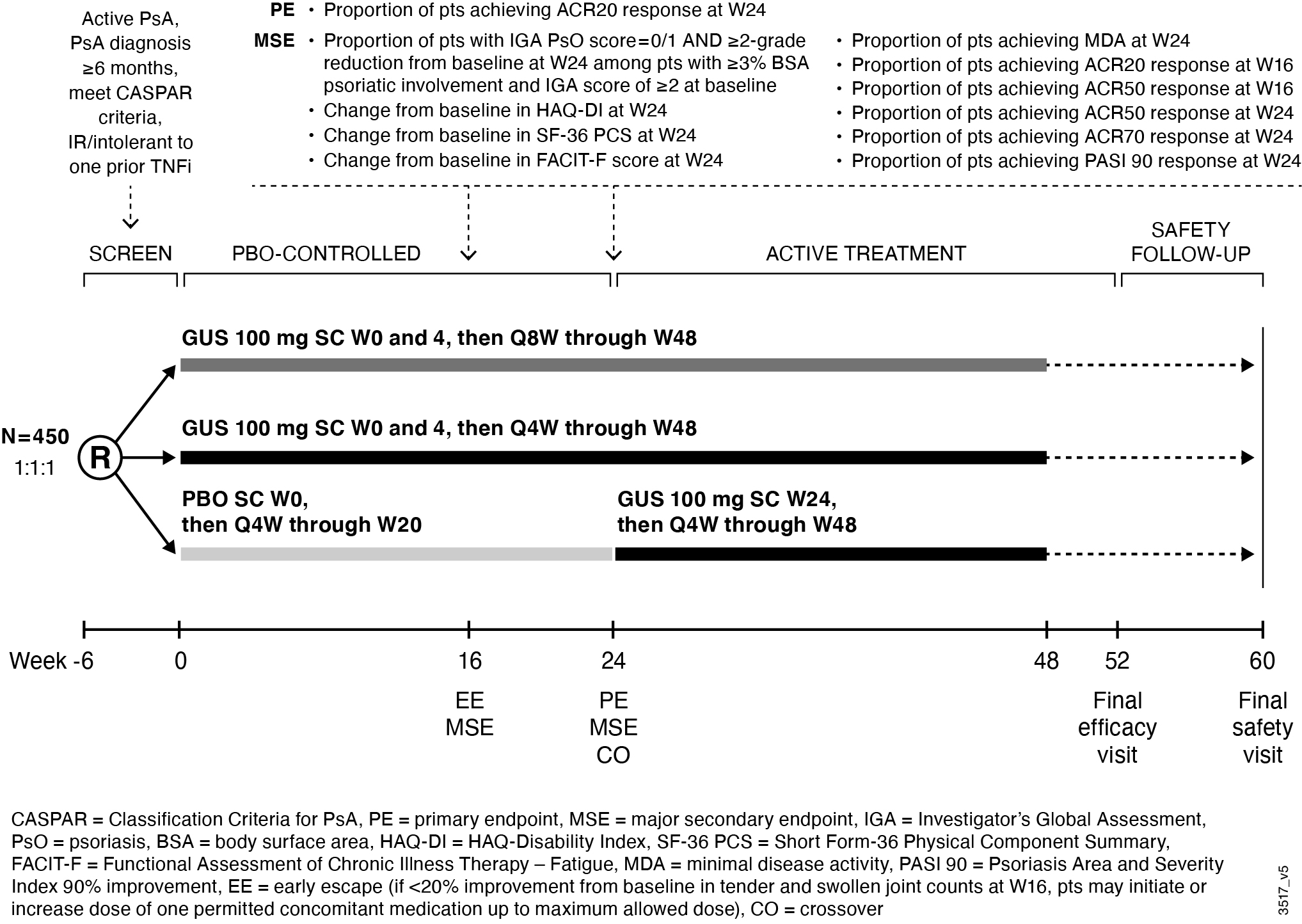 Figure. SOLSTICE study design.
Figure. SOLSTICE study design.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie-Beatty A, Merola J, Mease P, Ritchlin C, Scher J, Chan D, Chakravarty S, Langholff W, Choi O, Krol Y, Rowland K, Gottlieb A. Designing a Phase 3b, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study to Investigate the Effect of Guselkumab (TREMFYA®/sup>) Dosing Interval in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients with Inadequate Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibition [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/designing-a-phase-3b-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-to-investigate-the-effect-of-guselkumab-tremfya-sup-dosing-interval-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-with/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/designing-a-phase-3b-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-to-investigate-the-effect-of-guselkumab-tremfya-sup-dosing-interval-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-with/
