Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
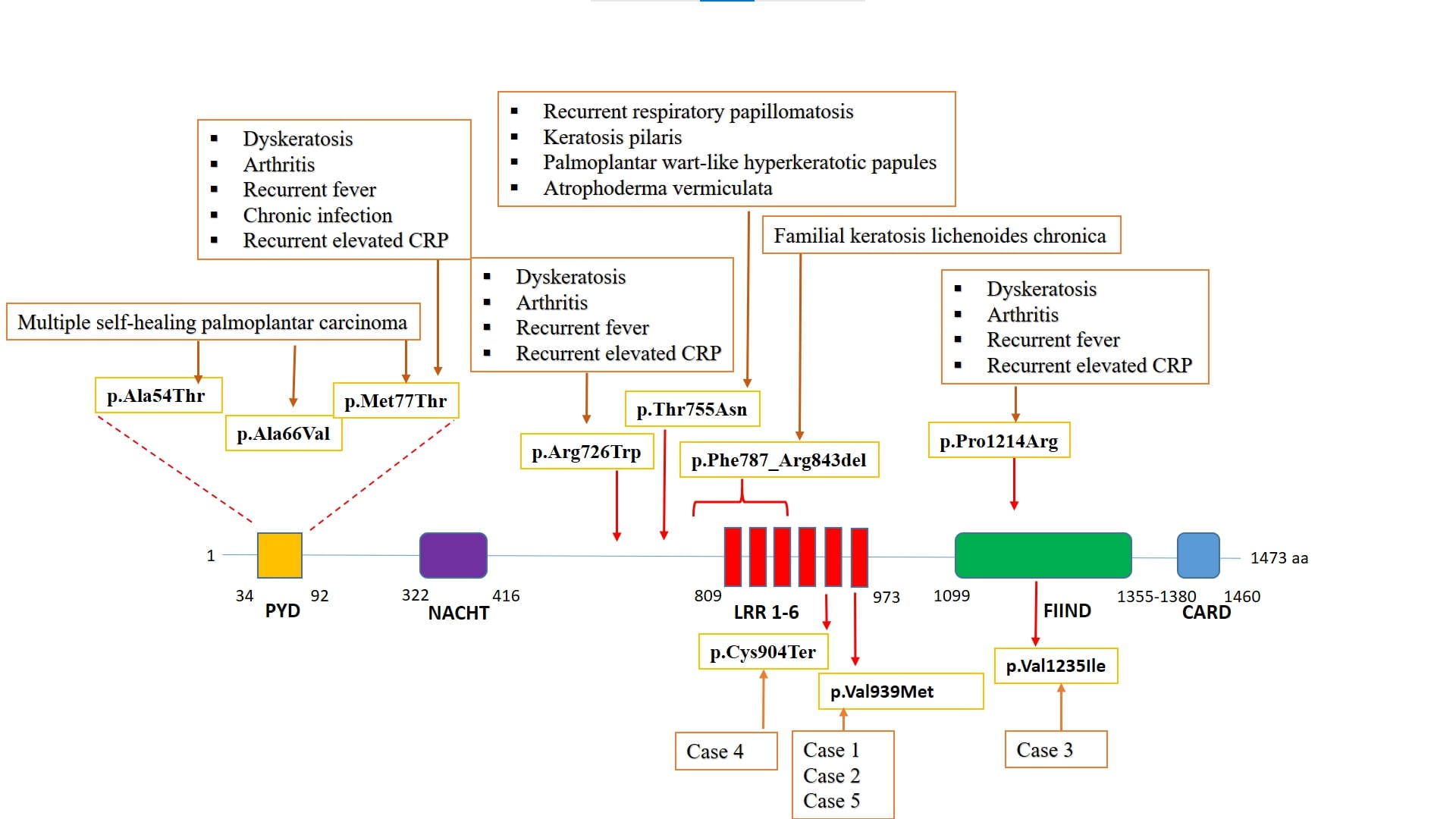
Background/Purpose: Although NLRP1 was the first identified member of the NOD-like receptors family, its role as a sensor of pathogen- or damage-associated signals and its connection with systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAIDs) have not been clarified yet. Missense or non-sense variations of the NLRP1 gene have already been associated with some clinical phenotypes including dyskeratosis, arthritis, recurrent fever, chronic infections, recurrent acute phase response, recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, keratosis pilaris, palmoplantar wart-like hyperkeratotic papules, atrophoderma vermiculata, and familial keratosis lichenoides chronica. Some polymorphisms have also been associated with autoimmune disorders. We herein report the clinical findings of 5 patients with NLRP1 variants.
Methods: The study group included the patients who were referred to our center with a potential diagnosis of SAID and screened for variants of 22 autoinflammatory genes. Those patients with NLRP3 variants were identified, and their clinical and laboratory findings were evaluated.
