Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science (2591–2596)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:45PM-2:00PM
Background/Purpose: TVB-009 is being developed as a proposed biosimilar candidate to the reference denosumab. Denosumab is a human IgG2 monoclonal antibody that binds to the human receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand to inhibit osteoclast formation and activation, thus reducing the risk of fracture in conditions such as osteoporosis. Biosimilarity of TVB-009 to US-licensed denosumab (US-denosumab) and EU-approved denosumab (EU-denosumab) was demonstrated in a 36-week Phase (Ph) 1 pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) study, and no clinically relevant differences in efficacy or safety between TVB-009 and US-denosumab were demonstrated in a Ph 3 study (NCT04729621). The objective of our analysis was to demonstrate that there are no clinically meaningful differences in immunogenicity between TVB-009 and US-/EU-denosumab in the Ph 1 and Ph 3 (52-week main treatment period) studies.
Methods: In the Ph 1 study, healthy participants aged 28–55 years were randomized 1:1:1 to receive a single 60-mg subcutaneous injection of TVB-009, US-denosumab, or EU-denosumab on Day 1. In the Ph 3 main treatment period, postmenopausal women aged 60–90 years with a diagnosis of osteoporosis were randomized 1:1 to receive TVB-009 or US-denosumab on Day 1 and Week 26. Safety and immunogenicity were evaluated similarly in both studies. Blood samples for anti-drug antibody (ADA) testing were collected predose on Day 1 and throughout each study. All samples were screened for ADA using bridging ELISA; ADA-positive (ADA+) samples were then analyzed in a confirmatory assay, and confirmed samples were tested for antibody titer determination and neutralization potential.
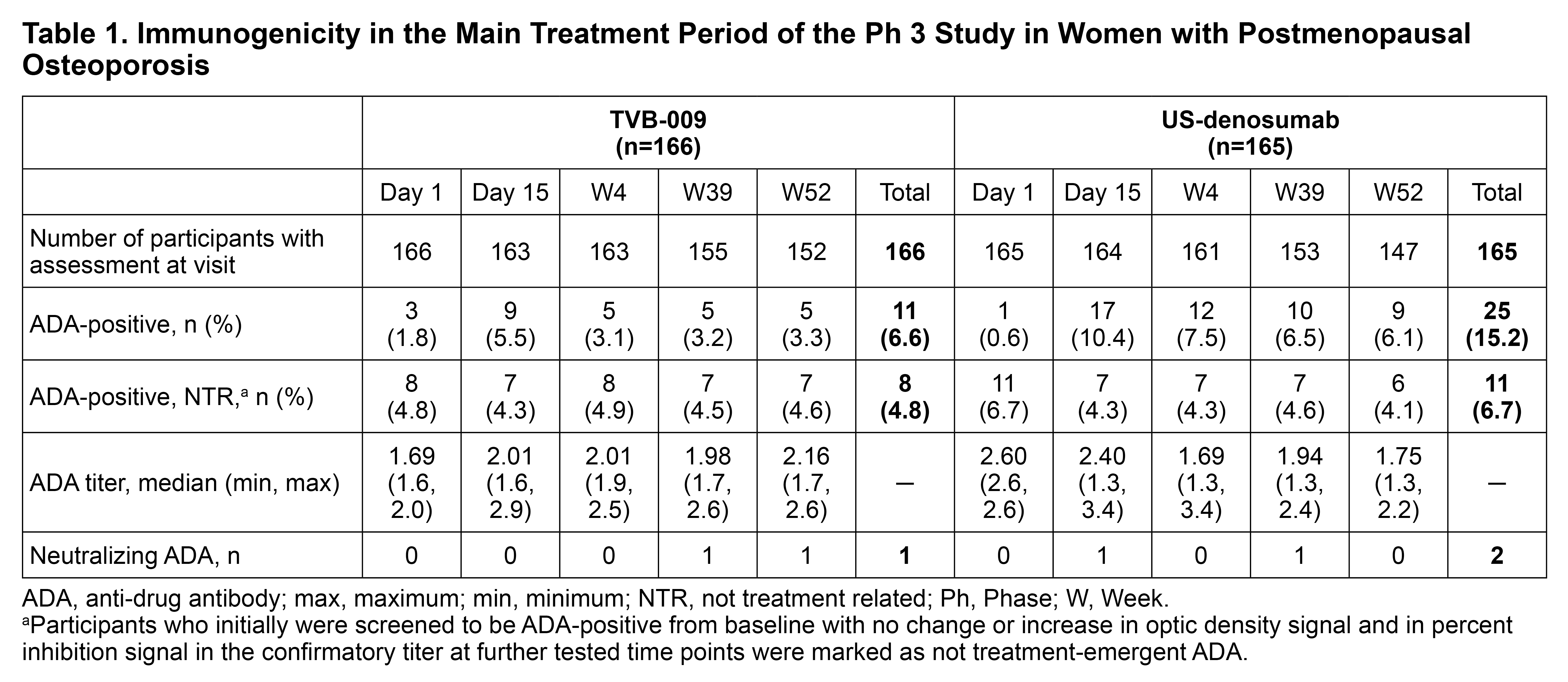
Results: In the Ph 1 study, 345 participants were randomized and included in the safety population (n=115 per treatment group). In the Ph 3 study, 331 of 332 participants randomized in the main treatment period were included in the safety population (TVB-009, n=166; US-denosumab, n=165). Baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups in both studies. In Ph 1, no ADAs against TVB-009 were observed, and therefore there was no impact on PK, PD, or safety related to ADA presence. In the Ph 3 main treatment period, a comparable proportion of participants on TVB-009 and US-denosumab were ADA+ (Table 1). One participant on TVB-009 and 2 participants on US-denosumab tested positive for neutralizing ADAs. However, ADA+ participants had a similar PD response as ADA-negative (ADA−) participants and experienced an increase in lumbar spine bone mineral density from baseline. Serum concentrations after TVB-009 and US-denosumab treatment showed high intersubject variability regardless of ADA presence, and the range of concentrations overlapped between ADA+ and ADA− participants for both treatment groups (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Immunogenicity profiles of TVB-009 and US-denosumab were similar in healthy participants and women with postmenopausal osteoporosis, with no detectable impact of ADA or neutralizing ADA on PK, PD, efficacy, and safety, further confirming that there are no clinically meaningful differences between TVB-009 and the reference denosumab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pavelka K, Schneider F, S D, Timan B, Barkay H, Buchner A. Comparing Immunogenicity Between TVB-009 and Reference Denosumab in Healthy Adults and Participants with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparing-immunogenicity-between-tvb-009-and-reference-denosumab-in-healthy-adults-and-participants-with-postmenopausal-osteoporosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparing-immunogenicity-between-tvb-009-and-reference-denosumab-in-healthy-adults-and-participants-with-postmenopausal-osteoporosis/

.jpg)