Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) accelerates bone loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures. We evaluated the effect of raloxifene and bisphosphonate on bone mineral density (BMD) and osteoporotic fractures in RA patients.
Methods: We retrospectively examined data of 112 seropositive RA patients who were diagnosed with osteoporosis and started on either raloxifene or bisphosphonate from January 2006 to December 2010 with no prior history of either medication. Patients with baseline BMD and at least one follow up BMD were included. The patients were examined for maximum of 3 years with mean follow up period of 2.1 years. Bisphosphonates consisted of risendronate, alendronate or oral ibandronate. Vertebral fractures were defined using Genant’s semiquantitative classification.
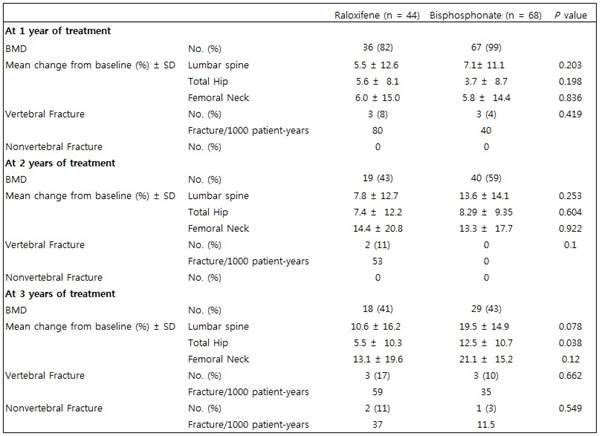
Results: Forty-four patients were in the raloxifene group and 68 patients were in the bisphosphonate group. The patients in the raloxifene group were older and lighter in weight compared to the bisphosphonate group (Table 1). The patients in the bisphosphonate group consumed higher doses of calcium and vitamin D through medication compared to the raloxifene group. There was no significant difference in duration of RA, the daily dosage of prednisolone and medication possession ratio between the 2 groups. Thirty-six patients in the raloxifene group and 67 patients in the bisphosphonate group had follow up BMD at 1 year of treatment (Table 2). Nineteen patients in the raloxifene group and 40 patients in the bisphosphonate group had follow up BMD at 2 years of treatment. There was no significant difference in the yearly change of lumbar, total hip and femoral neck BMD from baseline and the number of vertebral fractures between the 2 groups at 1 year and at 2 years of treatment. Eighteen patients in the raloxifene group and 29 patients in the bisphosphonate group had follow up BMD at 3 years of treatment. There was no significant difference in the mean change of lumbar and femoral neck BMD from baseline and the number of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures between the 2 groups at 3 years of treatment. However the mean change of total hip BMD was higher in the bisphosphonate group compared to the raloxifene group.
Conclusion: There was no significant difference in BMD changes and osteoporotic fractures in RA patients treated with raloxifene and bisphosphonate.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics
Table 2. Mean change of BMD from baseline and fracture outcomes.
Disclosure:
K. Joo,
None;
W. Park,
None;
S. R. Kwon,
None;
M. J. Lim,
None;
K. H. Jung,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effects-of-raloxifene-and-bisphosphonate-on-bone-mineral-density-and-osteoporotic-fracture-outcomes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/