Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Network meta-analyses (NMA) have been conducted to compare the efficacy and safety of sarilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against the interleukin 6 receptor α, vs other monotherapies for patients with RA who were inadequate responders to, inappropriate candidates for, or intolerant of conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD-IR)1 and vs other combination treatments with methotrexate in patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs1 or anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy2 (csDMARD-IR and TNF-IR, respectively). Using this comparative efficacy data, the present study evaluated 1-year costs associated with obtaining treatment response with sarilumab 200 mg subcutaneous (SC) vs other currently used therapies in these patient populations.
Methods: Cost-per-responder (CPR) analyses were conducted on 2018 US wholesale acquisition costs of drugs and administration. The number-needed-to-treat (NNT) to obtain one responder per American College of Rheumatology (ACR)50 was derived from the NMAs of sarilumab.1,2 Responders were assumed to receive treatment for 12 months; non-responders were assumed to stop treatment after 6 months without subsequent treatments. Scenario analyses were conducted on ACR20 and ACR70 criteria.
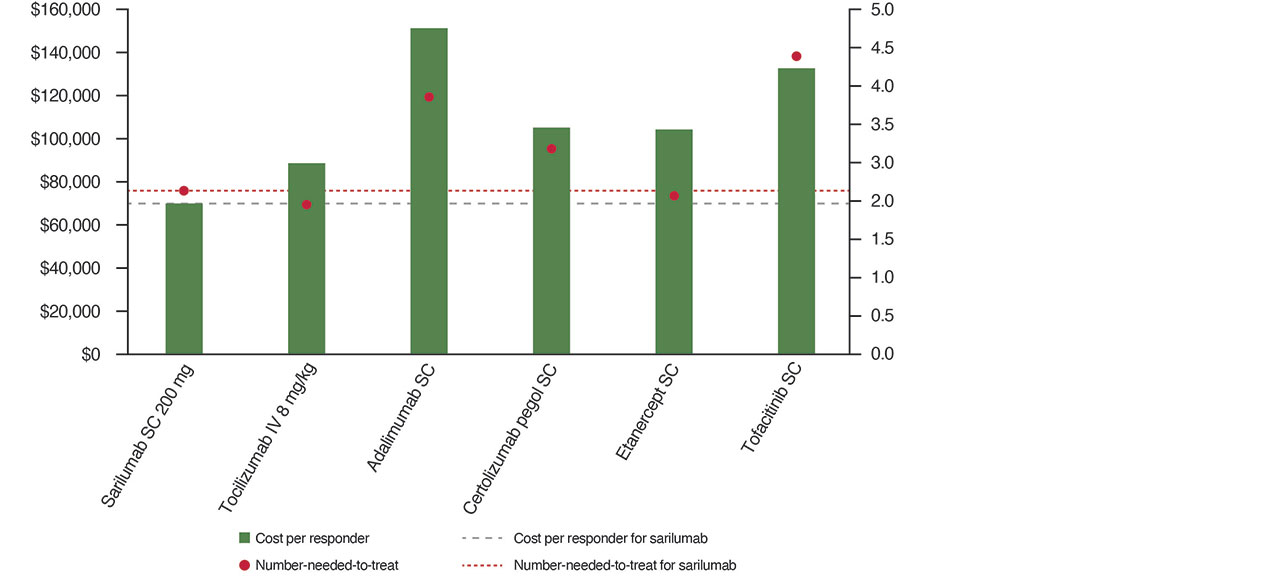
Results: For monotherapies in csDMARD-IR (Figure A), the NNT for sarilumab (2.4) was lower vs all comparators except etanercept (2.3) and tocilizumab intravenous (IV) 8 mg/kg (2.2). Sarilumab had the lowest CPR ($69,440) vs all treatments (ranging from $150,348 for adalimumab SC to $88,291 for tocilizumab IV 8 mg/kg). For combinations in csDMARD-IR (Figure B), the NNT for sarilumab (2.5) was lower vs all comparators except etanercept (2.1). Sarilumab CPR ($72,438) was lower vs all comparators ($119,559 for adalimumab SC to $80,409 for abatacept IV) except lower dose intensities of tocilizumab (IV and SC). In TNF-IR (Figure C), the NNT for sarilumab (3.2) was lower vs all combinations except vs tocilizumab IV 8 mg/kg (3.0). Sarilumab CPR ($87,047) was lower vs all comparators ($152,551 for golimumab SC to $107,761 for abatacept IV) except tocilizumab IV 4 mg/kg, baricitinib 2 mg and rituximab IV. Scenario analysis results were similar except per ACR70 lower CPRs for certolizumab and etanercept monotherapies, and a higher CPR for tocilizumab IV 4 mg/kg in combination (csDMARD-IR and TNF-IR populations).
Conclusion: Due to the lower NNT for sarilumab vs most comparators and reasonable cost, sarilumab achieved better CPR outcomes vs all monotherapies, vs all combinations except lower dose intensities of tocilizumab in csDMARD-IR and except baricitinib and rituximab in the TNF-IR population.
1. Choy E et al. RMD Open. 2019;5:e000798.
2. Choy E et al. Adv Ther. 2019;36:817–827.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fournier M, Boklage S, Joly F, Ford K, Kiss Z, Gal P, Choi J. Cost-per-Responder Analysis of Sarilumab for the Treatment of Moderately-to-Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cost-per-responder-analysis-of-sarilumab-for-the-treatment-of-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cost-per-responder-analysis-of-sarilumab-for-the-treatment-of-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/