Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
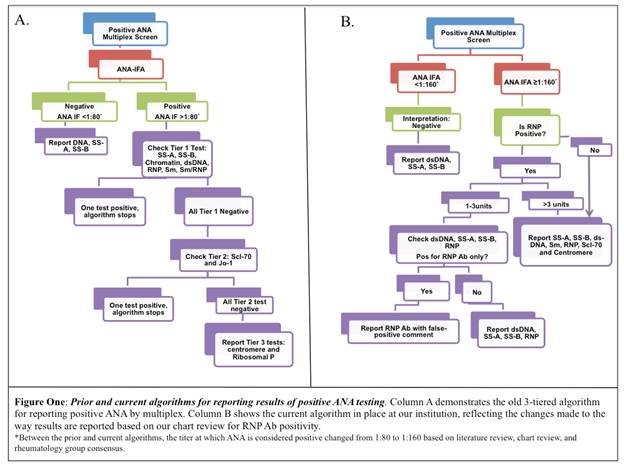
Background/Purpose: A large multicenter healthcare system recently adopted multiplex immunoassay as an initial screen for antinuclear antibody (ANA) with confirmatory reflex testing by immunofluorescence antibody assay (IFA). When both are positive, a 3-tiered cascade reporting algorithm is activated (Figure 1A). This ANA testing method led to an increase in rheumatology referrals for RNP antibody (ab) positivity in patients lacking clinical features of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD). We conducted a multiphase quality improvement project to determine the clinical significance of RNP ab positivity.
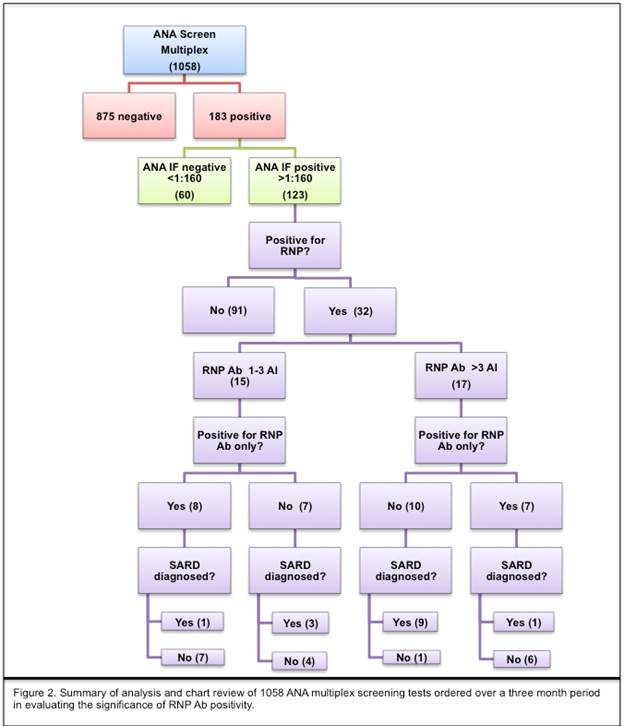
Methods: A retrospective review of all ANA tests completed at our institution was conducted from July to September 2016. Specimens positive in the multiplex assay were further reviewed for both RNP ab and ANA by IFA positivity. A titer of ≥ 1:160 was considered positive. Positive RNP ab results (> 1 antibody index (AI)) were characterized as either low (1-3 AI) or high (>3 AI). Two independent physicians conducted chart review on all RNP results to determine if diagnosis of SARD was made. Methods are summarized in Figure 2.
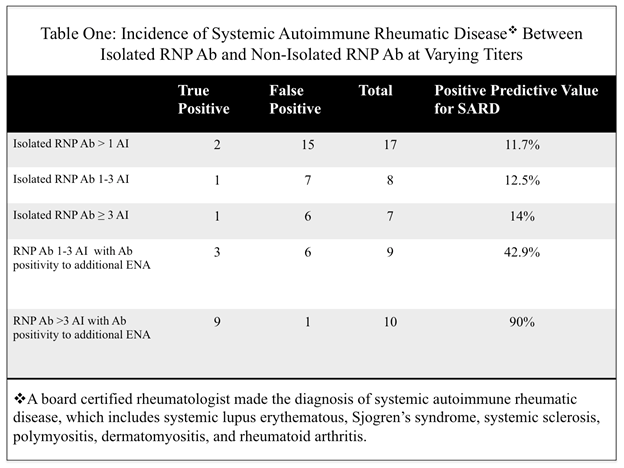
Results: Of 1058 ANA multiplex performed, 183 were positive (17.3%) and 60 were positive for RNP ab. Of the 60 RNP ab positive samples, 28 had negative ANA IFA testing (47%). One-hundred and twenty-three ANAs were positive both multiplex and IFA (11.6%), 32 of which were also RNP ab positive (26.2%). Fifteen out of 32 were positive to only RNP ab, and negative to abs to all other extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs). Thirteen of those 15 patients (87%) had no evidence of SARD. PPV for SARD among RNP ab positive patients, sorted by AI is summarized by Table 1.
Conclusion: Within our testing, an isolated positive RNP ab has a poor PPV for SARD and likely represents type I error. When RNP ab is positive with ≥ 1 additional ab to ENA, there is a higher probability for SARD. The highest probability for SARD exists when RNP ab is >3 AI with ≥ 1 additional ab to ENA. Healthcare systems should consider a modified algorithm for reporting RNP positivity as either low (1-3 AI) or high (>3) to help clarify the clinical significance of RNP ab positivity with multiplex testing (Figure 1B).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bukiri H, Dave A, Bauer E, Stone V, Chong C, Verma P. Clinical Significance of RNP Antibodies in Diagnosis of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease When Detected By Multiplex Immunoassay [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-significance-of-rnp-antibodies-in-diagnosis-of-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-when-detected-by-multiplex-immunoassay/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-significance-of-rnp-antibodies-in-diagnosis-of-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-when-detected-by-multiplex-immunoassay/