Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient
reported measures are influenced by many non-rheumatoid arthritis (RA) factors and
they are reflected variably among various composite disease activity scores
(DAS). We investigated relative contribution of patient reported measures and
changes over time in two most widely used DAS.
Methods: For RA subjects
enrolled in the University of Pittsburgh RA Comparative Effectiveness Research
(RACER), cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses were performed to compare
relative contribution of subjective patient reported components to DAS28-C-Reactive
Protein (CRP) and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI). Relative of the
contribution of the patient reported measures (Tender Joint Count (TJC) and
Patient Global Assessment (PtGA) in DAS28-CRP (DAS-P) and CDAI (CDAI-P) were
calculated at baseline and follow-up visit within 3 months. DAS28-CRP changes was
categorized by European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) response criteria and
CDAI changes were grouped into major (improvement ≥ 14), moderate (≥
6), mild (<6). Wilcoxon signed ranks tests were performed for comparison. Univariate
and multivariate regression analyses were performed to investigate factors
associated with changes of subjective domains.
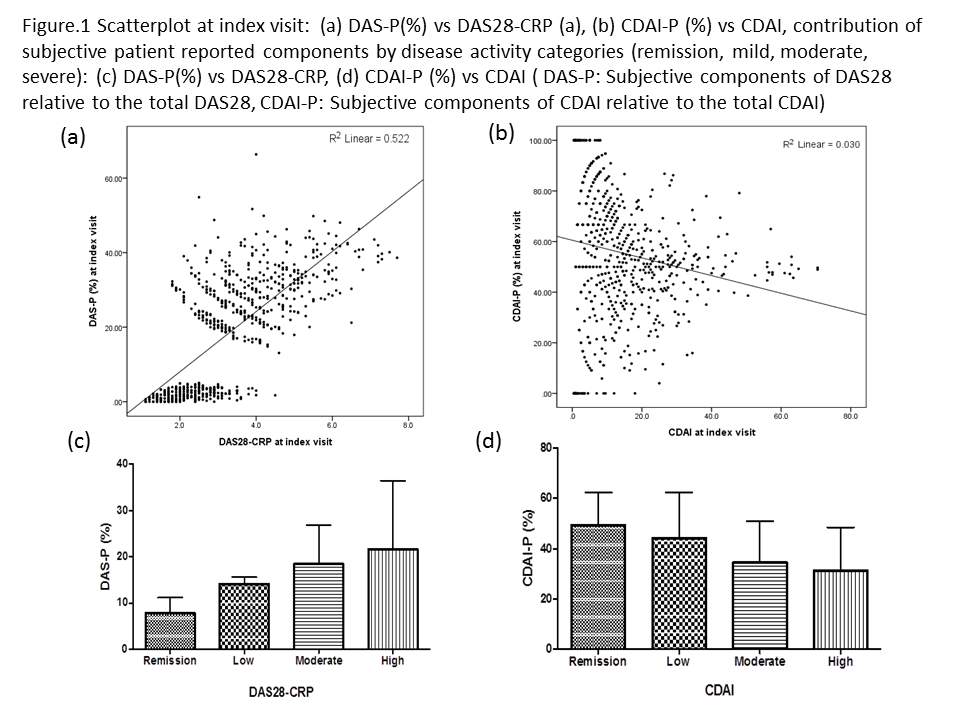
Results: For the 740 subjects analyzed, age
was 60.2 ±13.7 (Mean±SD) years with disease duration of 14.4 ±12.4 years. 312
subjects had follow up visit within 3 months (1.7 ± 2.2 month). DAS-P was
increased linearly with higher disease activity score. In contrast, CDAI-P
remains similar with wider variation in remission or low disease activity (CDAI
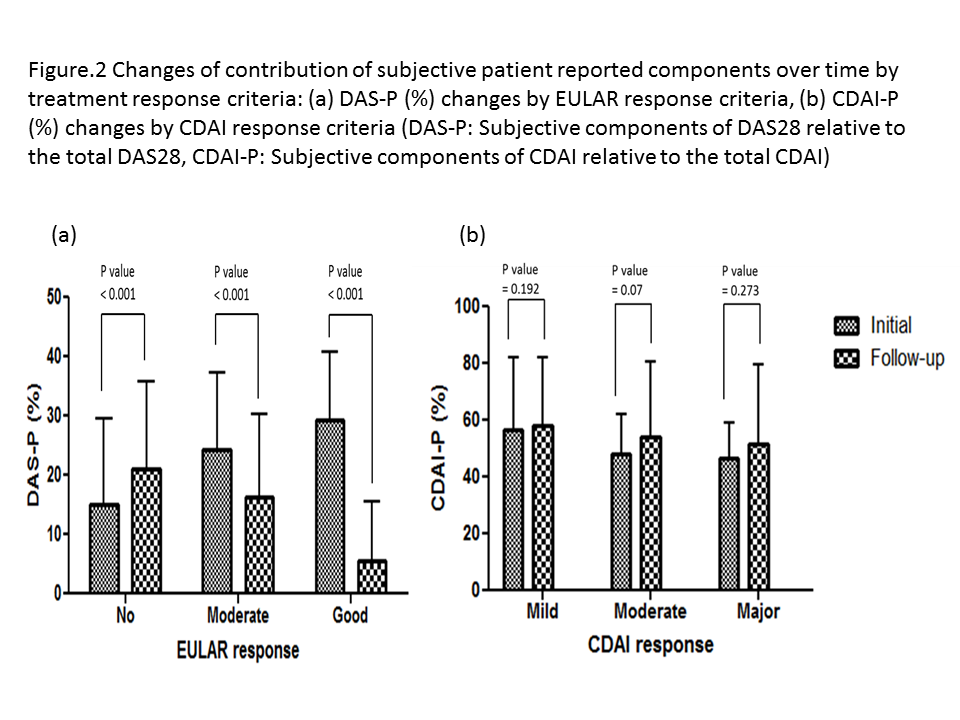
≤ 10) (Figure.1). Significant reduction in the DAS28-P score was observed
at follow up visit in all response groups, with greater reduction of DAS28-P in
good responders. However, CDAI-P did not differ between the index and follow up
