Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: An international task force has agreed that remission or low disease activity (LDA) are key treatment targets for patients (pts) with PsA, and recommends the Disease Activity Index in Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) or minimal disease activity (MDA) to assess respective disease activity states.1 Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA. In this post hoc analysis, we compared DAPSA LDA with MDA, and DAPSA remission with very low disease activity (VLDA) and DAS28-3(CRP) remission, in pts with PsA receiving tofacitinib.
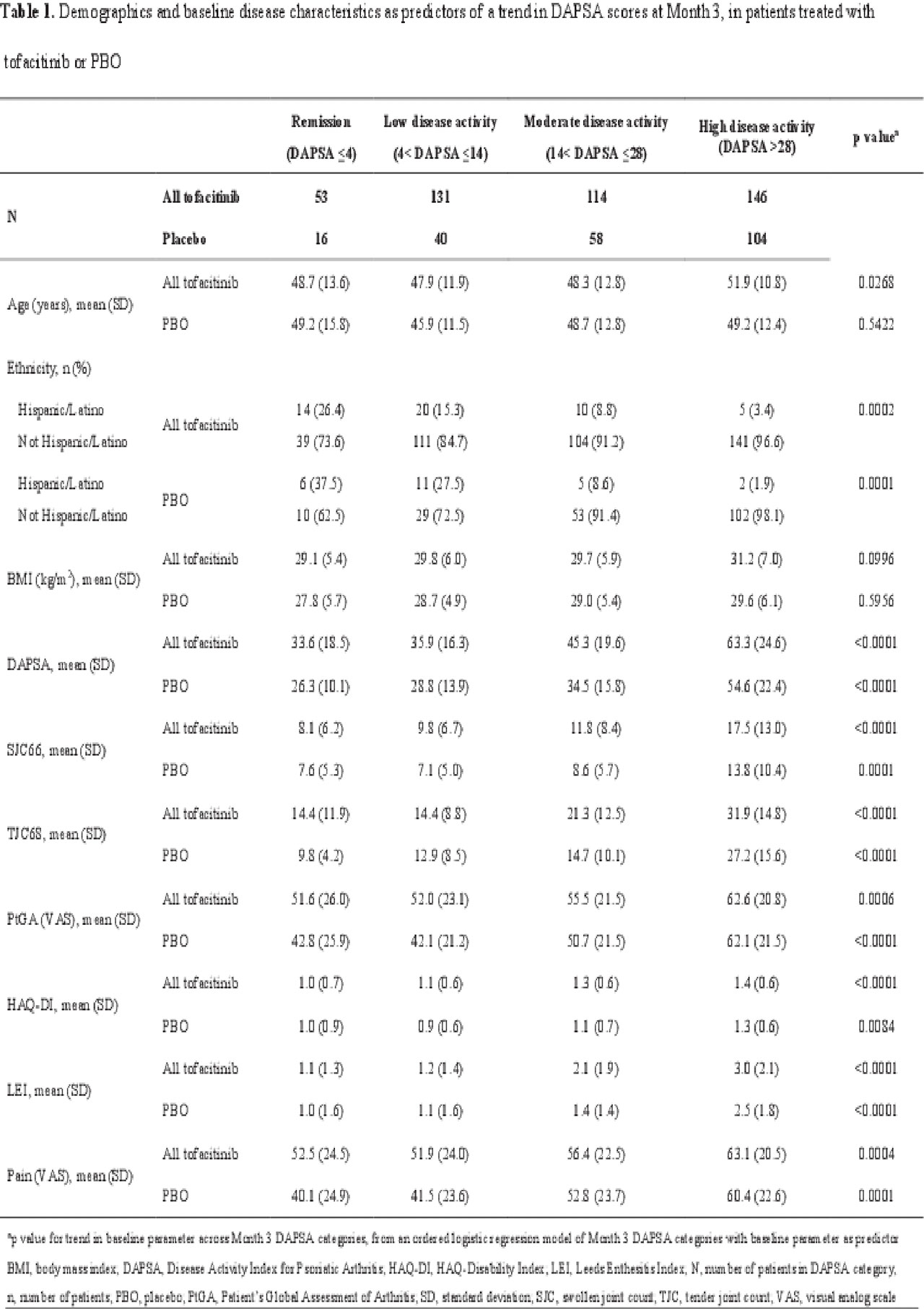
Methods: Data were pooled from 2 Phase 3 studies (OPAL Broaden [12 months; NCT01877668]; OPAL Beyond [6 months; NCT01882439]) for pts receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID) or placebo (PBO). DAPSA was determined by summing: swollen joint count (SJC66); tender joint count (TJC68); Patient’s Global Assessment of Arthritis (PtGA; visual analog scale [VAS]); pain (VAS); and CRP. Pts were classified as achieving MDA or VLDA when meeting ≥ 5 (MDA) or 7 (VLDA) of the following criteria: TJC68 ≤ 1; SJC66 ≤ 1; Psoriasis Activity and Severity Index ≤ 1 or body surface area ≤ 3%; pain (VAS) ≤ 15; PtGA (VAS) ≤ 20; HAQ-DI ≤ 0.5; tender entheseal points (using Leeds Enthesitis Index) ≤ 1. A logistic regression model was used to assess demographic and baseline characteristics as predictors of a trend in DAPSA scores at Month (M)3. DAPSA LDA (≤ 14), MDA, DAPSA remission (DAPSA ≤ 4), VLDA, and DAS28-3(CRP) remission (DAS28-3[CRP] < 2.6) rates were compared at M1, M3, and M6 for pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID, and at M6 for pts receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID. Agreement between disease activity indices at M6 was evaluated using a kappa test. The percentage of tofacitinib-treated pts who achieved MDA, VLDA, and non-response was reported at M6 stratified by achievement of DAPSA LDA, remission, or non-response.
