Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Preliminary research suggests that Health Literacy (HL) is associated with the functional status of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Single Item Health Literacy Screening (SILS) questionnaires are a convenient method of establishing the health literacy of patients. However, the wording of SILS, version 2 (SILS2, “How comfortable are you filling out medical forms by yourself?” Wallace LS, et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21:874-7.)) may be misinterpreted by RA patients as an query regarding their physical limitations. We assessed the construct validity of the SILS2 by correlating scores with standardized HL measures.
Methods: English-speaking adult RA patients at Denver Health enrolled in a cross-sectional study. Subjects were asked to complete the SILS2, an older version of the SILS (SILS1, “How often do you need to have someone help you when you read instructions, pamphlets, or other written material from your doctor or pharmacy?” Chew, et al. Fam Med 2004;36:588-594), as well as two longer HL measurement tools (Short Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults [STOFHLA] and the Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine [REALM]). Pearson correlation was used to assess the construct validity of the various tools.
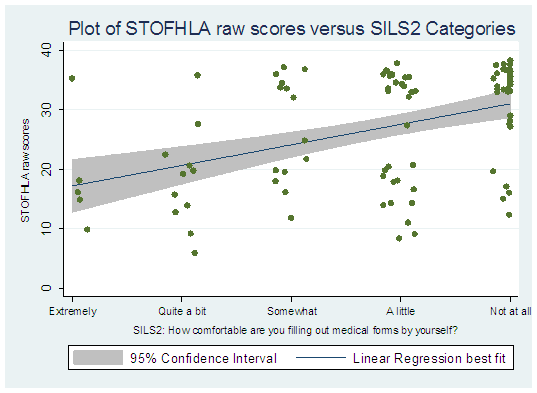
Results: 110 subjects participated in the study. There was a strong correlation between the two SILS versions (Table 1). The correlation of SILS2 and REALM or STOFHLA was less robust (Table 1), but still moderately well correlated, though the distribution of scores within each SILS2 category demonstrated substantial scatter. (Figures 1 and 2)
Conclusion: The SILS2 has construct validity in the assessment of HL in patients with RA. The SILS instruments are moderately good reflections of HL for groups of RA patients, however the substantial scatter of scores within each SILS category likely limits the clinical utility of the SILS in determining the HL on any one subject.
Table 1 : Correlations of various measures of health literacy in subjects with RA
|
SILS1
|
SILS2
|
REALM
|
|
|
SILS2
|
0.693 |
— |
— |
|
REALM
|
0.385 |
0.411 |
— |
|
STOFHLA
|
0.416 |
0.439 |
0.554 |
STOFHLA = Short Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults;
REALM = Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine;
SILS = Single-Item Literacy Screener
Disclosure:
I. Quinzanos,
None;
J. M. Hirsh,
None;
L. Caplan,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlations-of-single-item-health-literacy-screening-questions-with-established-measures-of-health-literacy-in-subjects-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/