Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster I: Clinical Characteristics/Presentation/Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
COMPLEMENT C3 AND C4 LEVELS AND ITS CORRELATION WITH DISEASE ACTIVITY IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
Background/Purpose: Cytokines play a major role in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid arthritis. However, some studies have also noticed the presence of increased levels of activated products of the complement system, not only in synovial fluid, but also in plasma of these patients, implying that the activation of complement could be another crucial event in the RA inflammatory cascade. Makinde et al. observed that plasma levels of complement C3 and C4 were significantly increased in RA patients when compared to healthy subjects, and they seemed to be correlated with disease activity. The aim of our study was to determine plasma levels of complement C3 and C4 in RA patients and to assess their correlation with disease activity.
Methods: Multicenter, cross-sectional, observational study, that included consecutively RA patients according to 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria. Connective tissue disorders (including secondary Sjögren´s Syndrome) and other conditions that might modify complement levels were excluded. Demographic and RA characteristics, disease activity measures and serological analysis [complement C3 and C4, erythrosedimentation (ESR) and C reactive protein (CRP)] were collected.
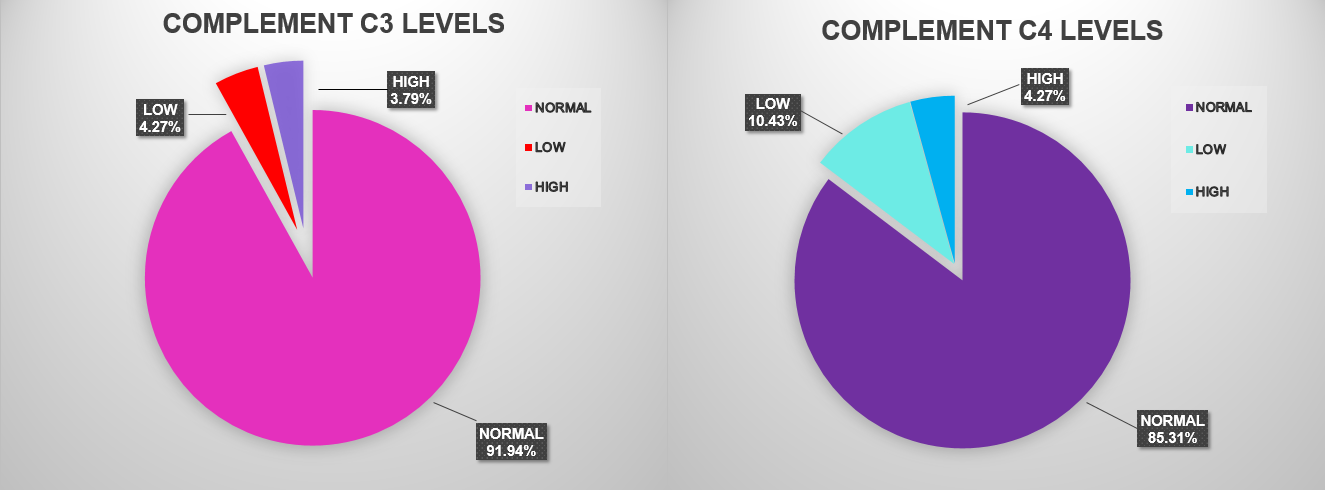
Results: Two hundred and eleven patients (98% females) were included. Mean age 50 years (SD 14.7). Fifty-nine percent were under treatment with NSAIDs, 61% with Corticosteroids, 77% with DMARDs (most of them with Methotrexate) and 20.6% patients were on biologic therapy. Mean DAS28 score was 4.29 (SD 1.55). The median ESR and CRP were 46 mm/h (IQR 12-40) and 1.1 mg/dl (IQR 0.3-3.8), respectively. Complement levels were mostly normal: C3 in 194 patients (92%) and C4 in 180 patients (85%). There was no correlation between DAS28 score and C3 (p=0.79) or C4 (p=0.07) levels. Patients with increased levels of C4 showed a median PCR higher than patients with low C4 levels (1,95 mg/dl versus 0,40 mg/dl, p=0,039). This association was not observed with C3 levels. There was no correlation between complement and ESR. DMARs and/or biologic therapy didn´t modify C3 or C4 levels. However, we observed an association between the use of Corticosteroids and C4 levels (p= 0,003): patients on Corticosteroid therapy showed a higher proportion of low C4 levels than those without Corticosteroids (13% versus 6%).
Conclusion: Despite the literature findings, most of our RA patients had complement levels within normal ranges. Plasma levels of complement C3 and C4 did not correlate with disease activity. We emphasize the association between RCP and C4 as well as a higher proportion of low C4 levels in patients treated with corticosteroids.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sosa J, Papasidero SB, Medina MA, Klajn D, Chaparro del Moral R, Caracciolo JA, Casalla L, Zárate L, Capozzi N, Marcos J, García MA, Quinteros A, Leal MO, Vásquez DL, Stancich MI, Alvarez A, Sanchez Andía C, Kirmayr K, Correa MDLÁ, Constantino A. Complement C3 and C4 Levels and Its Correlation with Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-c3-and-c4-levels-and-its-correlation-with-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-c3-and-c4-levels-and-its-correlation-with-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/