Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In previous studies, our group has demonstrated that a synthetic 20 amino acid peptide (“TIFI”) with structural similarity to Beta-2-Glycoprotein I Domain V (β2GPI DV) prevents endothelial cell (EC) activation and thrombosis in a mouse model of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). In order to improve its half-life and decrease its immunogenicity, TIFI was PEGylated but this process proved inefficient, with substantial loss of material during the process. Therefore, we have designed two synthetic peptides that would potentially improve efficiency of PEGylation, TIFI Mut1 and TIFI Mut2, and evaluated their ability to inhibit antiphospholipid antibody (aPL)-mediated EC activation.
Methods: Whole IgG fractions were purified from normal (IgG-NHS) and primary APS (IgG-APS) patients by ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by DEAE sepharose chromatography. A dose of 200μg/ml IgG was used to treat human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) alone or after 2 hours pre-incubation with 10μM TIFI WT, Mut1 or Mut2. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure E-selectin (E-sel), tissue factor (TF), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) mRNA expression. VCAM-1 and E-sel cell surface expression was also determined by cytoELISA on fixed ECs treated with IgG ± TIFI variants
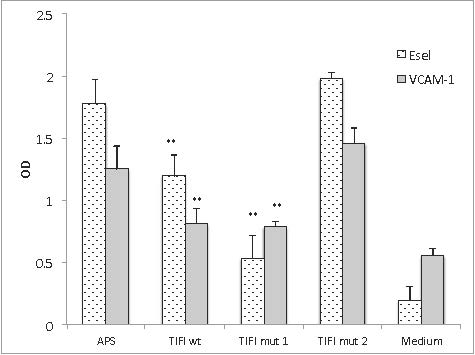
Results: TIFI-Mut1 was 1.3-2.3 fold more effective than TIFI-WT in inhibiting aPL-mediated inflammatory cytokine mRNA induction. Similarly, TIFI-Mut 1 was 3 times more effective in limiting cell-surface expression of E-sel compared to TIFI-WT and was equally as effective in limiting VCAM-1 surface expression. TIFI-Mut2 was ineffective at inhibiting aPL activation of HUVECs.
Conclusion: TIFI Mut1 peptide reduces aPL-induced inflammatory cytokine gene expression and cell surface expression significantly, indicating that PEGylation of this peptide variant will likely be effective in an in vivo application.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Willis R, Papalardo E, Jamaluddin M, Romay-Penabad Z, Schleh A, Brasier A, Gonzalez E. Comparative Efficacy of Beta-2-Glycoprotein I Domain V Structural Analogue Variants in Preventing Antiphospholipid Antibody-Mediated Endothelial Cell Activation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-of-beta-2-glycoprotein-i-domain-v-structural-analogue-variants-in-preventing-antiphospholipid-antibody-mediated-endothelial-cell-activation/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-of-beta-2-glycoprotein-i-domain-v-structural-analogue-variants-in-preventing-antiphospholipid-antibody-mediated-endothelial-cell-activation/