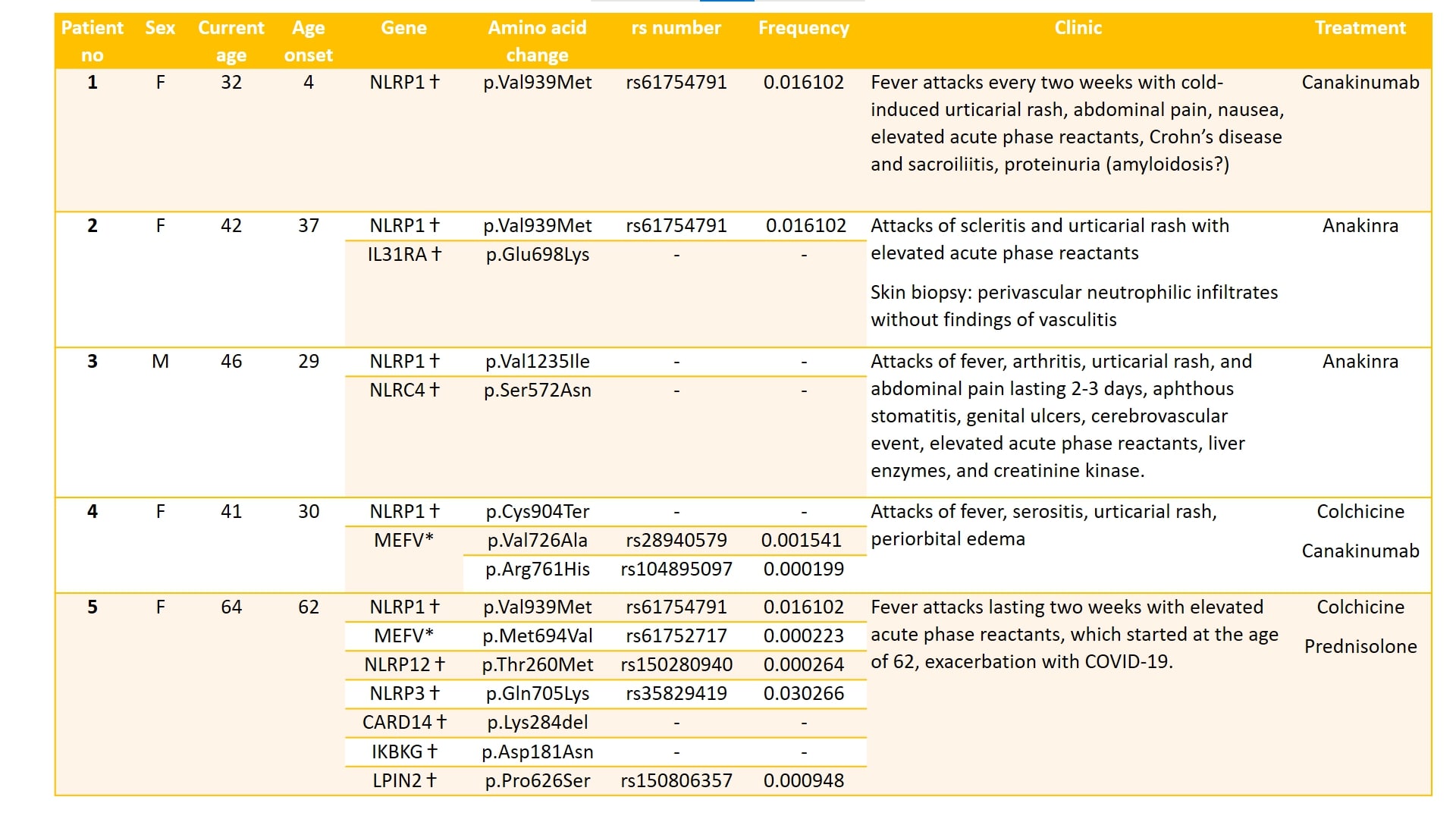
Results: A total of 146 cases with potential diagnosis of SAID were included, and their genetic analysis results were evaluated. NLRP1 variants were identified in 5 (3.4 %) cases. All of the NLRP1 gene variants were classified as variant of uncertain significance (VUS). All but one patients had additional variants in other autoinflammatory genes (Table 1). The most common clinical finding was recurrent urticaria (n=4). Case 1 had NLRP3-AID-like clinical phenotype in addition to Crohn’s disease with sacroiliitis. Case 2 had scleritis attacks and had a combination of two gene variants. Case 3 had Behçet’s disease-like phenotype with oral aphthous stomatitis, genital ulcers, and cerebrovascular event with VUS in both NLRC4 and NLRP1 genes. Case 4 had a TRAPS-like phenotype with serositis and periorbital edema with NLRP1 VUS and a pathogenic MEFV variant. Case 5 had an FMF-like phenotype with VUS in the NLRP1 VUS and a pathogenic variant in the MEFV genes along with five different gene variants. None of the patients had a family history for a phenotype compatible with SAIDs.
Conclusion: NLRP1-associated SAID has been emerging as a new entity, and the phenotypic features of the reported patients varied significantly according to the positions of the variants within the different domains of the gene (Figure 1). We herein report 4 patients with recurrent urticaria as the most common clinical feature in association with 3 different VUS in the NLRP1 gene, and none of the accompanying genetic variants have not been related to urticaria below. The NLRP1 gene p.Val939Met variant is a relatively common variant (allele frequency 0.01), but relatively frequent observation of this variant in the current patient group may suggest that it may have a functional role very similar to the relatively common variant of p.Gln703Lys in the NLRP3 gene. One of the remaining two variants (p.Val1235Ile) was not reported before, and the other one (p.Cys904Ter) was expected to have a pathogenic role due to early termination of the protein (Figure 1). Collection of more cases would help clarify the spectrum of clinical findings of the patients with NLRP1-AID.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Amikishiyev S, Kalaycı T, Deniz R, Yalçınkaya Y, Artim-Esen B, Inanc M, Sahin A, Ekmekci S, Abacı N, Ozturk S, Palanduz S, Gul A. Clinical Features of the Patients with NLRP1 Gene Variants and a Systemic Autoinflammatory Phenotype [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-of-the-patients-with-nlrp1-gene-variants-and-a-systemic-autoinflammatory-phenotype/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-of-the-patients-with-nlrp1-gene-variants-and-a-systemic-autoinflammatory-phenotype/