Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Romosozumab (romo) is a newly approved osteoporosis (OP) medicine for women with postmenopausal OP at high risk of fracture. The utilization pattern of romo has not been well described. This study aimed to evaluate the association between treatment compliance and baseline fracture risk among new users of romo.
Methods: Using fee-for-service Medicare data, women age ≥65 years newly initiating romo between 4/1/2019 and 6/30/2021 were identified. Claims data was linked to electronic medical record (EMR) data obtained from 9 data marts of 3 PCORNet Clinical Research Networks to obtain the needed covariates to estimate a FRAX score (with Body Mass Index).Comorbidities and medical history were identified from claims while biometric data were obtained from the EMR. The FRAX algorithm was used to calculate 10-year risk of hip and major fracture (clinical spine, forearm, hip, or shoulder) upon romo initiation. We set the median of FRAX (BMI) hip and major fracture risk as the cut-off for higher fracture risk. Treatment adherence (measured by the proportion of days covered [PDC]) and discontinuation rate (defined as gap > 30 days after the expected date of the next romo administration) were calculated. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate the discontinuation rate and 95% confidence interval [CI]. A Cox proportional hazard model was used to evaluate the association between baseline fracture risk and discontinuation, controlling for demographics and Charlson score.
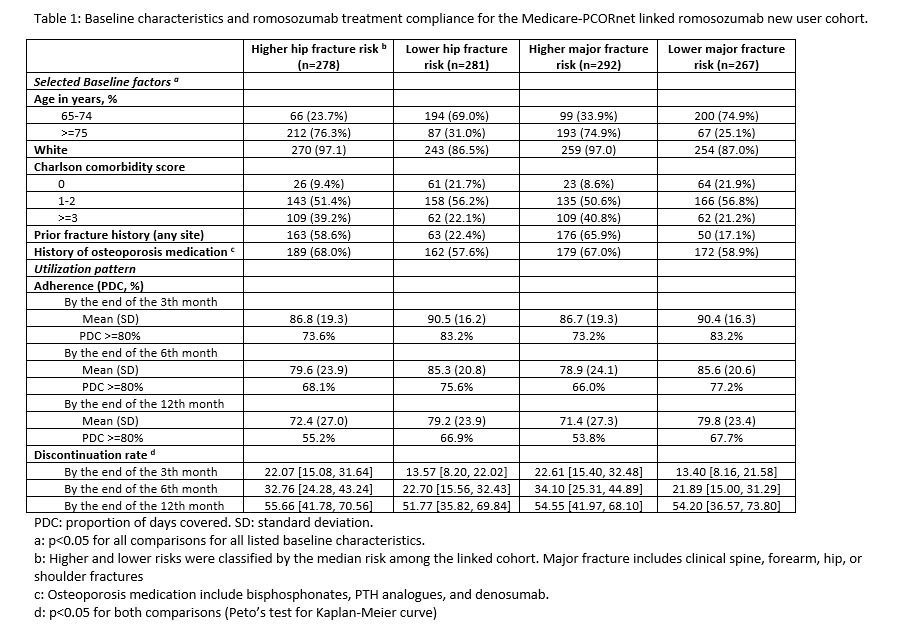
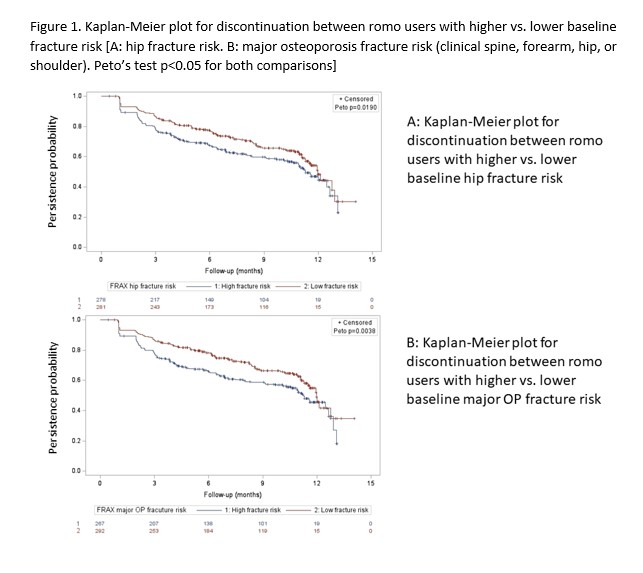
Results: There were 12,216 romo new users identified and among them, 559 were linked with PCORNet EMR data. Across PCORNet data marts, the proportion of women who linked ranged from 82% – 98%.The median (IQR) 10-year hip and major fracture risks estimated by FRAX were 11.0 (6.4, 19.0) and 26.0 (18.0, 35.0), respectively. Romo users with higher baseline fracture risk were older, had more history of fractures, were more likely to receive prior OP treatment, compared with those with lower risk (Table 1). They also had higher rate of romo discontinuation (Table 1, Figure 1). Cox regression showed that, after adjusting for age, race, geographic region, and Charlson comorbidity score, the HR (95% CI)for discontinuation associated with higher(above the median) hip and major OP fracture risk was 1.39 (1.01 – 1.91. p=0.043) and 1.51 (1.11 – 2.06. p=0.009), respectively.
Conclusion: In this cohort of women with high fracture risk and using administrative claims data linked to EHR data, romo users who had baseline higher fracture risk had poorer treatment compliance. These data suggest that physician should focus more on improving treatment adherence when prescribing new therapy such as romo for vulnerable patients with higher fracture risk.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu Y, Arora T, Curtis J, Zhang J. Compliance with Romosozumab and Fracture Risk Among Postmenopausal Women in the U.S [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/compliance-with-romosozumab-and-fracture-risk-among-postmenopausal-women-in-the-u-s/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/compliance-with-romosozumab-and-fracture-risk-among-postmenopausal-women-in-the-u-s/