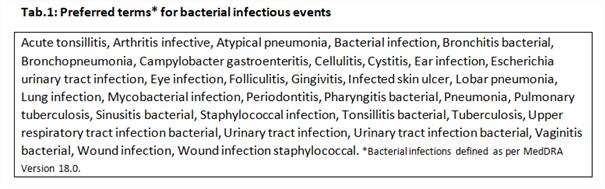
Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Baricitinib (BARI) is a selective inhibitor of Janus kinase 1/2, modulating responses to inflammatory cytokines, e.g. IL-6 or IFNs1. During acute inflammation, including those caused by bacterial infections (BI), IL-6 induces hepatic CRP synthesis; elevated CRP levels often represent a nonspecific, yet clinically useful marker of infections2. IL-6 blockers can lead to blunting of CRP signals3,4. This analysis evaluated CRP levels during BI in RA patients treated with BARI or placebo (PBO).
Methods:
Using a high sensitivity (hs) assay, CRP values were obtained from patients with moderate to severe active RA pooled from the BEAM, BUILD and BEACON studies who were treated with BARI 4-mg or PBO for 24 weeks and had BI TEAEs (Tab.1). Patient inclusion was based on the experience of ≥1 BI before rescue and availability of a CRP measure within ± 3days of the start of the BI. Multiple CRP measures per patient were aggregated into the median resulting in 2 observations per patient corresponding to the infection and infection-free period (Fig.1). Paired comparisons between CRP at infection and infection-free states were done within the same patients for each treatment group and p-values for the two differences were obtained from a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test.
Results:
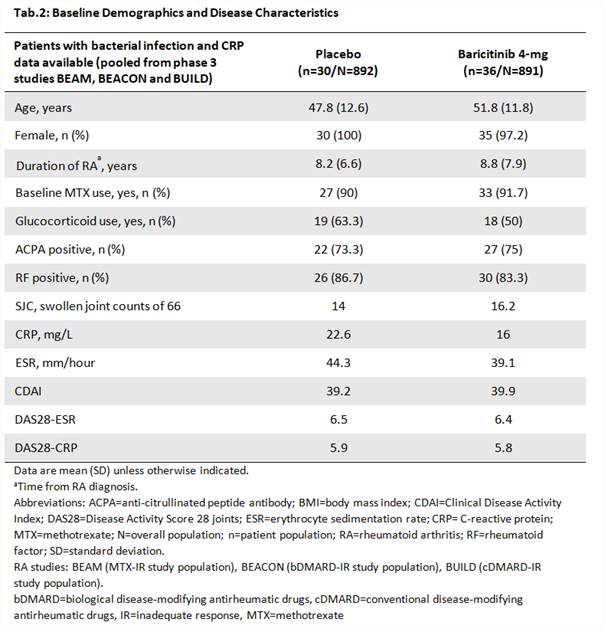
Overall, 36 and 30 patients treated with BARI and PBO (Tab.2) had CRP values during BI TEAEs, of which 60% were urinary tract infections. For BARI, the median CRP were 6.2 and 3.0 mg/L in the infection and infection-free period, (p < 0.001; Fig.1) and the maximum values were 99.2 and 25.4 mg/L, respectively. For PBO, the median CRP were 10.1 and 13.7 mg/L for the infection and infection-free period (p = 0.896); and the maximum values were 110.8 and 71.4 mg/L.
Conclusion:
CRP remains a useful monitoring tool for BI in BARI-treated patients. CRP elevations were observed in BARI-treated patients during BI, with no apparent blunting of response. In the PBO patients, elevations of CRP also were observed in infection-free periods, in line with the presence of active RA, and these values may be comparable to the CRP values observed on those patients during a BI.
References:
1O’Shea JJ, Plenge R. Immunity 2012;36(4):542-50
2Schaper F, Rose-John S. Cytokine & Growth Factor Review; doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.07.004
3Bari SF et al. BMJ Case Rep; doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-010423
4Fujiwara H et al. Mod Rheumatol 2009;19:64–8
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hendricks O, Chrysidis S, Gerwien J, Saifan C, de Leonardis F, Lopez-Romero P, Zhong J, Winthrop K, Smolen JS. CRP Changes during Bacterial Infections in Baricitinib-Treated Patients with RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/crp-changes-during-bacterial-infections-in-baricitinib-treated-patients-with-ra/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/crp-changes-during-bacterial-infections-in-baricitinib-treated-patients-with-ra/