Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose For patients with prior exposure to tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor (TNF-I), the likelihood of response to subsequent treatment with a TNF-I declines with the increasing number of previous treatment failures.1 Sarilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody directed against interleukin-6R, has shown efficacy in a study of adult rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with moderate-to-severe disease and an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX).2 Sarilumab’s safety and efficacy has been demonstrated at subcutaneous doses of 150 mg or 200 mg q2w + MTX. A further analysis of the clinical efficacy and safety of sarilumab in patients with/without prior biologic use (physician-reported) from this study is reported here. In the total population, 21.2% were exposed to biologics, of which 50% had received prior-TNF-I.
Methods This was a subanalysis of the ACR20 (primary efficacy endpoint) and ACR50 and ACR70 responses, reduction of DAS28-CRP, and CDAI scores in patients with/without prior biologic use in the intention-to-treat population of the Phase 3 aspect of the MOBILITY study. Patients previously nonresponsive to biologic treatment were excluded from study participation.
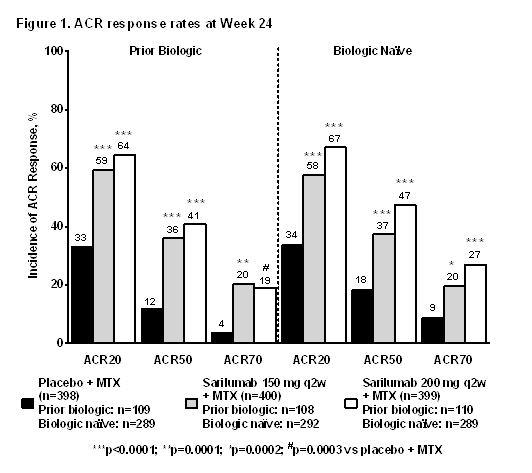
Results Both doses of sarilumab resulted in a statistically significant ACR20 response at Wk 24 vs placebo (p<0.0001); ACR50 and ACR70 responses were also statistically significant at Wk 24 (Fig 1). Statistically significant improvements in DAS28-CRP reduction were observed, with mean reductions at Wk 52 of –1.85, –2.80, and –3.15 in the placebo, sarilumab 150 mg, and 200 mg q2w groups, respectively, in patients with prior use of biologics, and –1.93, –3.24, and –3.29 in biologic-naïve patients (Figure 2). Similar improvements were seen in CDAI scores, with mean reductions at Wk 52 of –23.23, –28.45, and –28.81 in the placebo, sarilumab 150 mg, and 200 mg q2w groups, respectively, in patients with prior use of biologics, and –24.52, –31.35, and –30.33 in biologic-naïve patients (Fig 2). Most common TEAEs included infections and injection site reactions. A higher incidence of serious infections was observed with sarilumab. Lab abnormalities included decreases in neutrophils and increases in transaminases and lipids.
Conclusion Independent of prior use of a biologic, treatment with sarilumab resulted in clinically meaningful and statistically significant responses; given the modest number of biologic-experienced participants and the exclusion of prior non-responders, additional research is warranted.
References
1. Lloyd S et al. Rheumatology 2010;49(12):2313–2321.
2. Genovese M et al. Abstr. EULAR14-SCIE-3001, EULAR 2014.
Disclosure:
R. Fleischmann,
AbbVie, Amgen, Ardea, Astra Zeneca, BMS, Celgene, GSK, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Resolve, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, UCB.,
2,
AbbVie, Akros, Amgen, Antares, Ardea, Astra Zeneca, Augurex, BMS, Celgene, Covagen, Five Prime, GSK, Iroko, Janssen, Eli Lilly, McNeil, Merck, Pfizer, Plexxicon, Resolve, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Teva, UCB, Vertex. ,
5;
D. L. Decktor,
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
3,
Johnson & Johnson,
1;
C. Fan,
Sanofi ,
1,
Sanofi ,
3;
H. Van Hoogstraten,
Sanofi ,
3;
M. C. Genovese,
Eli Lilly and Company,
2,
Eli Lilly and Company,
5,
Sanofi ,
2,
Sanofi ,
5,
Regeneron,
2,
Regeneron,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparable-efficacy-with-sarilumab-plus-methotrexate-in-biologic-experienced-and-biologic-naive-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-from-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-pl/