Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis is a heterogenous disorder not only with respect to patterns and components of musculoskeletal involvement but also with respect to types of skin involvement and the timing of joint and skin disease. The interrelationships between characteristics of skin psoriasis, arthritis and the timing of arthritis are not well studied; we therefore sought to explore these in a large international cohort.
Methods: PsART-international is a web-based registry of PsA patients under routine care in Turkey, Italy and Canada including detailed disease history about type and onset of skin and joint disease. We extracted data on demographic characteristics, family history of psoriatic disease (regardless of skin or arthritis) , types of skin psoriasis, site of skin psoriasis onset, and components of psoriatic arthritis ever observed. For descriptive purposes we tabulated patient characteristics in three groups; arthritis-first, psoriasis-first and synchronous, the latter indicating the onset of skin and joint disease within 12 months. The primary analysis outcome was the absolute time elapsed in months after skin disease to arthritis (negative values indicating arthritis onset before psoriasis). We constructed a linear regression model for this primary outcome using demographic, skin disease and arthritis characteristics to explore the associations.
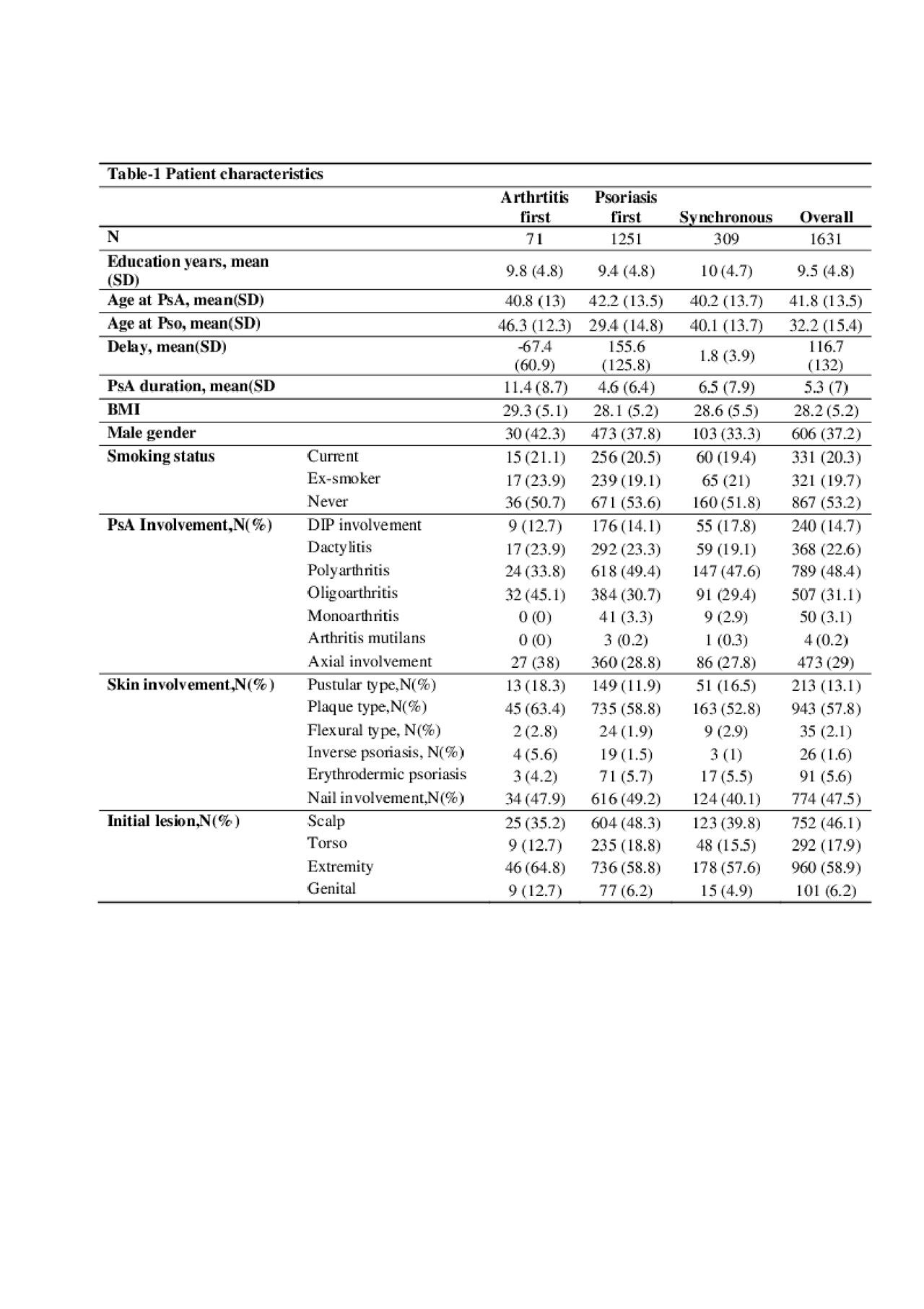
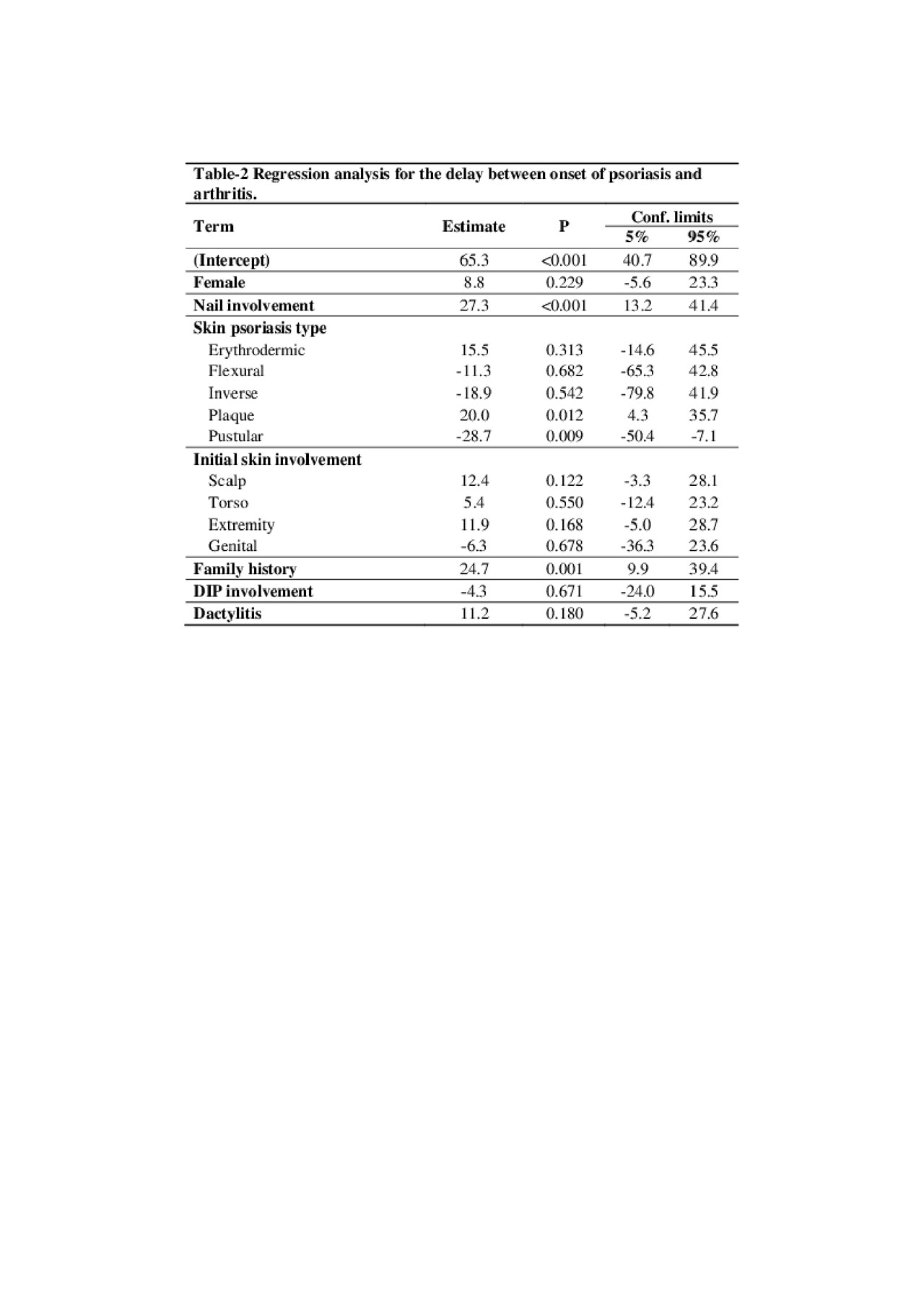
