Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster II: Co-morbidities and Complications
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Topical NSAIDs (tNSAIDs) have less systemic absorption than oral NSAIDs (oNSAIDs). Thus, tNSAIDs may be associated with a reduced cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk compared with oNSAIDs. We examined risk of incident CV events associated with tNSAIDs versus oNSAIDs among Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients in Taiwan.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort which included incident RA patients who newly started non-selective tNSAIDs or oNSAIDs. We used the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). The first date patients received NSAIDs was defined as the index date, and the 6 month baseline period before the index date was used to define covariates. Patients were excluded if they had NSAIDs exposures, cancer, HIV, psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis claims during the baseline period. Treatment episodes continued until there was a treatment gap more than 30 days. Follow-up was censored at the first of any of the following: 30-days after treatment was discontinued, switch/addition of other NSAIDs category, CV outcome, death, or the end of study. Patients without any NSAID use for at least 180 days could contribute a second treatment episode. The main outcome was a CV event, including myocardial infarction, unstable angina, heart failure, stroke or revascularization. Inverse probability of treatment weight (IPTW) weighted Cox regression model was used to compare the risk of CV events between tNSAIDs and oNSAIDs, with oNSAIDs as the reference group. Sensitivity analyses included varying the length of treatment gap and subgroups.
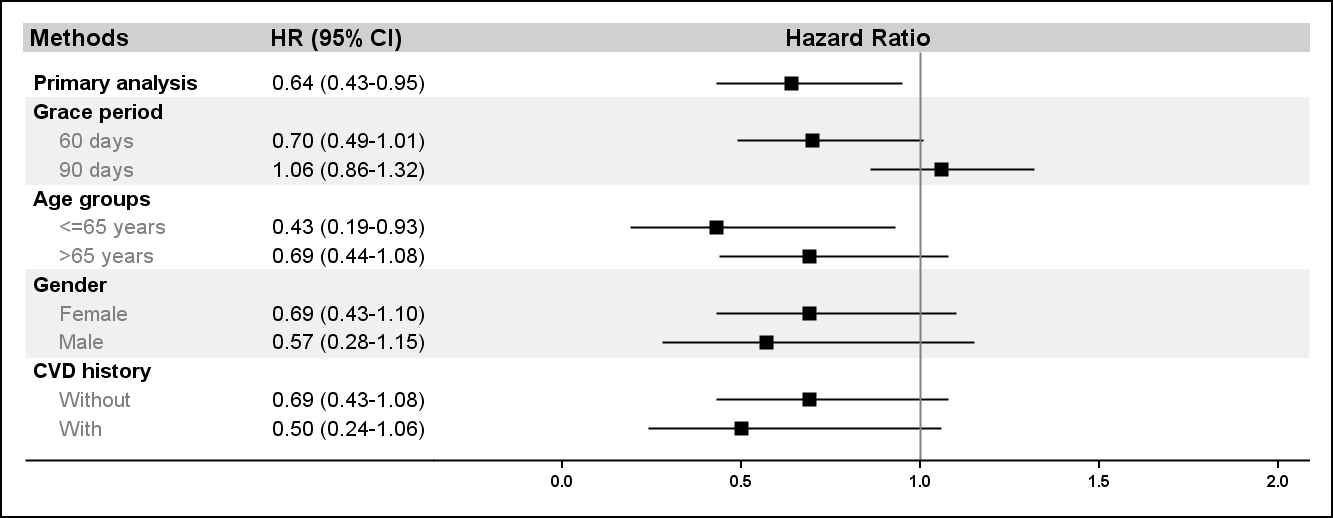
Results: There were 10,758 and 78,056 treatment episodes for topical and oral NSAIDs indentified from our cohort. The mean age was 55.1±15.4 years in tNSAIDs users and 51.7±15.1 years in oNSAIDs users. tNSAIDs users were also more prevalent in female (82.3% vs. 76.0%), CVD risk factors and co-medications than oNSAIDs users. After weighting by IPTW, the cohorts were well balanced. 34 CV events were found during 1,854.6 person-year follow-up in tNSAIDs users, and 433 CV events in 20,205.3 person-year in oNSAIDs users. The crude CV event rate was 1.87 and 2.14 per 100 person-year in topical and oral NSAIDs groups. Results of IPTW weighted Cox regression found tNSAIDs groups had 36% lower risk for CV events as compared with oNSAID group (table, HR: 0.64; 95%CI: 0.43-0.95). Consistent results were found in sensitivity analyses (figure).
Conclusion: We found tNSAIDs users experienced a reduced risk of CV events compared with oNSAID users. If future studies with larger sample size and longer follow-up confirm these results, NSAID prescribing might change accordingly. Table. Incidence and risk of composite CV events in topical and oral NSAIDs recipients
| Follow-up person-year | Event (N) | Crude incidence per 100 person-year | Propensity score adjusted HR* (95%CI) | |
| Topical NSAIDs
(N=10,758) |
1,855 | 34 | 1.83 | 0.64 (0.43-0.95) |
| Oral NSAIDS (N=78,056) | 20,205 | 433 | 2.14 | REF |
* Adjusted by Inverse probability of treatment weight (IPTW), conditioning on patient demographic information (age, gender, income levels), comorbid conditions and co-medications that correlated with CVDs and traditional and biologic DMARDs patients.
Figure. CV event risk comparing topical NSAIDs versus oral NSAIDs users in the primary analysis and in subgroups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lin TC, Solomon DH, Tedeschi SK, Yoshida K, Kao Yang YH. Comparative Risk of Cardiovascular Outcomes Between Topical and Oral Non-Selective Nsaids in Taiwanese Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-risk-of-cardiovascular-outcomes-between-topical-and-oral-non-selective-nsaids-in-taiwanese-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-risk-of-cardiovascular-outcomes-between-topical-and-oral-non-selective-nsaids-in-taiwanese-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/