Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes II: Imaging
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine and sacroiliac joints (SIJ) are important tools for the diagnosis of axial SpA and the presence of inflammation at baseline is associated with a better treatment response. However, data on the relevance of the complete resolution of inflammation / the presence of residual inflammation for a clinical response over time is missing. The purpose of the study was to evaluate whether the presence of residual inflammation in MRI of SIJ and spine after 6 months of treatment is associated with clinical response after 12 months in patients with early axial SpA.
Methods: In the ESTHER study, a total of 76 patients with early axial SpA with a symptom duration less than 5 years, and with active inflammation on MRI in the spine and/or SIJ at baseline were randomized to be treated with etanercept (n=40) or sulfasalazine (n=36) for 12 months.
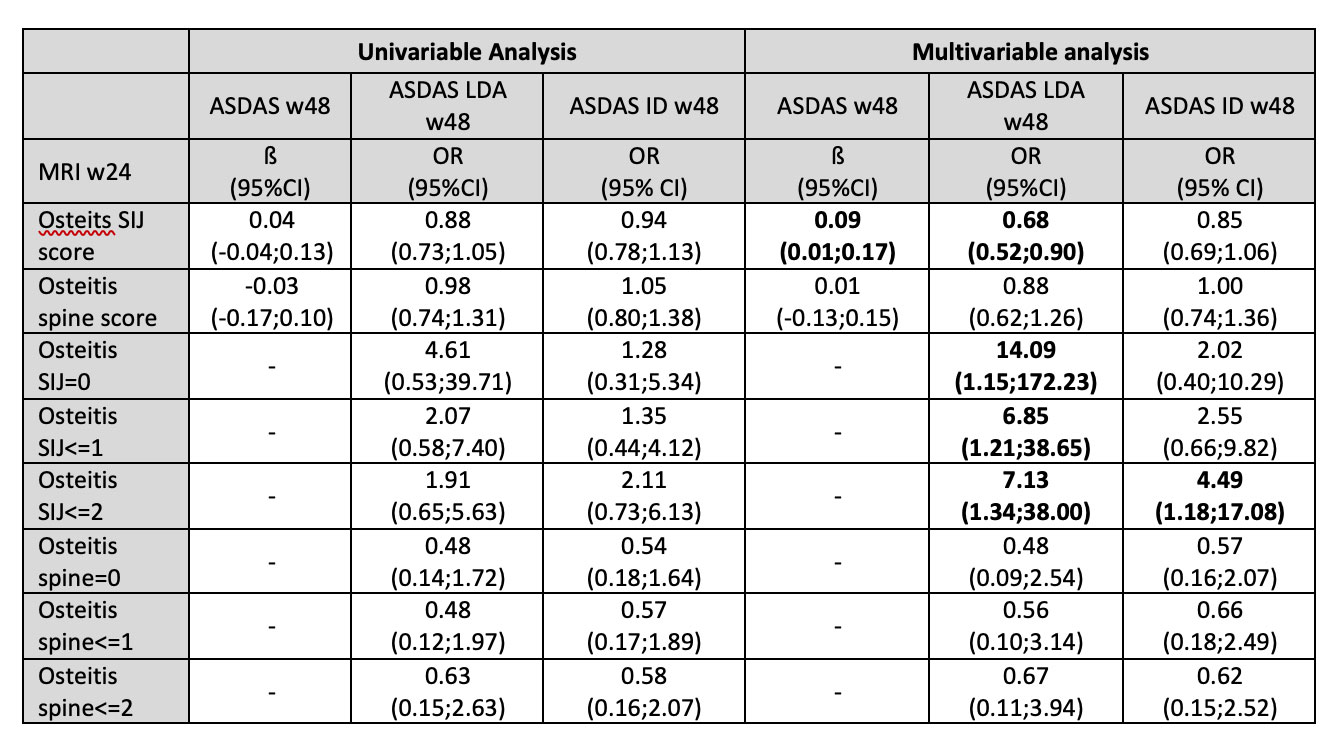
Clinical and laboratory assessments included C-reactive protein (CRP), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS). MRI of spine and SIJ were performed at weeks 0, 24, and 48; and were scored by two radiologists, who were blinded for all clinical data including treatment and time point, according to the Berlin scoring system. The final osteitis score for the SIJ and for the spine was calculated as the mean score of both readers. A multivariable regression analysis was performed to determine the effect of residual inflammation in MRI of SIJ and spine at week 24 for the ASDAS score and for the achievement of ASDAS low disease activity (LDA, < 2.1) and ASDAS inactive disease (ID, < 1.3) at week 48.
Results: A total of 67 patients with axial SpA were included for the analysis based on availability of MRIs at baseline and Week 48. The characteristics of patients included for this analysis were similar to the whole group of ESTHER study. SIJ and spine osteitis score on MRI at baseline (mean±SD) was 6.9±6.1 and 1.5±2.5, respectively. In the multivariable regression analysis, the presence of inflammation on MRI of SIJ at week 24 was associated with a higher ASDAS score at week 48 and lower odds of achieving ASDAS LDA and ASDAS ID at week 48 (Table). Complete resolution of inflammation in the SIJ at week 24 (Osteitis SIJ score=0) was associated, however, with higher odds of achieving ASDAS LDA at week 48: OR=14.09, (95%CI 1.15;172.23). This effect was less obvious for inflammation in the spine.
Conclusion: Resolution of inflammation on MRI of SIJ after 6 months of treatment is associated with a better clinical outcome in terms of achieving ASDAS ID and LDA over time in patients with early axial SpA. This data underlines the importance of complete inflammation control for a better clinical outcome in axSpA.
Each model in the multivariable regression analysis was adjusted for age, sex, symptom duration and HLA-B27 positivity. ASDAS, ankylosing spondylitis disease activity score; ASDAS ID, ASDAS inactive disease; ASDAS LDA, ASDAS low disease activity; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SIJ, sacroiliac joints; w24, week 24; w48, week 48.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rios-Rodriguez v, Torgutalp M, Althoff C, Haibel H, Hermann K, Proft F, Protopopov M, Rademacher J, Sieper J, Poddubnyy D. Complete Resolution of Inflammation on MRI Is Associated with a Better Clinical Response over Time in Patients with Early Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complete-resolution-of-inflammation-on-mri-is-associated-with-a-better-clinical-response-over-time-in-patients-with-early-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complete-resolution-of-inflammation-on-mri-is-associated-with-a-better-clinical-response-over-time-in-patients-with-early-axial-spondyloarthritis/