Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are immune mediated inflammatory disorders linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), mostly due to accelerated atherosclerosis. An imbalance between cholesterol inflow and outflow leads to lipid overload and is one mechanism for initiation of atherosclerosis. This study examines the effect of RA and PsA plasma compared to healthy control (HC) plasma on expression of genes responsible for cellular cholesterol efflux and influx by exposing naïve THP-1 human macrophages to RA, PsA and HC plasma. In addition, cytokine levels were measured in RA, PsA and HC.
Methods: THP-1 differentiated macrophages (106 cells/ml, phorbol dibutyrate, 100nM, 48h), were incubated (370C, 5% C02, 18h) in RPMI 1640 media in the presence of 10% plasma from the following subjects: 1) 22 RA, 2) 21 HC age and sex-matched to the RA group, 3) 8 PsA, 4) 8 HC age matched to the PsA group. The study was performed under a Winthrop University Hospital IRB-approved protocol. Cytokine levels were evaluated by ELISA. Cholesterol transport protein mRNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR using specific primers for each gene.
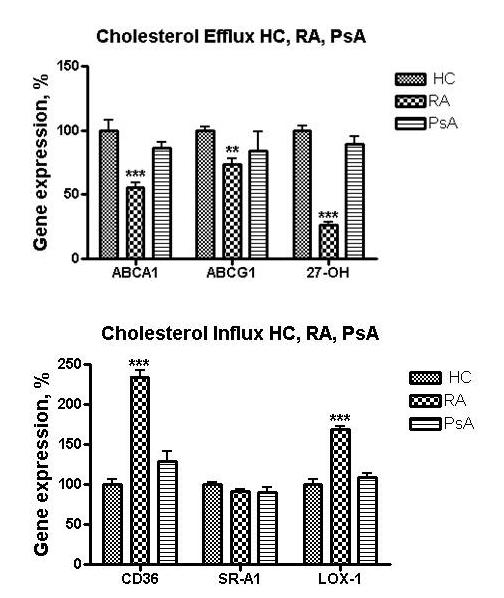
Results: 10% RA plasma increased macrophage expression of cholesterol influx genes (scavenger receptors CD36 and LOX-1). CD36 mRNA increased by 134.45±38.56% (P<0.001) and LOX-1 by 68.9±12.45% (P<0.001) above cells exposed to HC plasma (set at 100%). SR-A1 expression did not different in RA vs. HC. Expression of cholesterol efflux genes (ATP binding cassette transporter (ABC)A1, ABCG1 and 27-hydroxylase) was suppressed in macrophages treated with RA plasma vs. HC plasma. Mean ABCA1 mRNA expression decreased to 55.29±10.23% (P<0.001) compared to cells treated with HC plasma. ABCG1 mRNA fell to 73.65±9.67% (P<0.05) upon exposure to RA plasma vs. HC plasma. 27-Hydroxylase mRNA in THP-1 macrophages in the presence of RA plasma was diminished to 26.5±8.56% (P<0.01). In contrast, 10 % PsA plasma did not alter message level of the cholesterol influx or efflux proteins compared to HC (Figure). Pro-inflammatory cytokines were significantly higher in RA plasma compared to HC plasma: IL-6 (4.66±0.44 pg/ml vs. 1.71±0.045 pg/ml, P<0.01), TNF-α (4.34±0.40 ng/ml vs. 1.30±0.22 ng/ml, P<0.001) and IFN-γ (171.2±125.5 pg/ml vs. 9.54±0.7 pg/ml, P<0.001), respectively. In contrast, PsA plasma did not show significant elevations in IFN-γ, TNF-α or IL-6.
Conclusion: RA plasma but not PsA plasma induced a pro-atherogenic profile of genes responsible for cholesterol infux and efflux. This may be due to the significantly greater elevation of inflammatory cytokines, notably IFN-γ (which is known to alter cellular cholesterol flux in a pro-atherogenic manner) demonstrated in the RA plasma samples. A lack of significant effect on cholesterol transport gene expression by PsA plasma is consistent with less CVD risk in PsA compared to RA.
Disclosure:
B. Hafiz,
None;
I. Voloshyna,
None;
M. J. Littlefield,
None;
S. E. Carsons,
None;
E. Belilos,
None;
K. Belostocki,
None;
L. A. Bonetti,
None;
G. C. Rosenblum,
None;
A. B. Reiss,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-atherogenicity-of-plasma-from-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/