Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Some rheumatic disease patients have concomitant fibromyalgia. We wanted to determine treatment response in patients with and without concomitant fibromyalgia.
Methods: Patients were diagnosed by a rheumatologist. All patients also filled out a form to determine the presence of fibromyalgia based on the 2012 modifications of the ACR approved criteria for the diagnosis. The cut-off point was for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia was 12 or more points on a 1 to 31-point scale. Summarized counts and percentages of sex by derived DX group and for the total
- Descriptive statistics (N, mean, SD, median, min, max, etc) for the FMS score by derived DX group and for the total
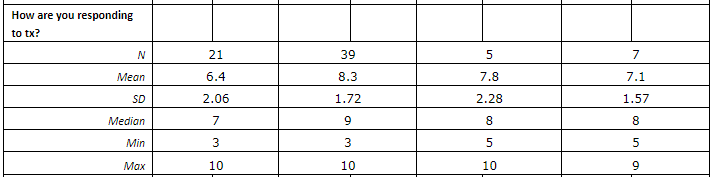
- Descriptive statistics (N, mean, SD, median, min, max, etc) for the responses to “How are you responding to tx” by DX group and for the total but also summary of the counts and percentages of the number of patients having each tx score (1, 2, 3, etc).
- A Kruskall-Wallis test to compare all 4 dx groups’ pain score and also the tx response score.
- Upon confirming that there’s indeed a difference between all 4 groups for both scores, comparisons were done, using the Mann-Whitney test and the Bonferroni correction
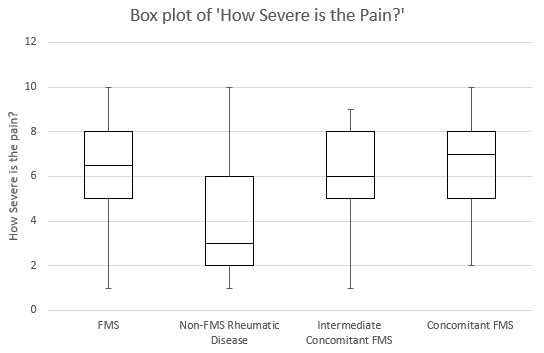
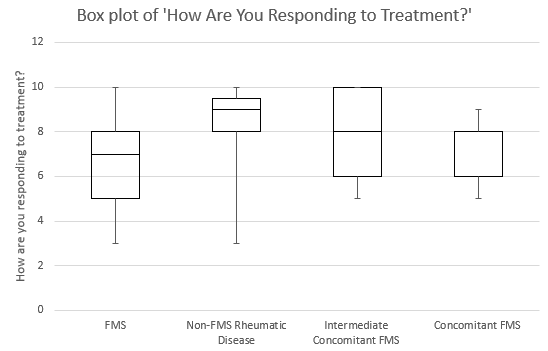
Results: There were 503 patients analyzed in this study; 75% were female and 25% were male. Of these, 108/503 (22%) had FMS diagnosis, 273/503 (54%) were determined to have other rheumatic diseases but no concomitant FMS (FMS score < 10), 39/503 (8%) were determined to have other rheumatic diseases and potential FMS (FMS score 10 or 11), and 83/503 (17%) were determined to have other rheumatic diseases and concomitant FMS (FMS score > 11). See table below for a summary of these patients’ pain scores and response to treatment scores.
The Kruskall-Wallis test for both scores and showed a significant difference between the 4 diagnosis groups for the pain score (p< 0.0001) and the response to treatment score (p< 0.0001), indicating that indeed there are differences in pain sensation and response to treatment between the 4 diagnosis groups. When multiple comparisons were performed, the ones that were statistically significantly different for the pain score were:
Concomitant FMS vs No Concomitant FMS (p< 0.0001)
No Concomitant FMS vs FMS (p< 0.0001)
No Concomitant FMS vs Intermediate/potential Concomitant FMS (p< 0.0001)
This means that there are significant differences between each of those pairs of dx groups in terms of the pain score. One can conclude from this that having FMS or Concomitant FMS seems to be associated with higher pain scores.
Conclusion: Those patients who scored 12 or more points on the ACR diagnostic criteria scale were diagnosed with having fibromyalgia. Some patients scored 10 to 12 on that scale and were considered to be intermediate in the determination of a fibromyalgia diagnosis. Patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases in addition to fibromyalgia (concomitant fibromyalgia) were evaluated for treatment response based on a visual analog scale.
There was a clear difference in patients’ response to therapy in those rheumatic disease patients who had concomitant fibromyalgia and those that do not.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katz R, Polyak Wokurka J, Small B. Concomitant Fibromyalgia in Patients with Other Rheumatic Diseases and Response to Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/concomitant-fibromyalgia-in-patients-with-other-rheumatic-diseases-and-response-to-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/concomitant-fibromyalgia-in-patients-with-other-rheumatic-diseases-and-response-to-treatment/