visit (Figure.2). Multivariate analyses showed Swollen Joint Count (SJC) and Physician
Global Assessment (PhGA) at the index visit had significant association with
DAS-P changes at the follow up visit. CDAI-P changes were also significantly
associated with HAQ (Table.1).
Conclusion: Contribution
of patient reported components and their changes over time are substantially
different between DAS28-CRP and CDAI. Objective findings such as SJC and PhGA predict
changes of subjective patient reported measures at the follow up visit.
|
Table.1 Associations of subjective patient reported component changes with clinical variables at baseline by multiple linear regression analyses (β unstandardized coefficient, SE: Standard Error, DAS-P: Subjective components of DAS28 relative to the total DAS28, CDAI-P: Subjective components of CDAI relative to the total CDAI, SJC: Swollen Joint Count, PhGA: Physician Global Assessment, HAQ: Health Assessment Questionnaire) |
||||||
|
|
DAS-P change |
CDAI- P change |
||||
|
|
β |
SE |
P value |
β |
SE |
P value |
|
SJC |
-.029 |
.008 |
.001 |
-.293 |
.065 |
.000 |
|
PhGA |
-.069 |
.022 |
.002 |
-.502 |
.171 |
.004 |
|
HAQ |
-.181 |
.096 |
.061 |
-2.070 |
.758 |
.007 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hwang YG, Feng J, Eng H, Lyons J, Fabio A, Moreland LW. Contribution of Subjective Patient Reported Components of Disease Activity Scores Differs in Disease Activity Measures and Their Changes over Time Are Closely Associated with Objective Measures [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-subjective-patient-reported-components-of-disease-activity-scores-differs-in-disease-activity-measures-and-their-changes-over-time-are-closely-associated-with-objective-measures/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-subjective-patient-reported-components-of-disease-activity-scores-differs-in-disease-activity-measures-and-their-changes-over-time-are-closely-associated-with-objective-measures/