Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Measures Of Healthcare Quality Poster I: Testing, Screening, & Treating
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) induced retinal toxicity remains a major concern because it can lead to irreversible damage to retinal pigment epithelium and blindness. American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) 2016 guidelines recommend to use HCQ at dosages ≤5 mg/kg real body weight to minimize toxicity [1]. Important risk factors for retinal toxicity are daily and cumulative dosage of HCQ, duration of treatment, patient age and concomitant renal or liver diseases [1].
Methods: This is a quality improvement project, a retrospective electronic medical records (EMR) review of patients who have been treated with HCQ since April 2016 through February 2019 at the State University of New York Upstate Medical University. Primary outcome was to identify patients whose dose exceeded the recommended dosage (≤5 mg/kg real body weight) according to 2016 AAO guidelines. Data on cumulative dosages, real body weight, height, age, adherence to the screening ophthalmologic exams within the last 5 years and concomitant renal or liver disease were extracted from EMR. Importantly, we also identified the details of number of patients who were discontinued HCQ use due to retinal toxicity.
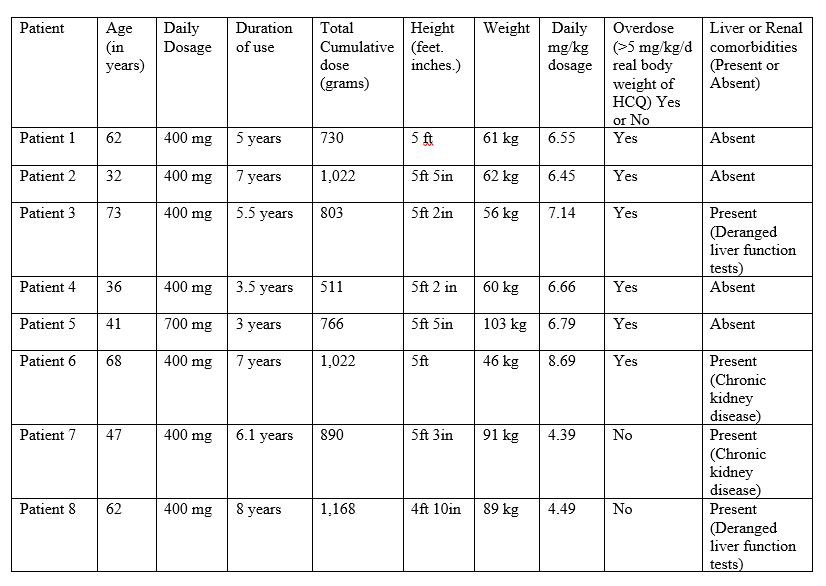
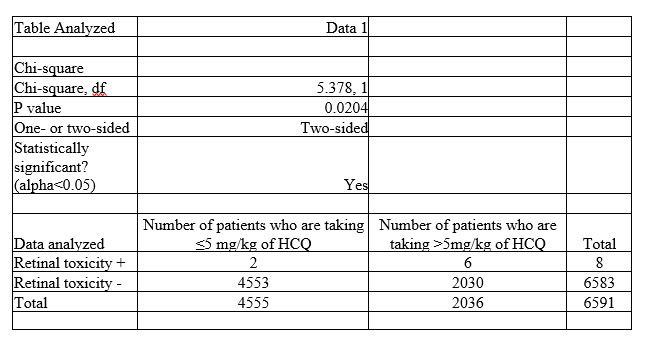
Results: A total of 6591 patients on HCQ were identified. The average age was 50 years. Most common indications for HCQ usage were 33% for systemic lupus erythematous, 32% for undifferentiated connective tissue disease, 15.5% for rheumatoid arthritis. 2036/6591 (30.8%) patients were receiving more than 5 mg/kg/day of HCQ. 827/6591 (12.5%) patients had eye exams. Eight patients (0.96%) were diagnosed with HCQ induced retinal toxicity by ophthalmologists (Table 1) and discontinued HCQ. Among eight patients with retinal toxicity, 6 patients were taking > 5 mg/kg/day real body weight of HCQ. Their cumulative dosage ranged from 511 grams to 1,168 grams. Two patients have comorbid chronic kidney disease and two other patients have deranged liver function tests. Their duration of HCQ therapy ranged from 3 years to 8 years. The more than 5 mg/kg/day dosages were associated with increased retinal toxicity {chi-square = 5.378; p=0.02} (Table 2).
Conclusion: 69.2 % of patients were correctly administered HCQ with dosages based on the 2016 AAO guidelines. Retinal toxicity from HCQ is a rare phenomenon (0.96%) and apparently related to more than 5mg/kg/day of real body weight dosing. It is imperative to adjust the HCQ dosage according to body weight.
References
- Marmor MF, Kellner U, Lai TY, et al.; American Academy of Ophthalmology. Recommendations on Screening for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy (2016 Revision). Ophthalmology. 2016 Jun; 123(6):1386-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.058. PMID: 26992838
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Swe T, Perl A. Compliance with Hydroxychloroquine Dosage According to 2016 American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) Guidelines: A Study with 6591 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/compliance-with-hydroxychloroquine-dosage-according-to-2016-american-academy-of-ophthalmology-aao-guidelines-a-study-with-6591-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/compliance-with-hydroxychloroquine-dosage-according-to-2016-american-academy-of-ophthalmology-aao-guidelines-a-study-with-6591-patients/