Results: We included 1631 patients; 71 had arthritis first, 309 had synchronous onset and 1251 had psoriasis first. Data shows that the age of psoriasis onset and not that of arthritis determined whether arthritis or psoriasis would be the first to appear (Table-1). Results of the regression analysis shows that the model intercept, delay of arthritis after psoriasis when other independent variables are set to their baseline values, is 65 months, pustular psoriasis is associated with onset of arthritis circa 2 years earlier than the intercept interval whereas nail involvement, plaque psoriasis or family history of psoriasis are associated with an increased delay from psoriasis to arthritis, by approximately 2 years-each (Table-2). Adding all types of articular involvement into the model did not cause a material change in the point estimates however reduced the precision of terms for skin psoriasis type (data not shown).
Conclusion: The age of psoriasis determines whether arthritis or psoriasis starts first in PsA patients. Pustular psoriasis is associated with a shorter time interval after psoriasis to arthritis while nail involvement, plaque psoriasis and psoriatic family history are associated with a longer interval.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tascilar K, Aydin S, Akar S, Aksu K, Bakirci S, Bayindir O, Can M, Cetin G, Çınar M, Dalkılıç E, Dogru A, Erden A, Ersözlü E, Erten �, Kaşifoğlu T, Kimyon G, Küçükşahin O, Omma A, Ozisler C, Senel S, Solmaz D, Tarhan E, Tinazzi I, Yavuz S, Yılmaz S, Kalyoncu U. Delay Between the Onset of Psoriasis and Arthritis in PsA Patients from the PsART International Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/delay-between-the-onset-of-psoriasis-and-arthritis-in-psa-patients-from-the-psart-international-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/delay-between-the-onset-of-psoriasis-and-arthritis-in-psa-patients-from-the-psart-international-cohort/