Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis characterized by enthesitis, that primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. While several studies had described sensorineural deafness in AS patients, conductive hearing loss has been reported as rare. We studied the prevalence hearing loss (HL) among patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Methods: We studied 100 patients of ankylosing spondylitis fulfilling modified New York criteria after excluding patients with coexisting external and middle ear pathology. Pure tone audiometry was done in recruited patients. Hearing loss was considered to be present when the audiometric tests disclosed pure-tone thresholds greater than 20 dB (decibel) in at least 2 frequencies (0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 kilohertz (kHz)) of the audiogram. Mild, moderate, moderately-severe, severe and profound hearing loss were defined as hearing loss range 25-40, 40-55, 55-70, 70-90, >90 dB respectively. Clinical details such as age, disease duration, BASDI, BASFI, BASMI, cumulative NSAID dose etc. were noted of each patient. Cumulative NSAID dose was calculating using defined daily dose as given by WHO. All variables are expressed as median (25th -75th Interquartile range)
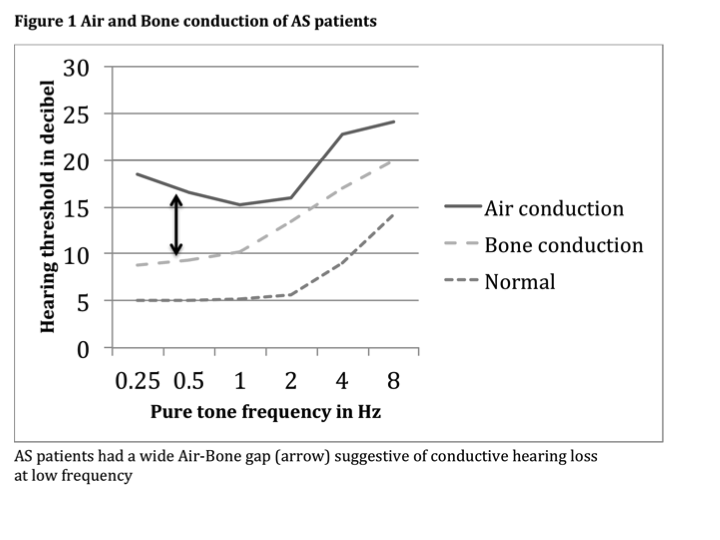
Results: Ninety-six of the 100 patients were male and the median age was 32 (23-42) years and median duration of illness was 6 (2-12) years. Median BASDAI, BASFI, BASMI and cumulative NSAID dose were 3(1.7-4.9), 2(1-4.15), 3.6(1.6-5.5) and 726 (210-1825) respectively. Of the 48 with hearing loss 28 patients had bilateral hearing loss. Twenty-nine patients had pure conductive hearing loss while 16 had mixed hearing loss (components of both sensory and conductive) and only 3 had pure sensory neural hearing loss. Hearing loss was mild in 38 patients while 10 had moderate to severe hearing loss. Presence of hearing loss was associated with higher age (p=<0.05). Conductive HL, when present, was at low frequency (0.25, 0.5, 1 kHz) in 70% cases. Sensorineural HL, when present, was at high frequency (4, 8 kHz) in 75% cases. Mean air and bone conduction of the patients in comparison to normal for age is depicted in Figure-1. There was no association of hearing loss with BASMI, BASDI, BASFI or cumulative NSAID dose.
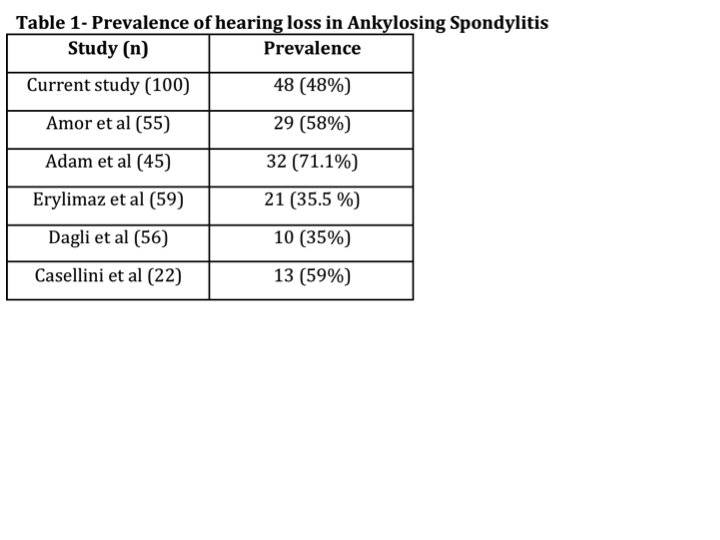
Conclusion: Hearing loss is common among patients of ankylosing spondylitis (Table-1) and it is predominantly conductive type. HL is usually mild and occurs at low frequency.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ajmani S, Keshri A, Srivastava R, Lawrence A. Conductive Hearing Loss Is Common in Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/conductive-hearing-loss-is-common-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/conductive-hearing-loss-is-common-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/