Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects: Novel Biomarkers and Other Measurements of Disease Activity
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: There is an extensive list of composite scores of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) activity status for the use in clinical practice including Disease Activity Score (DAS) and DAS-28. Much less common are validated definitions and scores of RA activity and severity for use in healthcare databases. The Record based Index of Severity (RARBIS) and the Claims-based Index for RA Severity (CIRAS) are methods used for this purpose. Our objective was to assess the dynamics of the CIRAS and RARBIS as measures of RA disease severity over time and to assess their correlation with DAS28.
Methods: A population-based inception cohort of 525 patients with incident RA (as per the 1987 ACR Criteria) in 1988-2007 was retrospectively identified and followed until 7-1-2012. The available data to calculate the RARBIS (joint surgeries, erosions, extra-articular manifestations, arthritis flares, morning stiffness, rheumatoid factor [RF] positivity, acute phase reactants and antirheumatic medications) were collected at every visit via medical record review. Claims data were used to calculate the CIRAS at every visit using 1 year prior data on number of inflammatory marker tests, platelet counts, chemistry panels, rheumatology visits, rehabilitation visits, assessment of RF, and Felty’s syndrome. DAS28 was also collected, when available. RA flare was defined based on OMERACT 9 definition. Scores were compared using Spearman’s correlation.
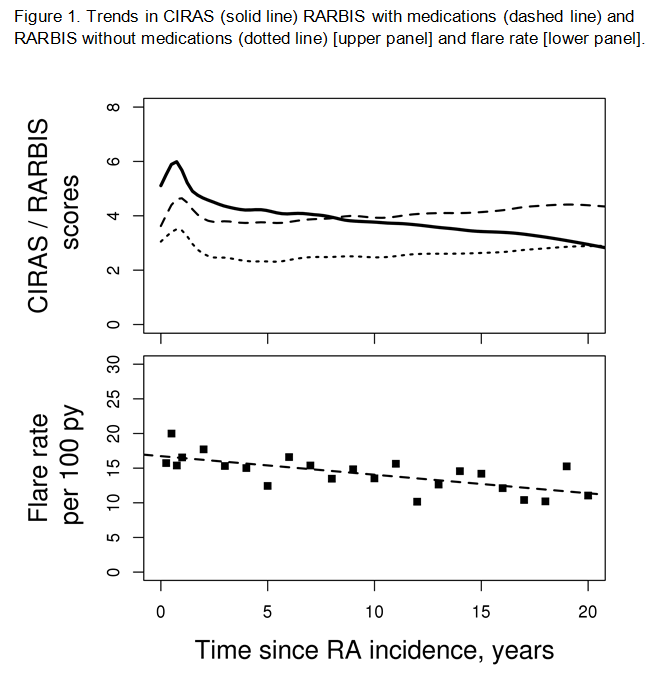
Results: The 525 patients (mean age 55; 71% female) in our cohort had 15,649 visits (mean 30 visits per patient) with an average of 10.3 years follow-up. The mean RARBIS with medication at RA incidence was 3.3 (SD 1.4) and the CIRAS was 4.5 (SD 1.9). There was an increase in both, CIRAS and RARBIS scores during the first year of disease (Figure). Thereafter, the CIRAS scores tended to decrease, but the RARBIS values showed little change over the disease course. The flare rate decreased significantly during the follow-up by 0.3 per 100 person-years per year (p<0.001). There was a statistically significant correlation between RARBIS and CIRAS scores (r=0.19, p<0.001). DAS28 was available in only 278 visits. There was a moderate correlation between DAS28 and RARBIS (r=0.40; p<0.001) and a weaker correlation between CIRAS and DAS28 (r=0.16; p=0.008).
Conclusion: The uniform increase in CIRAS and RARBIS values during the first year after index date may reflect initial spike of RA activity and initial extensive work up of RA disease. Subsequent decline in CIRAS scores is concordant with decreasing flare rates, and could be due to the gradual decrease in the need for comprehensive laboratory workup and decreased frequency of rheumatology visits in patients with established disease. CIRAS and RARBIS scores were found to be significantly correlated with DAS28 suggesting that these indices may be helpful measures of RA activity/ severity in healthcare database research.
Disclosure:
A. K. Chandran,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2;
C. S. Crowson,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2;
B. İlhan,
None;
C. J. Michet III,
None;
E. L. Matteson,
None;
E. Myasoedova,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-dynamics-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-and-disease-severity-measures-using-rarbis-ciras-and-das28-in-a-population-based-cohort-of-patients-with-ra/