Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Response to treatments in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is assessed by symptomatic changes, such as ACR-response and DAS28. However, such assessments do not provide information about the effect of the treatment at tissue level. Chronic inflammation is a harmful mechanism, which manifests in upregulated tissue remodeling and release of extracellular matrix (ECM) metabolites into circulation. Released ECM metabolites are biomarkers of tissue remodeling and give insight to treatment effect at tissue level. The purpose of this study was to investigate if tissue remodeling is modulated by tocilizumab (TCZ) and methotrexate (MTX) in the AMBITION study.
Methods: The AMBITION study is a phase III RCT in which TCZ monotherapy (8 mg/kg every 4 weeks) was compared to MTX monotherapy (starting at 7.5 mg/kg and titrated to 20 mg/kg) over 24 weeks in patients with early RA. Tissue metabolites were measured in baseline and 8-weeks sera from 387 patients by validated ELISA assays. Connective tissue remodeling was measured by C1M and C3M (type I and III collagen degradation), cartilage degradation by C2M (type II collagen degradation), basement membrane remodeling by C4M (type IV collagen degradation), systemic inflammation by C-reactive protein (CRP) and tissue specific inflammation by CRPM (an MMP-derived CRP metabolite). Comparison between treatment and response groups were done by ANCOVA, Spearman’s correlation and Logistic regression adjusted for age, gender, BMI and disease duration.
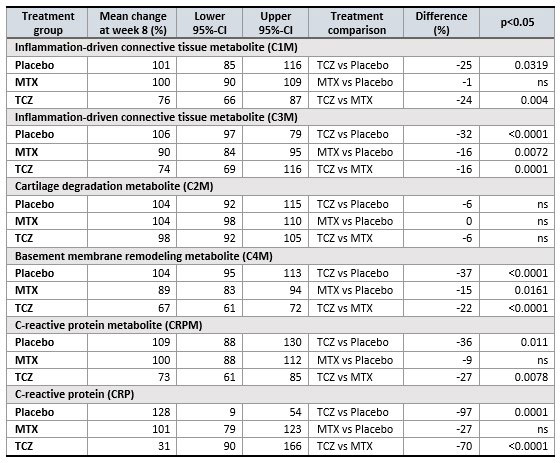
Results: Connective tissue remodeling biomarkers, C1M and C3M, were significantly (P< 0.05) inhibited by TCZ and C3M by MTX (P=0.0072) compared to placebo (see table 1). The inhibition of C1M and C3M with TCZ was respectively 24% and 16% greater than that of MTX (P=0.004 and P=0.0001). C4M was likewise inhibited by both TCZ and MTX, but the effect of TCZ was 22% greater than MTX (P< 0.0001). In contrast, TCZ and MTX had minimal effect on C2M when compared to placebo or baseline. MTX had no effect on CRP and CRPM compared to placebo or baseline, whereas TCZ reduced the level of CRP and CRPM to 31% and 73% of baseline. In the patients treated with TCZ none of the tested biomarkers correlated to 8 and 16-week changes in DAS28. In the MTX group changes in C4M and CRPM were correlated to 8-week changes in DAS28 (rho=0.21 and 0.19, P< 0.05), whereas only C4M correlated to 16-week changes in DAS28 (rho=0.19, P< 0.05). Patients with ACR70 response at week 8 had the highest difference between treatments in the inhibition of C1M; 36% for TCZ and 14% for MTX.
Conclusion: This study shows that tissue remodeling in the RA patients can be differently modulated by Tocilizumab and Methotrexate. Both treatments downregulate tissue remodeling and slower the disease progression. Tocilizumab showed a more tissue-protective effect and greater improvement of the disease symptoms than that of Methotrexate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Drobinski P, Bay-Jensen A, Karsdal M, Siebuhr A. Connective Tissue Remodeling Is Differently Modulated by Tocilizumab versus Methotrexate Monotherapy in Patients with Early RA: The AMBITION Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/connective-tissue-remodeling-is-differently-modulated-by-tocilizumab-versus-methotrexate-monotherapy-in-patients-with-early-ra-the-ambition-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/connective-tissue-remodeling-is-differently-modulated-by-tocilizumab-versus-methotrexate-monotherapy-in-patients-with-early-ra-the-ambition-study/