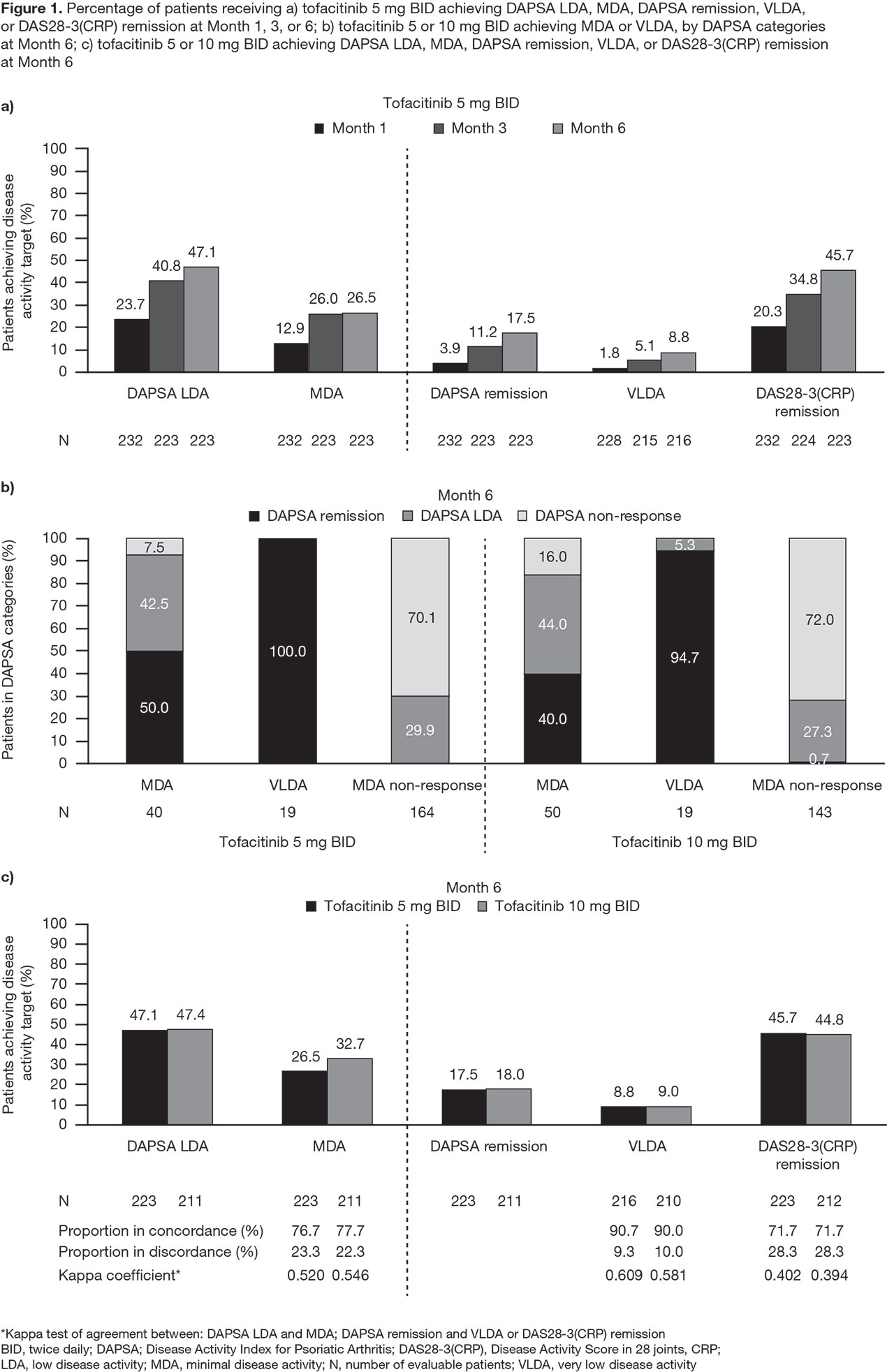
Results: This analysis included 709 pts: tofacitinib 5 mg BID, n=237; tofacitinib 10 mg BID, n=236; PBO, n=236. Older pts treated with tofacitinib, and pts with higher baseline PsA activity and HAQ-DI treated with tofacitinib or PBO were significantly (p < 0.05) more likely to have a worse DAPSA response at M3; Hispanic/Latino pts treated with tofacitinib or PBO were significantly more likely to have a better DAPSA response at M3 than pts of other ethnicities (Table 1). DAPSA LDA, MDA, remission (DAPSA and DAS28-3[CRP]), and VLDA rates generally increased from M1 to M6 (Figure 1a). At M6, most tofacitinib-treated pts who achieved MDA, and all who achieved VLDA, were also in DAPSA remission or LDA (Figure 1b). Moderate agreement (defined by kappa values 0.41−0.60) was observed between DAPSA LDA and MDA, and between DAPSA remission and VLDA (Figure 1c).
Conclusion: Remission and LDA rates generally increased over time in pts with PsA receiving tofacitinib. DAPSA LDA showed moderate agreement with MDA, and DAPSA remission showed moderate agreement with VLDA, confirming that DAPSA is a useful measurement tool to assess disease activity in pts with PsA treated with tofacitinib.
- Smolen JS et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:3-17.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Sarah Piggott of CMC Connect and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Citera G, Schneeberger E, Nash P, Smolen J, Mease P, Soriano E, Matulic V, Helling C, Szumski A, Mundayat R, Graham D, Ponce de Leon D. Comparison of Different Remission Indices in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of Data from Phase 3 Tofacitinib Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-different-remission-indices-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-data-from-phase-3-tofacitinib-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-different-remission-indices-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-data-from-phase-3-tofacitinib-studies/