Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: While difficult to directly compare effectiveness of biologics in observational settings, drug discontinuation can be a useful substitute. We compared the discontinuation rates of individual and groups of biologics, by mechanism of action, mode of delivery, previous biologic use, line of treatment, and concomitant MTX and/or prednisone.
Methods: Using a large US-wide observational cohort, the National Data Bank for Rheumatic Diseases (NDB), we characterized patients with RA who initiated a biologic from 2005 through 2015. For simplicity, we included tofacitinib as a non-TNF (NTNF) biologic. Baseline characteristics were assessed by each biologic and by grouped mechanism of action. Discontinuation, described using Kaplan-Meier survival curves, was defined as either stopping the drug or adding another DMARD. Sensitivity analyses defined discontinuation only as stopping the drug. Discontinuation rates were further analyzed by stratifying several factors: route of administration (SC vs PO vs IV), line of treatment (1st, 2nd, 3rd+), prior use of biologics (TNF or NTNF) and concomitant use of MTX and/or prednisone.
Results: A total of 2458 patients initiated a TNF and 1349 a NTNF, representing 6326.5 and 2987.5 patients-years of follow-up, respectively. Overall, median survival (IQR) was 1.5 (0.5-3.0) for TNFs and 2 (1- 3.5) for NTNFs, or 4 (2-9) and 4 (2-7.5) in sensitivity analysis. Figure illustrates individual biologic survival curves by mechanism of action. Grouping by route of administration, the median survival was for PO of 3.0 (2-6) years and did not differ between IV and SC (1.5 (0.5 – 2.5) years). When considering later lines of treatment, the rates of discontinuation were similar with median survival (IQR) of TNF vs NTNF: 1st line 3.5 (1-9.5) vs 2.5 (1-5.5), 2nd line 4 (1.5 -9.5) vs . (5.5-.) and 3rd+ line of treatment 3.5 (2-8) vs 3 (1-5). Stratifying by prior use of TNF, the survival was longer for TNF vs. NTNF 1.5 (1-3.5) vs 0.5 (0.5 -0.5) years, but the reverse occurred with prior use of NTNF, 1 (0.5 -1.5) vs. 2 (1.-3.5) years. For both groups, discontinuation rates were lower with no concomitant MTX, TNF 8.5 (3.5-.) vs. NTNF 6 (3.5 -.).
Conclusion: As more medication options became available over the past decade, discontinuation rates of biologics for patients with RA have increased and have become more similar. Surprisingly we found rates to decrease when biologics were taken without MTX, an area for further investigation. 
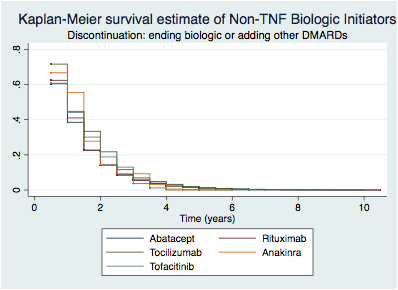
Figure – Discontinuation curves of TNF and NTNF biologic initiators.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pedro S, Michaud K. Comparison of Discontinuation Rates Among Patients with RA Initiating Biologics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-discontinuation-rates-among-patients-with-ra-initiating-biologics/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-discontinuation-rates-among-patients-with-ra-initiating-biologics/
