Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
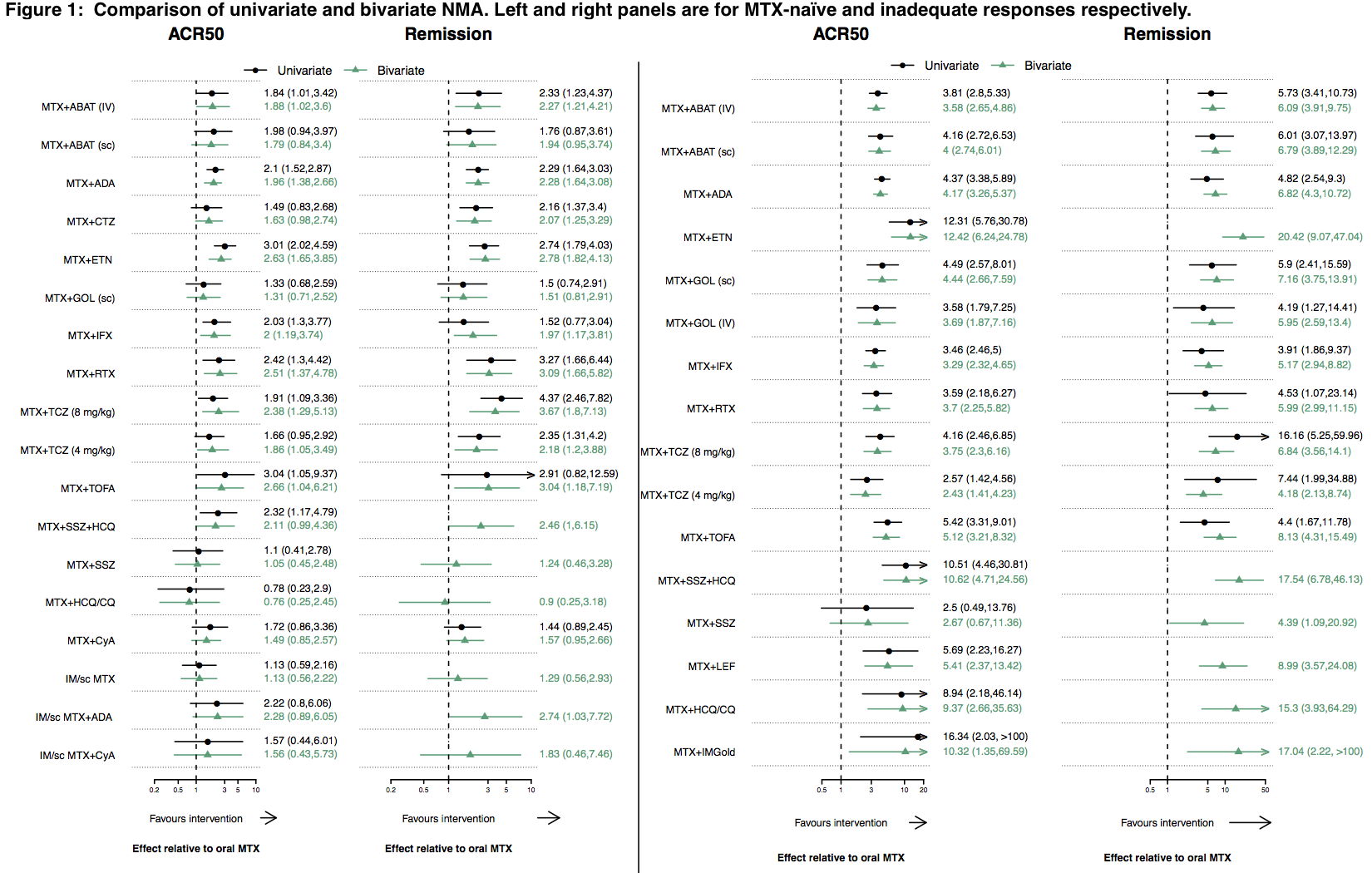
Background/Purpose: Remission is the goal of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment, but ACR responses are more commonly measured in clinical trials. As such, data on remission are lacking for some treatments, or may be imprecise. The objective of this study was to jointly estimate remission and ACR50 responses for methotrexate (MTX)-based treatment options in early RA.
Methods: We conducted a Bayesian bivariate network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate-based DMARD combinations for RA. The correlation between the outcomes was derived from an observational study (CATCH cohort), whereas the treatment outcomes were derived from randomized trials that formed the connected network of evidence. The analyses were conducted separately for MTX-naïve and MTX-inadequate response populations in a Bayesian framework with uninformative priors. Comparisons were made to a univariate NMA that estimated each outcome separately.
Results: From the incident RA cohort study, the correlation between ACR50 response and DAS28 remission at 6 months was moderate (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.58) for the 900 patients in the CATCH cohort who had moderate-high disease activity at baseline. For MTX-naïve patients, the NMA included 74 trials in total; 39 measured both outcomes, whereas 64 and 49 measured only ACR50 response or remission respectively. Two treatments that were not statistically superior to methotrexate alone for remission in the univariate NMA, were in the bivariate model [Figure 1: bivariate odds ratio (OR) (95% credible interval (CrI)): MTX + infliximab 2.0 (1.2, 3.7), MTX + tofacitinib 2.7 (1.0, 6.2)]. Six treatments had no data for remission in the univariate model, but could be estimated in the bivariate approach. Of these, only triple therapy (MTX + sulphasalazine + hydroxychloroquine) was superior to MTX alone for remission (OR (95%CrI): 2.5 (1.0, 6.1)). In the MTX-IR analysis, all 16 treatments were superior to MTX alone for both ACR50 response and remission in both the univariate and bivariate models, but the CrI were usually more precise in the bivariate approach and remission could be estimated for several treatments not possible in the univariate model, including triple therapy (OR (95%CrI): 17.5 (6.8, 46.1)).
Conclusion: By borrowing the strength across treatments and outcomes, a bivariate NMA allowed the estimation of both ACR50 response and remission for all treatment comparisons. In particular, our results add data on remission for several MTX-based DMARD combinations (including triple therapy and biologic combinations) not demonstrated in the univariate NMA model.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pokharel G, Deardon R, Barnabe C, Bykerk VP, Bartlett SJ, Bessette L, Boire G, Hitchon C, Keystone EC, Pope JE, Tin D, Thorne C, Hazlewood G. Combining Observational and Randomized Controlled Trial Data Evidence to Jointly Estimate Remission and Response for Biologic and Non-Biologic Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Bivariate Network Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combining-observational-and-randomized-controlled-trial-data-evidence-to-jointly-estimate-remission-and-response-for-biologic-and-non-biologic-therapies-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-bivariate-network-me/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combining-observational-and-randomized-controlled-trial-data-evidence-to-jointly-estimate-remission-and-response-for-biologic-and-non-biologic-therapies-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-bivariate-network-me/