Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: GO-VIBRANT is a Phase 3 trial of intravenous (IV) golimumab (GLM) in adult patients (pts) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Clinically meaningful improvements in skin and nail psoriasis (PsO) and in Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) that were significantly greater than placebo (PBO) at weeks (wks) 14 & 24 were previously reported.1
To evaluate improvement in skin and nail PsO and DLQI with IV GLM through wk52.
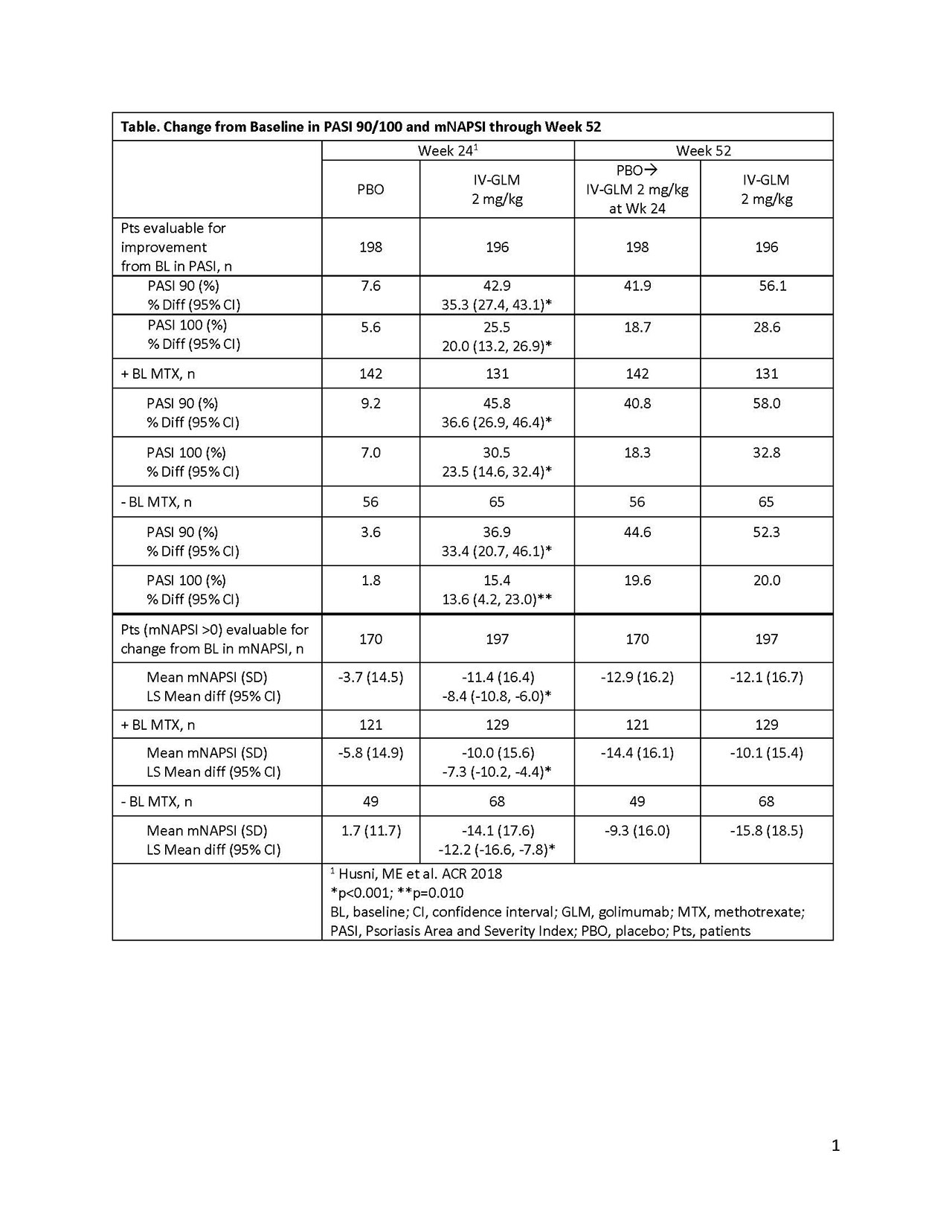
Methods: Adult bio-naïve PsA pts with active disease (≥5 swollen & tender joints, CRP ≥0.6mg/dL, active plaque psoriasis or documented history), despite treatment w/csDMARDs &/or NSAIDs, were randomized to IV GLM 2mg/kg at wks 0/4 & every 8 wks thereafter or PBO at wks 0/4/12/20 with crossover to GLM at wk24. Pts with ≥3% body surface area (BSA) psoriasis at baseline (BL) were assessed using Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI, 0-72) of 75/90/100% improvement scale, modified Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (mNAPSI, 0-130) in pts with mNAPSI >0 at BL, and DLQI (0-30) scale.
