Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite the negative clinical trials, B-cell depletion by antibodies has been used off-label to treat refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Emerging evidence shows that CD19 CAR T cell therapy can profoundly deplete B cells in SLE patients, potentially leading to sustained, drug-free remission.
Methods: Pseudobulk expression profiles were generated from single-cell RNA sequencing data from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of five SLE patients, collected before and after CD19 CAR T cell therapy (1). Whole blood transcriptome samples were obtained from patients with moderate to severe SLE at baseline (n=20), and 6 months (n=9) after initiation of treatment with rituximab. Response to treatment was defined as attainment of Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) or DORIS remission at 6 months. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using the DEseq2. Pathway enrichment analysis was performed using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA).
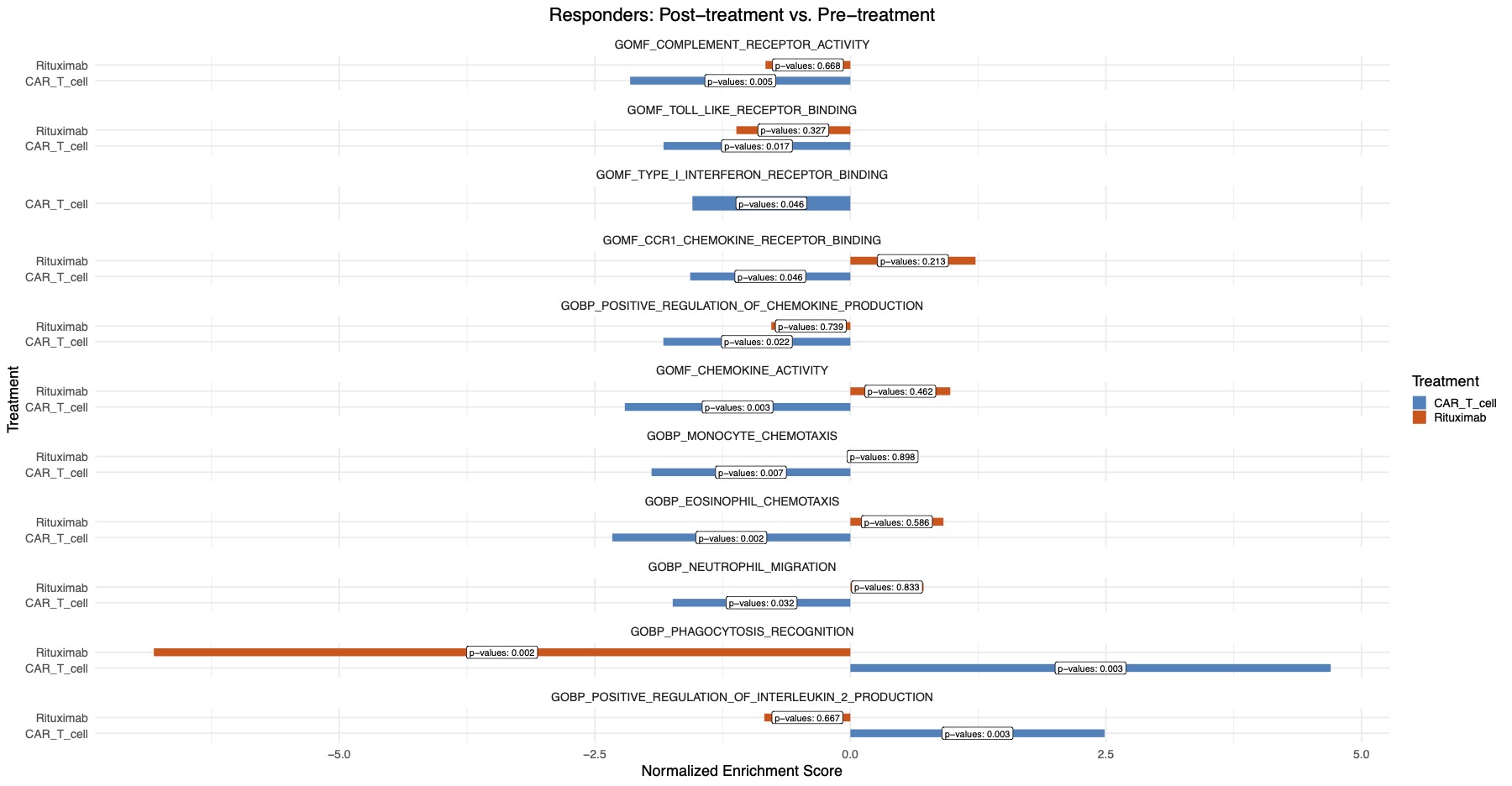
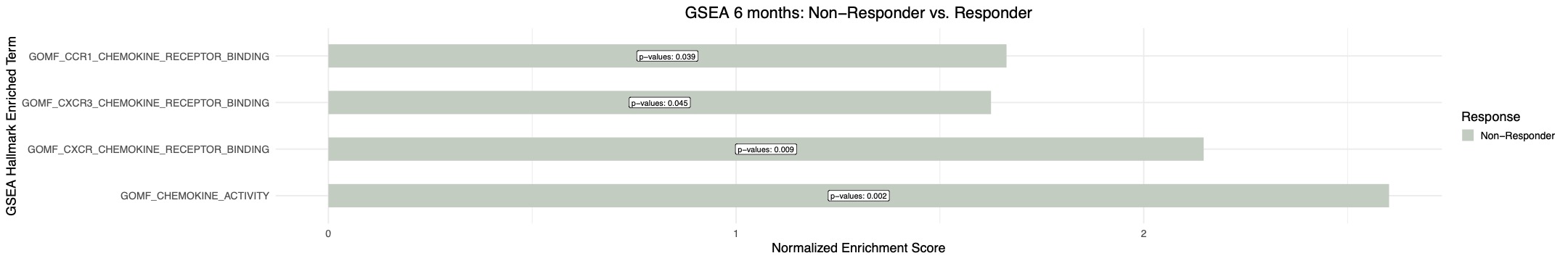
Results: Response to CD19 CAR T cell induced widespread transcriptional changes, with 196 upregulated (P< 0.05) and 669 and downregulated (P< 0.05) genes. CD19 CAR T cell treatment was linked to more pronounced downregulation of pathways related to complement activation, toll-like receptor and type I interferon signaling compared to the rituximab treatment (Figure 1). Upregulation of the phagocytosis pathway, associated with effective clearance of apoptotic material, was uniquely observed with CD19 CAR T cell treatment (Figure 1). CD19 CAR T cell treatment resulted in the upregulation of the IL2 production pathway (Figure 1). Chemokine signaling perturbations, linked to insufficient treatment response (Figure 2), were exclusively reversed by CD19 CAR T cell therapy (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Remission induced by CD19 CAR T cell therapy uniquely features suppression of the type I interferon pathway, restoration of IL-2 levels, enhanced apoptotic material clearance, and reversal of immune cell trafficking disturbances, distinguishing it from rituximab-induced B cell depletion in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garantziotis P, Parodis I, Bertsias G, Boumpas D, Schett G. Comparing the Molecular Landscape of the CAR-T Cell and Rituximab Mediated Remission in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparing-the-molecular-landscape-of-the-car-t-cell-and-rituximab-mediated-remission-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparing-the-molecular-landscape-of-the-car-t-cell-and-rituximab-mediated-remission-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/