Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Achieving low disease activity (LDA) or remission is a main treatment target in PsA. Composite indices used to assess disease activity include Disease Activity index for PsA (DAPSA) and PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS), which both have cut points for the states of remission and LDA. In addition, LDA and remission can be assessed by the pure state instrument Minimal Disease Activity (MDA)/Very Low Disease Activity (VLDA). These analyses aim to identify overlap and differences between these composite indices in PsA patients treated with upadacitinib (UPA), a Janus kinase inhibitor, or adalimumab (ADA) in the phase 3 SELECT-PsA 1 trial.
Methods: In SELECT-PsA 1 (phase 3, randomized controlled trial, with long-term extension up to 5 years), patients with moderate to severely active PsA with prior inadequate response or intolerance to ≥1 non-biologic DMARD were randomized to oral UPA at doses of 15 mg or 30 mg (once daily), subcutaneous ADA 40 mg (every other week), or placebo.1 LDA was assessed using MDA (threshold: 5/7 criteria), DAPSA (≤14), PASDAS (≤3.2), and Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PtGA; ≤3).2,3 These post-hoc descriptive analyses include 1-year (cut off: week 56) as observed data from UPA 15 mg and ADA.
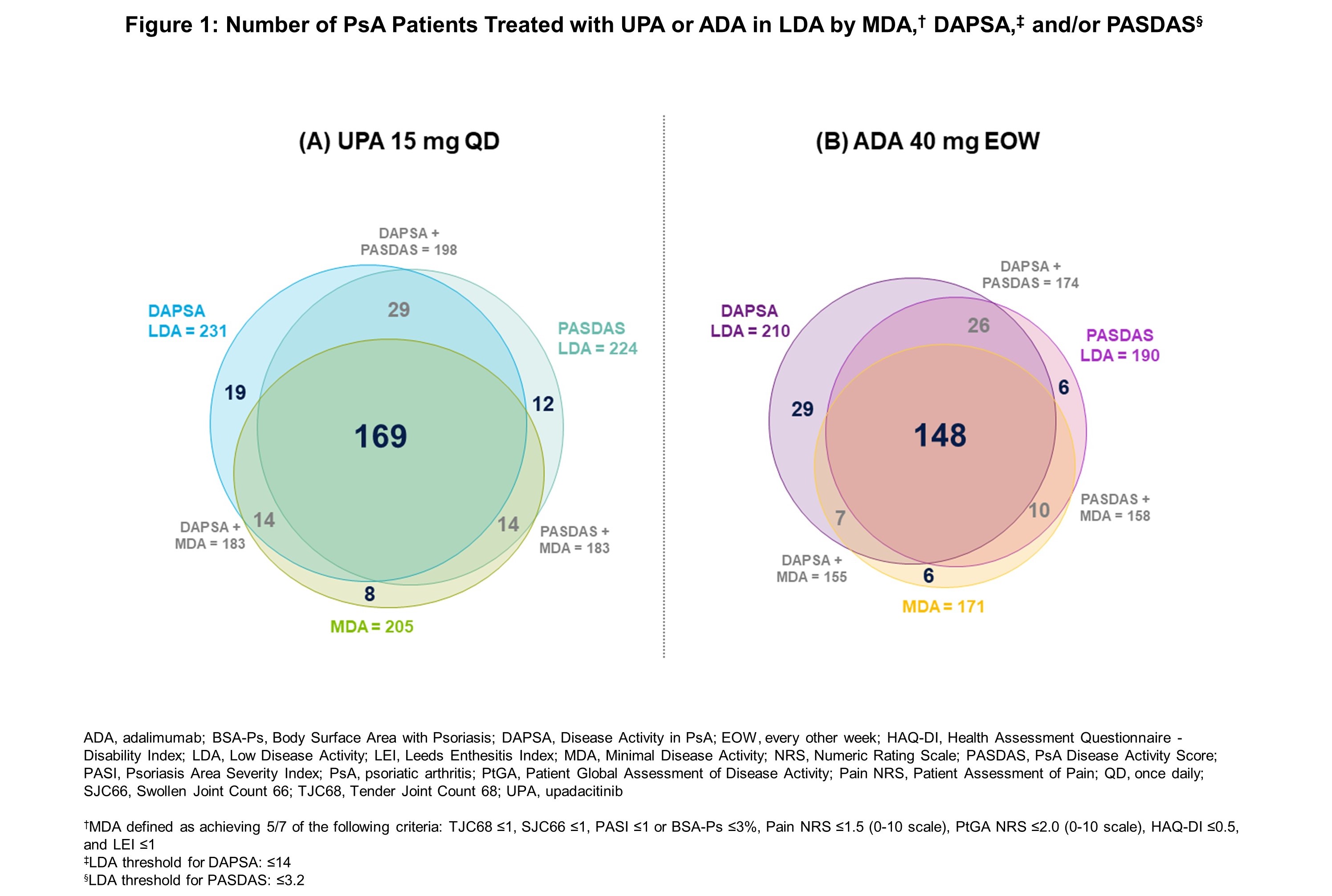
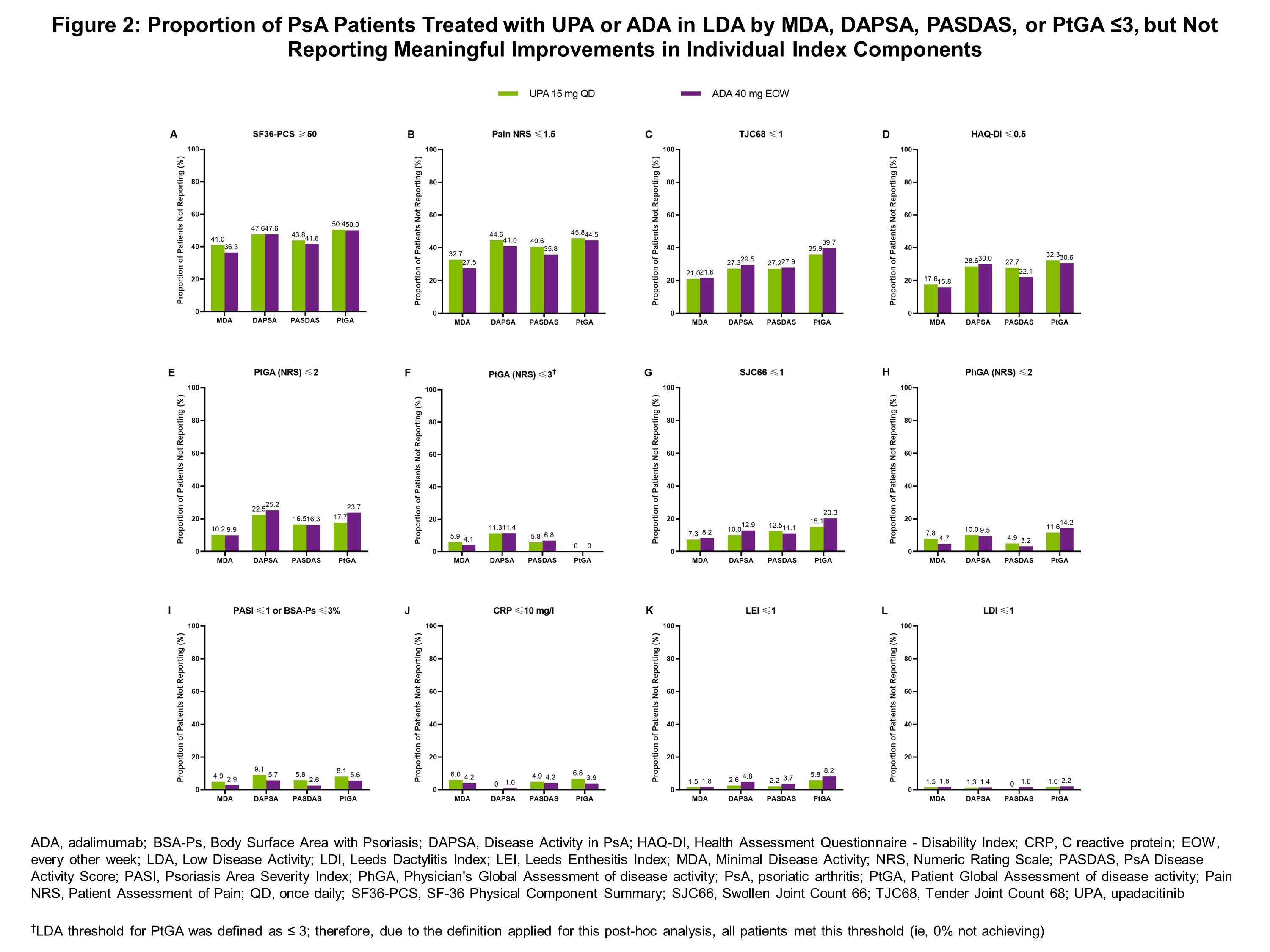
Results: In total, 858 patients (UPA 15 mg: n=429; ADA: n=429) were included in these analyses. Patients receiving UPA and ADA were on average 52 years of age, 54% were female, with an average disease duration of approximately 6 years.1 With both UPA and ADA, there was a high degree of overlap in the proportion of patients achieving LDA thresholds in MDA, DAPSA, and PASDAS (Figure 1), with reported PtGA improvements showing a similar trend. Defining LDA according to MDA or respective cut points for DAPSA, PASDAS, or PtGA, the proportion of “non-responders” (ie, patients who did not reach such states) is shown in Figure 2. Of the individual components included