Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Depression is a prevalent (24-30%) and significant comorbidity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (1). As the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) classifies depression as a neuropsychiatric manifestation of SLE (2), many clinicians assume that depressed affect fluctuates with SLE disease activity. In the present study, we leveraged the well-characterized longitudinal SLE cohort at Washington University Lupus Clinic to address the following questions: 1) what is the longitudinal course of depressed affect among outpatients with SLE, and 2) what is the relationship between SLE disease activity and depressed affect.
Methods: Longitudinal data from patients with ACR or SLICC-classified SLE managed in the Lupus Clinic were analyzed. Depressed symptoms were assessed at each visit using the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale, Revised (CESD-R). Scores were obtained from individual patients over an average of 30.2 months (SD: 13.3; range: 2.6-48.0). Standard CESD-R scores of < 16, 16-21, and >21 were used to define no depression, depressed affect, and major depression. SLE disease activity was measured via the SLEDAI2K Responder Index-50 (S2K RI-50). Group-based trajectory modeling (GBTM) was applied to identify groups of patients with similar temporal trajectories of depressed symptoms over time. Baseline characteristics of individuals in each depressed trajectory group were compared using chi-square tests, Fisher’s exact tests, or ANOVA. The relationship between disease activity and depression over time was assessed using multilevel linear regression models.
Results: The sample (n=144) was 91.0% female, 56.3% African American, and 38.9% White, with a mean age of 40.4 (SD: 12.6; range: 19-74). GBTM revealed 5 distinct groups of patients who demonstrated consistent trends in depression overtime (Figure 1). Members of groups 1 and 2 (n=17, 11.8%; n=27, 18.8%) had consistently normal CESD-R scores, group 3 (n=12, 8.3%) had rising CESD-R scores over time, and groups 4 (n=44, 30.6%) and 5 (n=44, 30.6%) demonstrated symptom patterns consistent with depressed affect and major depression, respectively. While visit-to-visit scores varied considerably, patterns remained durable over time documenting the prevalence of persistent major depression. Of note, African American patients were much more common in Group 5 (n=32, 72.7%, p< 0.02). Analyses did not identify an association between CESD-R and disease activity over time.
Conclusion: 61.2% of patients had scores indicating persistent depressed affect or major depression for up to 4 years. A relatively small group of patients (8.3%) reported CESD-R scores increasing from the ‘normal’ to depressed during the study. These data reinforce the disquieting pervasiveness of depression in SLE patients. The lack of a relationship of CESD-R to SLE disease activity highlights the need to identify non-clinical factors, particularly race, that contribute to and moderate this co-morbidity.
References
- Zhang, L., et al., BMC Psychiatry, 2017;17:70.
- Aiinala, H., et al., Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2001;45:419-423.
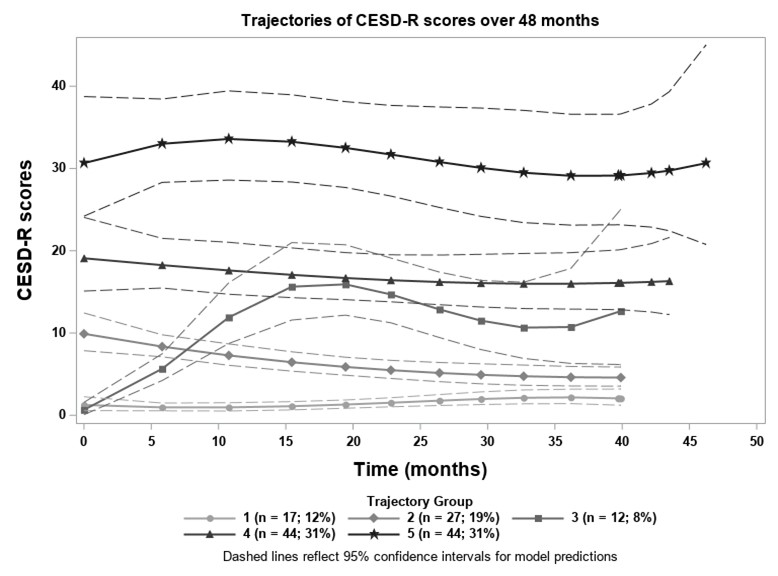 Figure 1. Identified trajectories of depression scores over time
Figure 1. Identified trajectories of depression scores over time
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kellahan S, Huang X, Lew D, Xian H, Eisen S, Kim A. Depressed Symptomatology Persists over Time in the Majority of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Is Independent of Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/depressed-symptomatology-persists-over-time-in-the-majority-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-and-is-independent-of-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/depressed-symptomatology-persists-over-time-in-the-majority-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-and-is-independent-of-disease-activity/
