Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Scleroderma renal crisis (SRC), characterised by accelerated hypertension and acute kidney injury, is a life-threatening complication of systemic sclerosis (SSc). Most SSc cases have a disease-specific circulating antibody, including the anti Scl-70, anti-centromere and anti RNA polymerase III (ARA) antibodies. Previous studies confirm ARA as a powerful serological predictor of SRC, and cases of SRC more than 5 years after the diagnosis of SSc are rare. We developed an innovative approach to identify genetic susceptibility loci for SRC, comparing ARA positive patients with and without the occurrence of SRC.
Methods:
From a well-characterised SSc cohort (n=415), we selected 100 ARA+ patients with more than 5 years of follow-up data. 50 had a history of SRC and 50 had not developed SRC. All cases were of northern European ancestry. Cases were genotyped using the Illumina Human Omni-express chip. Quality control checks were performed in PLINK (Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium p <0.001; genotyping rate >90%). Based on the results of logistic regression analysis, ten SNPs were put forward for validation in a separate US cohort of 256 ARA+ patients (40 SRC+), using ThermoFisher TaqMan genotyping probes. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on SRC biopsy samples to identify proteins associated with our genes of interest.
Results:
After quality control checks, 641,489 SNPs were analysed in the first cohort. In logistic regression analysis of our initial cohort, the SNPs within genes and gene regions most strongly associated with SRC were for POU2F1 (p=4.12 x 10-5), CTNND2 (p=2.92 x 10-5), HECW2 (p=2.71 x 10-5), GRIA3 (p=2.16 x 10-5) and GPATCH2L (p=2.06 x 10-5). The SNP within the GPATCH2L region was also significantly associated with SRC in our validation cohort (p=0.025). GPATCH2L polymorphisms have been associated with essential hypertension in previous GWAS analysis.
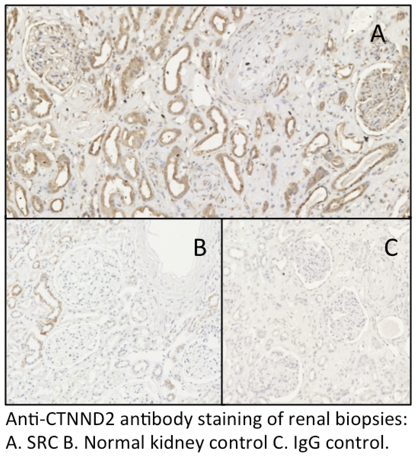
Polymorphisms in the CTNND2 gene have been demonstrated to be associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension, another vascular complication of SSc, in previous studies. We performed IHC for this protein on 8 renal biopsy samples from confirmed cases of SRC and 8 normal human kidney controls (see figure). Tubular epithelial staining was present in cases and controls. Glomerular staining was markedly increased in the SRC cases compared with controls, with 5 cases showing significant staining in this compartment compared with 0 controls (FisherÕs Exact p=0.026).
Conclusion:
A novel autoantibody-based extreme phenotype method identifies risk alleles for SRC within a rare disease cohort. Using genetic and histological validation methods we identify CTNND2 and GPATCH2L as candidates for investigation of SRC aetiopathogenesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stern E, Guerra S, Chinque H, Gonzalez Serna D, Ponticos M, Martin J, Mayes MD, Assassi S, Fonseca C, Denton C. Defining Genetic Risk for Scleroderma Renal Crisis in RNA-Polymerase III Antibody Positive Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/defining-genetic-risk-for-scleroderma-renal-crisis-in-rna-polymerase-iii-antibody-positive-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/defining-genetic-risk-for-scleroderma-renal-crisis-in-rna-polymerase-iii-antibody-positive-patients/