Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease that primarily affects the axial skeleton and frequently affects the peripheral joints and entheses. AxSpA encompasses ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axSpA. Sex differences have been described for patient reported outcomes (PROs) in SpA; however, more research is needed to better understand the overall clinical burden of axSpA in women, particularly in the United States. We aim to compare the patient demographics, clinical characteristics, treatment profiles, disease activity, quality of life, and work productivity between men and women with axSpA in the US-based Corrona PsA/SpA Registry.
Methods: This study included patients aged ≥ 18 years with axSpA enrolled in the Corrona PsA/SpA Registry between March 2013 and November 2018. Patients who were concurrently diagnosed with PsA were excluded. Patient demographics, clinical characteristics, treatment profiles, disease activity, quality of life, and work productivity were characterized for all patients with axSpA at enrollment and were compared between men and women using t tests or Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for continuous variables and χ2 or Fisher exact tests for categorical variables.
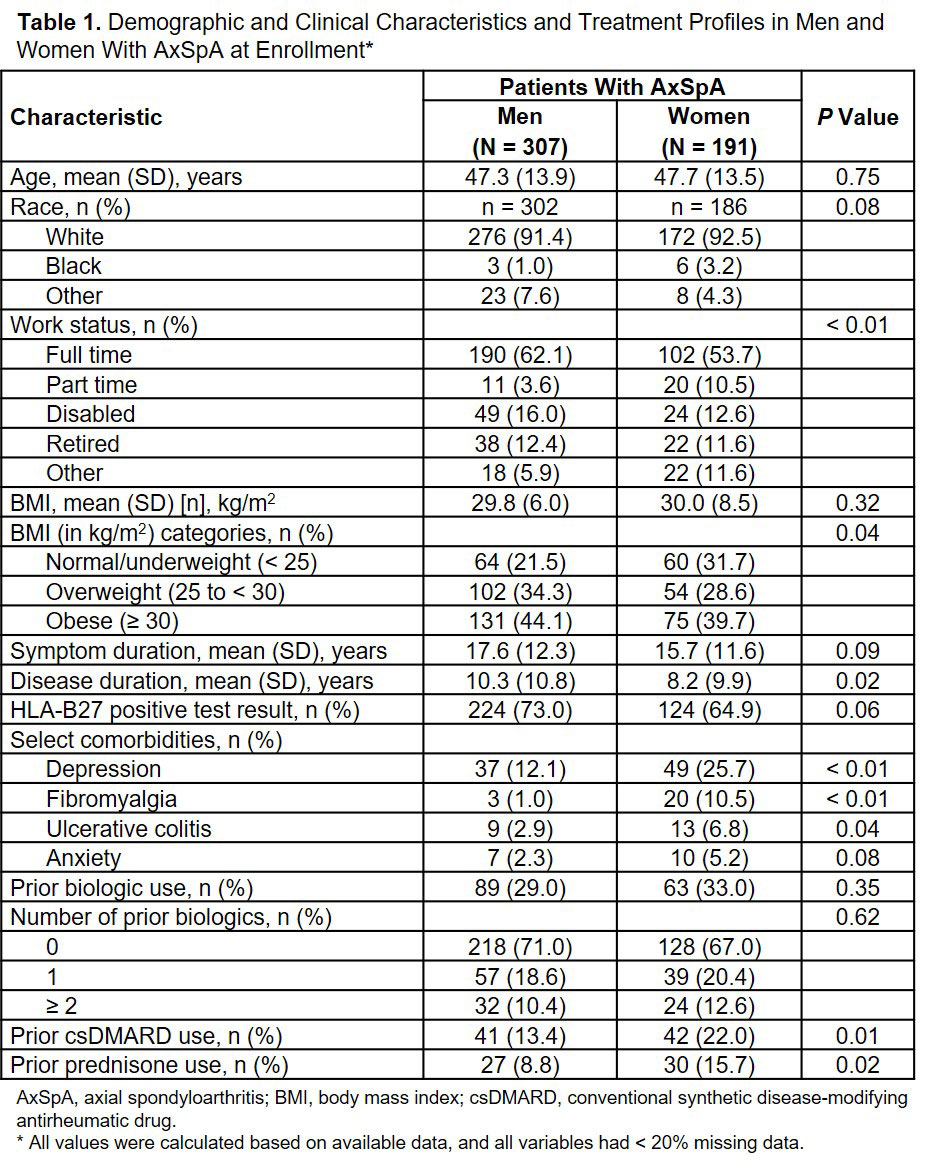
Results: Of 498 patients with axSpA who were included in the study, 307 (61.6%) were male and 191 (38.4%) were female. Compared with men, women were less likely to work full time, were more likely to be normal weight/underweight, had a shorter disease duration, and were more likely to have depression, fibromyalgia, and prior csDMARD and prednisone use (Table 1; all P < 0.05). At enrollment, women with axSpA had a shorter occiput-to-wall distance, but also had worse disease activity compared with men, as reflected by higher BASDAI and BASFI scores, higher enthesitis and tender/swollen joint counts, worse pain and fatigue, worse physical function (HAQ-S) and health state today (EQ VAS), and more severe work and activity impairment (Table 2; all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In this US registry of patients with axSpA, women had an increased overall burden of disease compared with men, including higher patient reported symptoms, higher disease activity, and greater work productivity impairment. Women also had lower scores for spinal mobility with increased signs of peripheral arthritis (eg, higher tender/swollen joint and enthesitis counts), suggesting that conventional definitions of axSpA centered around axial symptoms may not be representative of the female population with disease. Improved awareness of sex differences in presentation of axSpA may aid physicians in earlier identification and improved management of the disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Liu M, Rebello S, McLean R, Dube B, Glynn M, Yi E, Park Y, Ogdie A. Comparison of Men and Women with Axial Spondyloarthritis in the US-Based Corrona Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondyloarthritis (PsA/SpA) Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-men-and-women-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-the-us-based-corrona-psoriatic-arthritis-spondyloarthritis-psa-spa-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-men-and-women-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-the-us-based-corrona-psoriatic-arthritis-spondyloarthritis-psa-spa-registry/