Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare, systemic necrotizing small-vessel vasculitis, with only a few published North American series. This project aimed to describe main clinical characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes of patients with EGPA enrolled in the Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium (VCRC).
Methods: Retrospective analysis of patients with EGPA participating in the VCRC Longitudinal Study (LS) or One-Time DNA (OT) collection from 2003-2019. Patients were at least 18 years old at enrollment and fulfilled the modified American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria. Main demographics, time of onset of asthma to diagnosis, main organ involvement, ANCA status, type of treatments received since diagnosis, relapses, and deaths were analyzed. Patient subsets were compared according to ANCA status and use of cyclophosphamide (CYC).
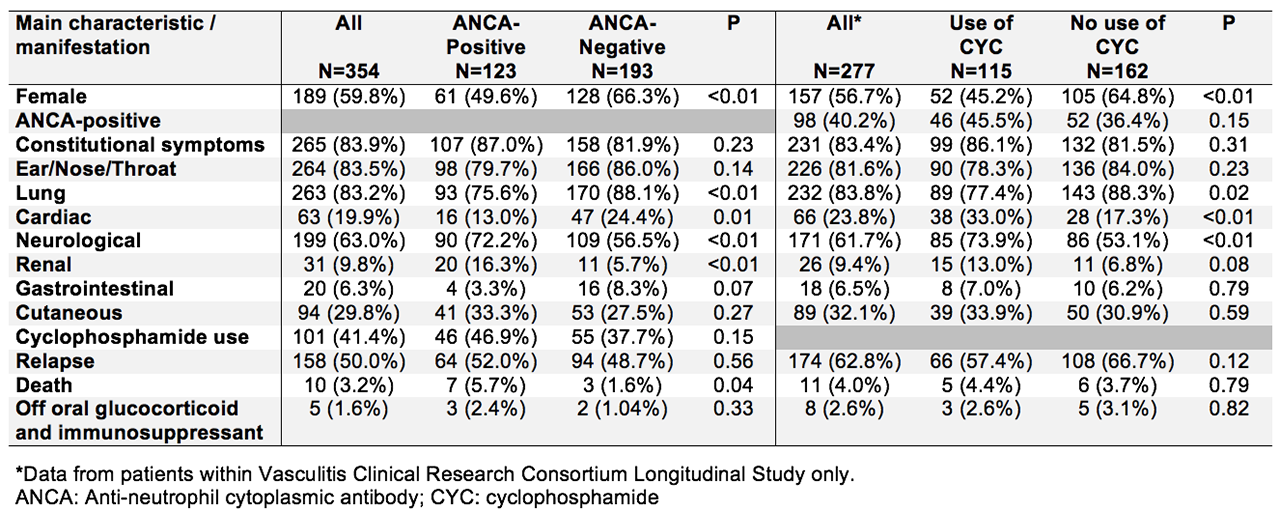
Results: 354 patients (277 LS; 77 OT) were included; 309 (87.3%) were white, 20 (5.7%) Asian, and 7 (2%) Black or African American; male/female ratio was 145/209. Mean age at diagnosis and enrollment was 50.0 (±14.2) and 53.5 (±13.6) years, respectively; 246 (69.5%) had a diagnosis of asthma prior to the diagnosis of EGPA, for a mean of 8.6 (±12.2) years; 329 (92.9%) were eventually diagnosed with asthma. Of those tested for ANCA, 38.9% were positive, mostly with MPO-ANCA (86.2%). Main manifestations at diagnosis, and over the entire course of the disease (until last study visit), are listed in Table 1. With a mean follow-up from diagnosis of 7.0 (±6.2) years, 49.4% of patients had at least one relapse, with 35.7% of the 277 VCRC-LS patients relapsing post-enrollment. Characteristics of these first relapses post-enrollment included active asthma (35%), other lung disease (46%), ear/nose/throat (39%), cardiac (9%), skin manifestations (8%), and/or neuropathy (18%). Eleven (4%) of the VCRC-LS patients died after a mean of 4.7 (±2.5) years post-diagnosis (2 myocardial infarctions, 1 intestinal perforation, 1 metastatic cancer, 7 unknown). In the VCRC-LS, 115 (41.5%) patients received CYC at some point in their disease, 29 (10.5%) rituximab, 25 (9.0%) mepolizumab, 145 (52.4%) azathioprine, 109 (39.4%) methotrexate, and 25 (9%) mycophenolate mofetil. ANCA-positive patients had more kidney and neurologic involvement and a higher mortality, but less lung or cardiac manifestations (Table 2). Patients who received CYC had more cardiac and neurologic manifestations. At last study visit, 221 (79.8%) patients were off glucocorticoids (GC), but only 8 (2.9%) have been off systemic GC and immunosuppressant medications for >2 years during their follow-up.
Conclusion: This first detailed analysis of the large VCRC cohort of patients with EGPA highlights the broad range of clinical manifestations seen in this disease and confirms that some clinical manifestations differ based on ANCA status, and that relapse rates are high. The extremely low number of patients able to stop GC and other immunosuppressant medications strongly supports the need for more effective treatments and identification of disease subsets to better tailor treatments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Doubelt I, Cuthbertson D, Carette S, Khalidi N, Koening C, Langford C, McAlear C, Moreland L, Monach P, Seo P, Specks U, Sreih A, Ytterberg S, Merkel P, Pagnoux C, Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium V. Clinical Manifestations of Patients with Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis in a Large North American Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-manifestations-of-patients-with-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-in-a-large-north-american-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-manifestations-of-patients-with-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-in-a-large-north-american-cohort/