in these indices, fewer patients reported low levels of SF-36 Physical Component Summary (SF36-PCS), Patient Assessment of Pain Numeric Rating Scale (Pain NRS), and Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index (HAQ-DI) scores, as well as Tender Joint Count 68 (TJC68), with similar responses observed across all indices.
Conclusion: In this post-hoc analysis from the SELECT-PsA 1 trial, there was a high degree of overlap between patients in LDA across the composite indices, including MDA, DAPSA, and PASDAS, irrespective of treatment with UPA 15 mg or ADA and despite variability in inclusion of certain components in some indices but not others. Across all indices, fewer patients reported low levels of SF36-PCS, Pain NRS, and HAQ-DI scores, and TJC68. These data show that improvements in (subjective) “patient-driven” components were the most challenging to achieve. These data indicate a similar pattern of residual disease activity, or influence by residual damage or external factors, regardless of composite endpoint utilized.
References:
1. McInnes IB et al. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(13):1227-39
2. Kerschbaumer et al. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018; 32:401-14
3. Gorlier et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019; 78:201-208
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen J, Lubrano E, Kishimoto M, Bălănescu A, Strand V, Gao T, Vranich N, Lippe R, Tillett W. Comparison of Composite Indices for Disease Activity in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Upadacitinib: A Post-Hoc Analysis from SELECT-PsA 1 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-composite-indices-for-disease-activity-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-upadacitinib-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-select-psa-1/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-composite-indices-for-disease-activity-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-upadacitinib-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-select-psa-1/