Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immunofluorescent antinuclear antibody (ANA) test using HEp-2 cells still plays an important role in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical relevance of ANA according to titers and patterns.
Methods: We identified patients who were newly positive in the ANA test between December 2010 to November 2016, and collected data such as, diagnosis, ANA titer and pattern, and specific autoantibody test results.
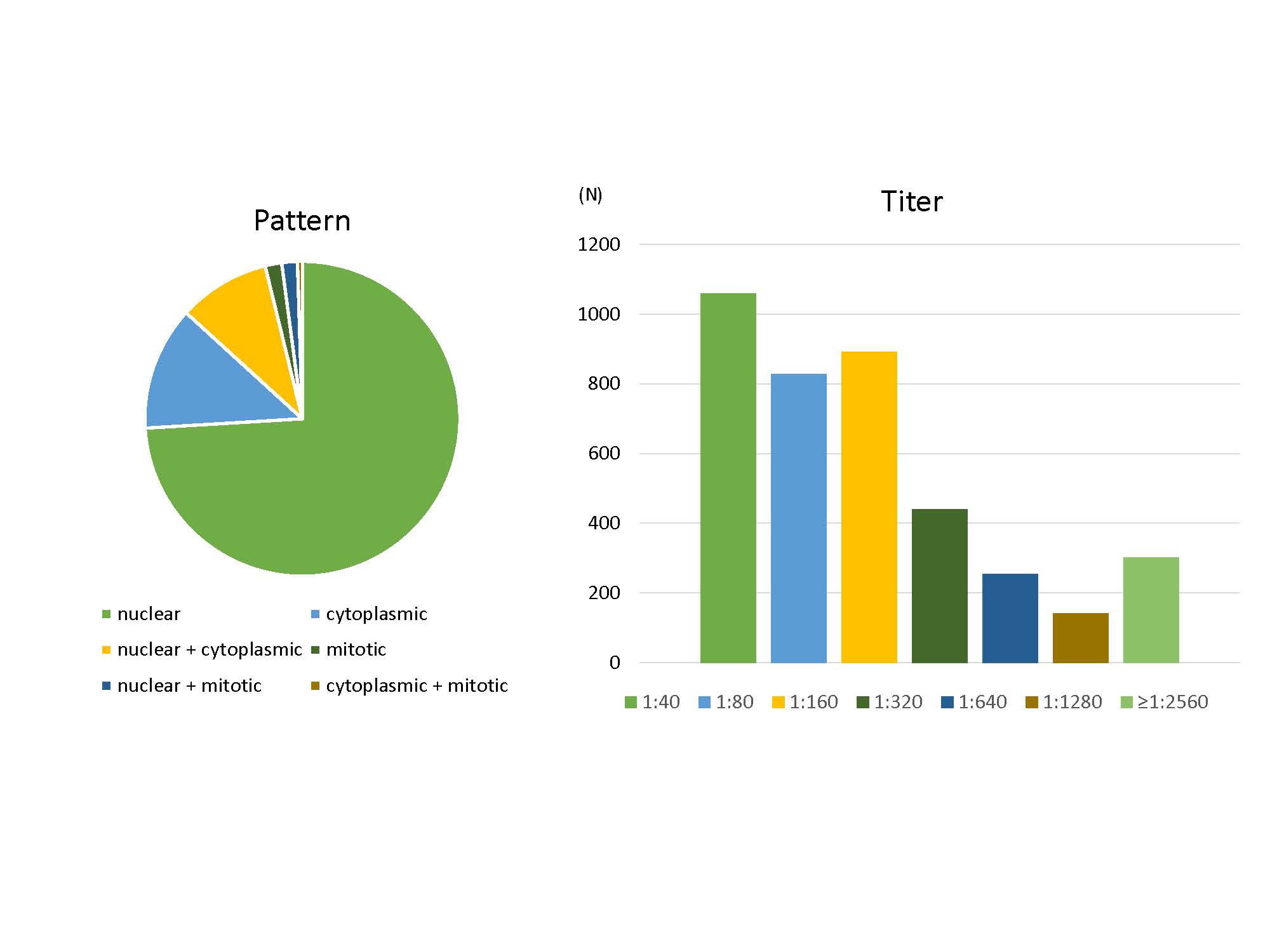
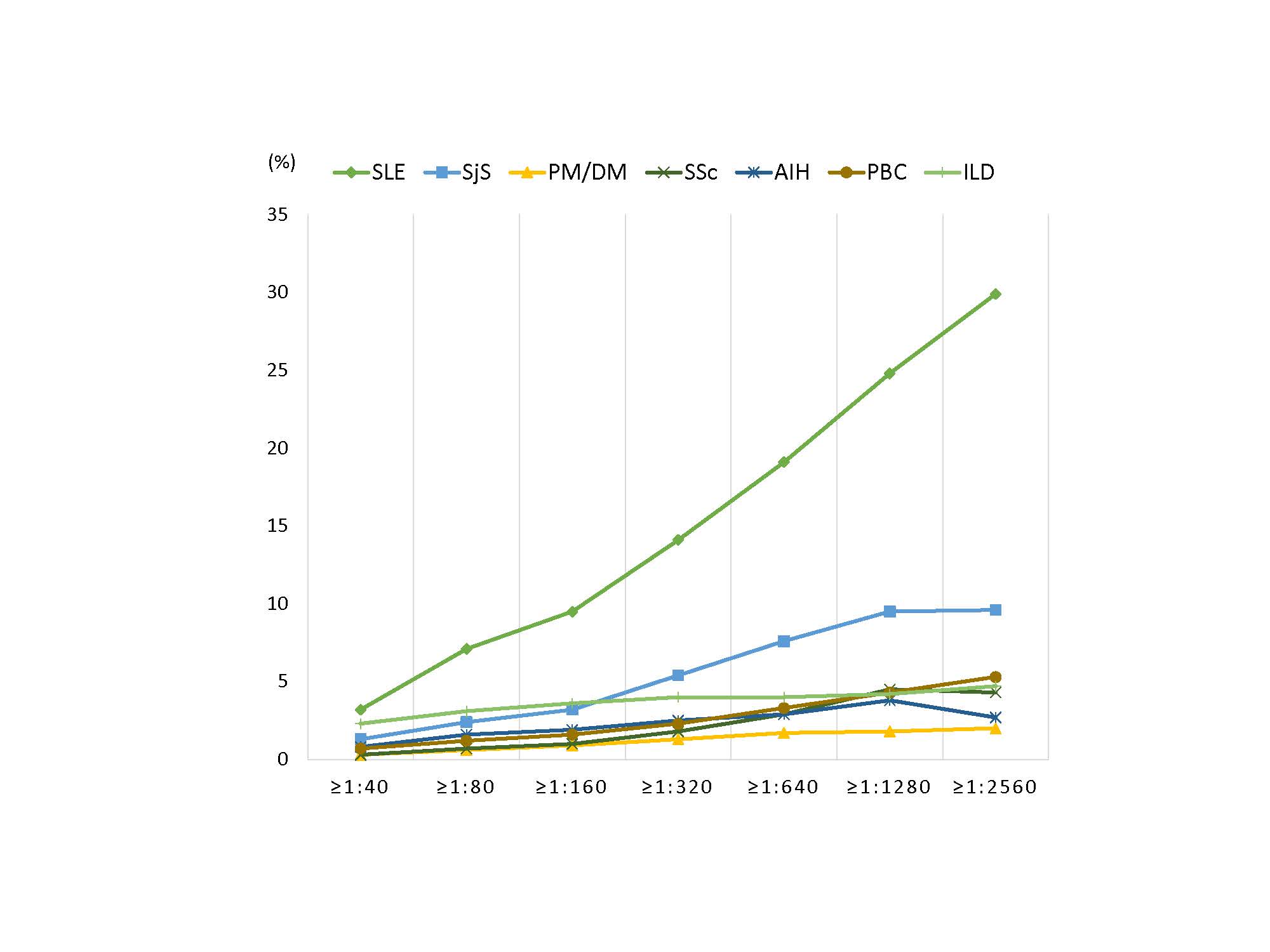
Results: In total, 7591 patients were included in this study. The average age was 51 (interquartile range (IQR): 35-63) years, and 69.4% were women. Figure 1 showed the patient distribution by ANA titer and pattern. The diseases with a difference in prevalence according to ANA titer were systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome (SjS), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), systemic sclerosis (SSc), autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), liver cirrhosis, hemolytic anemia, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, interstitial lung disease (ILD), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/bronchiectasis (COPD/BE), cerebrovascular accident, and crystal induced arthropathy (CIA). A multivariable analysis was conducted to determine whether ANA titer was an independent factor. As a result, diseases with increased prevalence with increasing ANA titer were SLE, SjS, PM/DM, SSc, AIH, PBC, and ILD, and the opposite result showed in COPD/BE and CIA (Figure 2).
SLE was the most prevalent in patients with mixed pattern of nuclear and cytoplasmic (6.4% in ≥1:40, 40% in ≥1:2560). SjS and SSc showed the same results (SjS: 1.9% in ≥1:40, 10% in ≥1:2560, SSc: 0.5% in ≥1:40, 6.7% in ≥1:2560). The prevalence of PM/DM, AIH, PBC and ILD was highest in mixed pattern of nuclear and cytoplasmic in all patients, but it was highest in cytoplasmic pattern from 1:160 or more of ANA titer.
Conclusion: SLE, SjS, PM/DM, SSc, AIH, PBC and ILD were the diseases in which ANA titer independently affected disease prevalence. Patients with mixed pattern of nuclear and cytoplasmic had a higher prevalence of SLE, SjS and SSc than purely nuclear pattern. It is necessary to note that the cytoplasmic pattern is accompanied by the nuclear pattern in the ANA test.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Seo M, Yeo J, Ryu H, Choi H, Baek H. Clinical Relevance According to Staining Patterns and Titers of Antinuclear Antibody [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-relevance-according-to-staining-patterns-and-titers-of-antinuclear-antibody/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-relevance-according-to-staining-patterns-and-titers-of-antinuclear-antibody/