Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: PsA, a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by peripheral arthritis, axial inflammation, dactylitis, enthesitis and skin/nail psoriasis, causes impaired physical function, disability, and loss of work productivity. We evaluated associations between PsA clinical characteristics and outcomes including fatigue and work productivity using Work Productivity & Activity Impairment Questionnaire: PsA (WPAI-PsA).
Methods: Phase 3 DISCOVER-2 trial assessed guselkumab (GUS), an anti-IL-23p19-subunit human mAb, in bio-naïve adults with active PsA (swollen joint count [SJC] ≥5, tender joint count [TJC] ≥5, CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) despite standard therapies.1 Patients (Pts) were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at Week (W)0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO). WPAI-PsA assesses PsA-related work time missed (absenteeism), impairment while working (presenteeism), productivity loss (absenteeism+presenteeism), and daily activity during previous week. Spearman correlation testing evaluated relationships between pt demographics & PsA disease characteristics and WPAI domain scores based on observed values at baseline. Univariate linear regression assessed associations between WPAI, and these variables based on observed data at W0 and W24. Variables with p< 0.10 were included in a multivariate analysis employing a mixed-effects model for repeated measures, controlling for all other variables; resulting p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
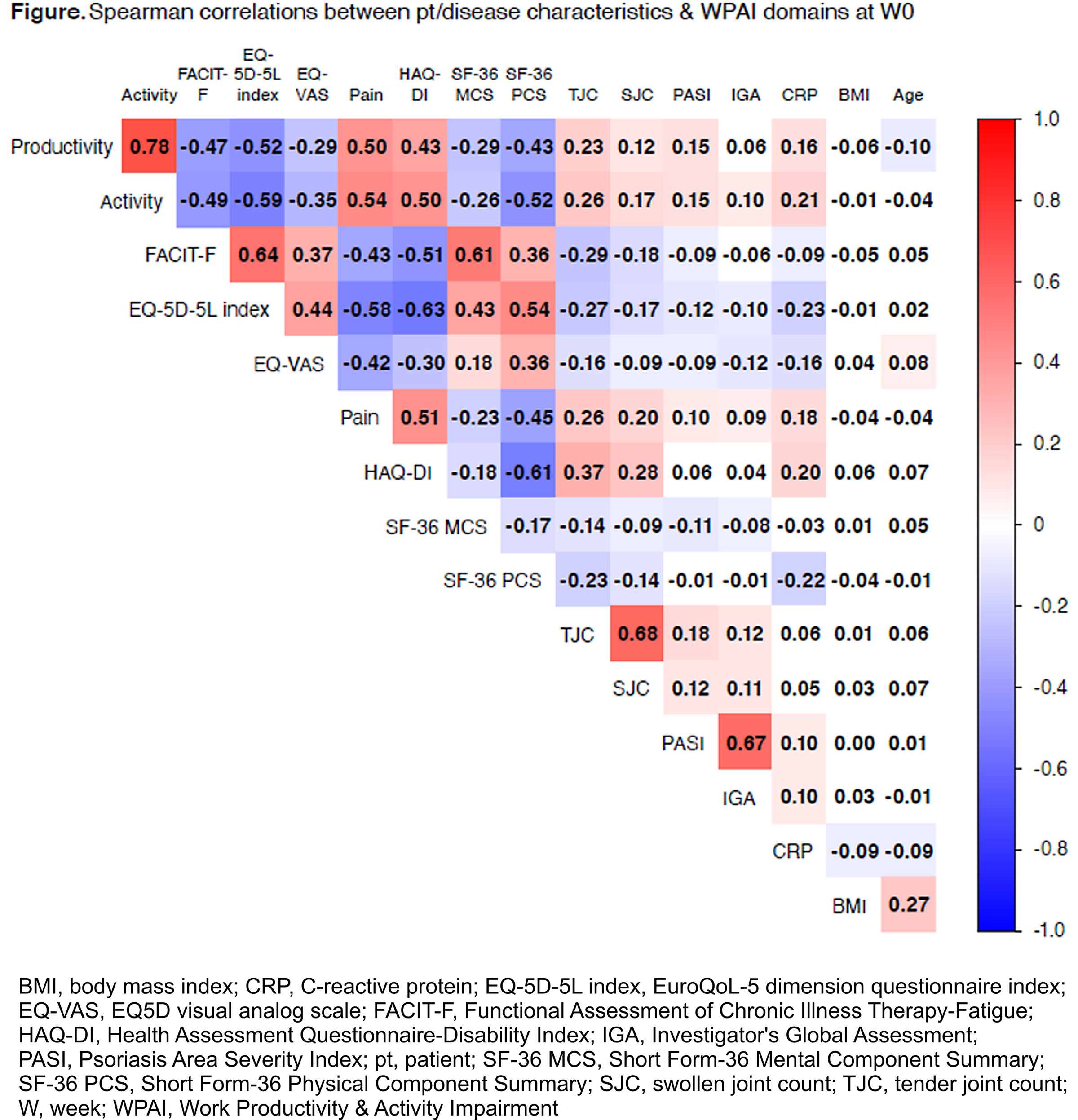
Results: As reported,2 least-squares mean % changes from baseline at W24 were -3.8/‑19.5/-20.0/-20.5 for GUS Q4W, -3.1/-19.4/-19.7/-21.5 for GUS Q8W, and -3.5/-10.2/-10.9/-10.3 for PBO for absenteeism, presenteeism, absenteeism+presenteeism, and daily activity impairment, respectively. Among 738 pts, WPAI domain scores were moderately to strongly correlated (ie, ≥0.4) with pt-reported pain (0-10 visual analog scale), physical function (Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index [HAQ-DI]), fatigue (Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue [FACIT-F] scale) and 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) Physical Component Summary (PCS) score, but weakly correlated with other variables (Figure). Based on univariate analyses and evaluation of collinearity between variables, attributes included in multivariate models were age, BMI, gender, CRP, FACIT-F, pain, Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI), TJC, SJC, enthesitis and dactylitis. In final model, CRP, FACIT-F, and pain were statistically significantly associated with all WPAI domains (Table). Presence of enthesitis and higher PASI score were significantly associated with higher loss of work productivity and activity outside work.
Conclusion: In PsA pts, extra-articular symptoms, fatigue, pain, and elevated CRP were significantly associated with WPAI-assessed work and activity impairment. Treating all major clinical manifestations of PsA is needed to improve work and activity impairment. GUS effectively treats all major clinical manifestations1 and improves work and activity impairment in PsA.2
1. Mease P. Lancet 2020;395:1126-36
2. Curtis J. ACR 2020; Poster 0332
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, McInnes I, Rahman P, Gladman D, Yang F, Peterson S, Agarwal P, Kollmeier A, Hsia E, Han C, Shawi M, Tillett W, Mease P. Clinical Characteristics & Outcomes Associate with Work Productivity in Bio-naïve Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Through Week 24 of the DISCOVER-2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-outcomes-associate-with-work-productivity-in-bio-naive-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-through-week-24-of-the-discover-2-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-outcomes-associate-with-work-productivity-in-bio-naive-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-through-week-24-of-the-discover-2-study/