Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Interleukin-17 (IL-17) plays a role in the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease of both skin and joint. We sought to assess long-term efficacy and safety of brodalumab, a human anti-IL-17 receptor A monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in an open-label extension (OLE) of a Phase 2 study (NCT01516957).
Methods: Adults with active PsA (Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis and ≥3 tender and ≥3 swollen joints) for ≥6 months were randomized to brodalumab (140 or 280 mg Q2W) or placebo. At week 12, subjects could enroll in an OLE; all subjects received 280 mg brodalumab. Outcomes based on available data up to week 52 from the ongoing study included American College of Rheumatology 20% response (ACR20), ACR50, changes in DAS 28, CDAI, and ACR response components. Safety was assessed by monitoring adverse events (AEs).
Results: The majority of enrolled subjects (113 brodalumab and 55 placebo) were female (64%), white (94%), and rheumatoid factor negative (92%). Mean age, weight, and duration of PsA at baseline were 52 years, 91 kg, and 9 years, respectively. 156 subjects entered the OLE (52 prior placebo, 53 prior 140 mg, 51 prior 280 mg).
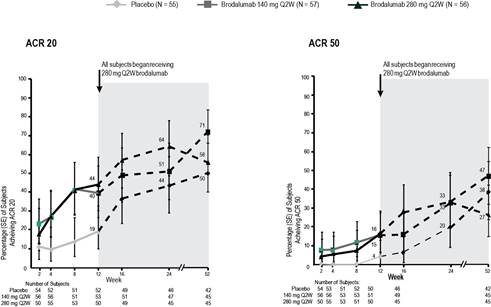
ACR20 and ACR50 response rates (observed), which were higher in brodalumab arms than in placebo at week 12, continued to improve and were sustained through week 52 across all groups (Figure 1). Improvements in DAS 28, CDAI, and several ACR components, observed from baseline to week 12, continued through week 52.
During the OLE (through week 52), 142 subjects reported AEs; most frequently reported (≥5% of subjects in any treatment group) were nasopharyngitis, arthralgia, psoriatic arthropathy, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, nausea, sinusitis, and oropharyngeal pain. Ten subjects reported serious adverse events during the OLE through week 52: including 1 case each of acute myocardial infarction, invasive ductal breast carcinoma, metastatic lung cancer, melanoma, pyelonephritis, and streptococcal septic arthritis. Exposure adjusted AE rates (per 100 subject years) were 706 (all brodalumab) and 757 (placebo). Exposure adjusted SAE rates were 11 (brodalumab) and 8 (placebo). No deaths, clinically significant neutropenia (≥ Grade 2), or mycobacterial/fungal/opportunistic infections were reported.
Conclusion: Brodalumab treatment was associated with significant clinical response with continued improvement from weeks 12 to 52.
Disclosure:
M. C. Genovese,
Amgen Inc.,
2,
Amgen Inc.,
5;
P. J. Mease,
Research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Vertex,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene, Covagen, Crescendo, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Vertex,
5,
AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Crescendo, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, and UCB ,
8;
M. W. Greenwald,
Amgen Inc.,
2;
C. T. Ritchlin,
Amgen, Janssen, and UCB ,
2,
Abbott, Amgen, Janssen, Regeneron, Roche, and UCB,
5;
A. Beaulieu,
Amgen Inc.,
2;
A. A. Deodhar,
AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB,
5;
R. Newmark,
Amgen Inc.,
1,
Amgen Inc.,
3;
J. Feng,
Amgen Inc.,
1,
Amgen Inc.,
3;
N. Erondu,
Amgen Inc.,
1,
Amgen Inc.,
3;
A. Nirula,
Amgen Inc.,
1,
Amgen Inc.,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-response-in-subjects-with-psoriatic-arthritis-following-one-year-of-treatment-with-brodalumab-an-anti-interleukin-17-receptor-antibody/