Results: 394 pts (PBO:n=198; GLM:n=196) had ≥3% BSA psoriasis at BL; 76.5% had mNAPSI >0 at BL (mean 18.6). Pts on IV GLM achieved a greater PASI 75 response rate (RR) vs PBO at wk24 (64.8% vs 13.1%, p< 0.001). At wk52, PASI 75 RR was maintained in pts who continued IV GLM treatment and increased numerically in those who crossed-over from PBO to IV GLM (PBO→IV GLM) at wk24 (71.9% and 60.6%, respectively). At wk24, pts on IV GLM achieved significantly greater PASI 90/100 RR vs PBO. At wk52, PASI 90/100 RR was maintained among those continually on IV GLM and increased numerically in PBO→IV GLM pts (Table). At wk24, significantly greater proportions of pts on IV GLM ± BL methotrexate (MTX) achieved PASI 90/100 vs PBO. By wk52, both ± BL MTX, PASI 90/100 responses were maintained in those continually on IV GLM and increased numerically in PBO→IV GLM pts (Table). The mean decrease (improvement) from BL in the mNAPSI score was also greater with IV GLM vs PBO at wk24, overall and in groups ± BL MTX. At wk52, mNAPSI RR was maintained with continual IV GLM and increased numerically in PBO→IV GLM pts (Table). At wk24, the mean decrease (improvement) from BL in DLQI was greater with IV GLM vs PBO (−8.1 vs −1.9, p< 0.001). At wk52, mean DLQI improvement was maintained in pts continually on IV GLM and increased numerically in PBO→IV GLM pts (-7.8 vs -5.8). Similar patterns were seen in subgroups ± BL MTX. In pts with DLQI improvement >1 at baseline, rate of simultaneous achievement of both PASI 50 response & improvement in DLQI ≥5 was greater at wk24 with IV GLM (59.2%) vs PBO (8.1%, p< 0.001). At wk52, both were achieved by 56.6% continually on IV GLM vs 41.4% of PBO→IV GLM pts. Similar patterns were seen for simultaneous achievement of both improvement in DLQI ≥5 & PASI 75/90/100 at wks 24 and 52.
Conclusion: Clinically meaningful improvements in skin and nail psoriasis and psoriasis quality of life after IV GLM treatment of PsA pts were maintained from 24 to 52 weeks of treatment.
- Mease P et al. EULAR June 2018, Amsterdam, NL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Husni M, Chakravarty S, Kafka S, Harrison D, Parenti D, Kim L, Lo K, Hsia E, Kavanaugh A. Clinically Meaningful Improvement in Skin and Nail Psoriasis in Bio-naïve Active Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Treated with Intravenous Golimumab: Results Through Week 52 from a Phase-3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinically-meaningful-improvement-in-skin-and-nail-psoriasis-in-bio-naive-active-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-treated-with-intravenous-golimumab-results-through-week-52-from-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinically-meaningful-improvement-in-skin-and-nail-psoriasis-in-bio-naive-active-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-treated-with-intravenous-golimumab-results-through-week-52-from-a-phase-3-study/