Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial disease in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has been reported to occur in anywhere from 25% to 75% of PsA patients (pts). It can be associated with more severe disease characteristics.1 Our objective was to describe the characteristics of clinical registry PsA pts with physician-identified spondylitis, at treatment initiation and 6 months post-treatment with biologic (b) or targeted synthetic (ts) disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and to determine whether treatment response differs by HLA-B27 status.
Methods: The Corrona Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondyloarthritis Registry is a prospective, multicenter, observational disease-based registry launched in March 2013 that currently has information on over 3000 enrolled pts. Pt assessments are completed at approximately 6-month intervals. The PsA pts included in this analysis initiated treatment with either bDMARDs or tsDMARDs at a Corrona visit (baseline) and had a 6-month follow-up, fulfilled Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR), had physician-reported spondylitis with Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) scores ≥4 at baseline, and had known HLA-B27 genotype. Disease characteristics at baseline and 6-months are described via means (SD) and counts (%) by HLA-B27 status (+/–). A multivariable-adjusted linear mixed model was used to test for association (regression coefficient) of HLA-27 status with outcomes at 6-months.
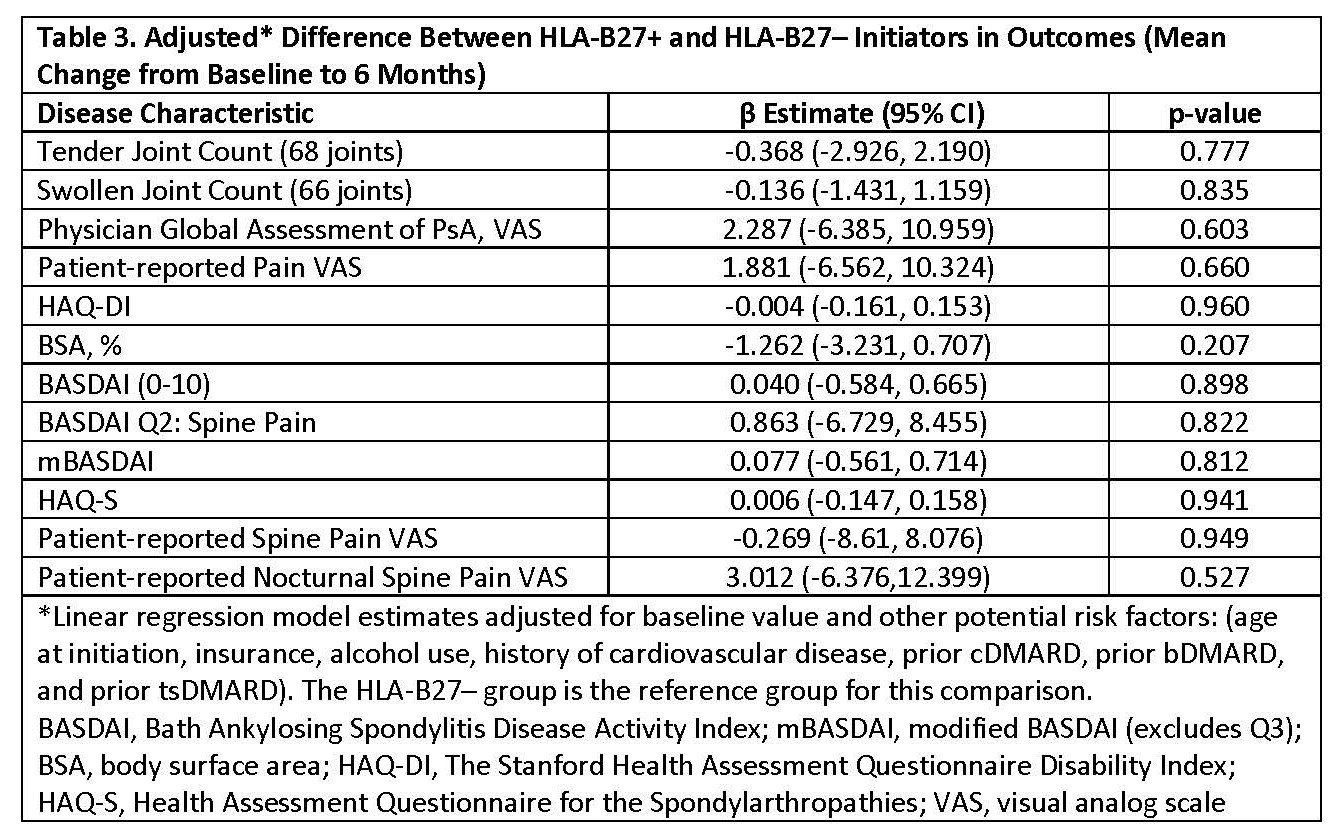
Results: Among the 173 initiations, 31% were HLA B27+ and 69% were HLA B27–. Baseline demographics, comorbidities (Table 1), and disease characteristics (Table 2) were similar between HLA-B27+ and HLA-B27– groups. Axial disease-related outcome measures, including BASDAI, BASDAI Q#2, modified BASDAI (mBASDAI, Q#3 removed), and ASDAS-CRP, all consistently indicated either active disease or high disease activity at baseline. In HLA-B27+ and HLA-B27– pts, respectively, 85% and 80% initiated a bDMARD, while 15% and 20% initiated a tsDMARD. Six-months post-treatment, axial disease-related measures reflected only mild improvement and were still indicative of active disease or high disease activity, irrespective of HLA-B27 status (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences between HLA B27+ and HLA B27– pts in changes from baseline in the axial disease-related outcome measures assessed (Table 3). In an exploratory analysis of a subgroup of these pts with radiologic confirmation of axial involvement (n=21), similar outcomes were observed (data not shown).
Conclusion: In this registry study of PsA pts with physician-reported axial disease, after 6 months of treatment with bDMARD or tsDMARD therapy, only mild improvements in axial disease-related outcome measures were observed. Furthermore, response did not differ based on HLA-B27 status. The continued high disease activity of these pts reflects a critical unmet need for additional safe and effective therapies for PsA axial disease.
Reference: 1. Mease et al. J Rheumatol 2018; 45:1389.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Chakravarty S, McLean R, Blachley T, Kawashima T, Lin I, Uy J, Kavanaugh A, Ogdie A. Clinical Characteristics of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients with Physician-Identified Spondylitis, According to HLA-B27 Status: An Analysis from the Corrona Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondyloarthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-with-physician-identified-spondylitis-according-to-hla-b27-status-an-analysis-from-the-corrona-psoriatic-arthritis-spondyloarthritis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-with-physician-identified-spondylitis-according-to-hla-b27-status-an-analysis-from-the-corrona-psoriatic-arthritis-spondyloarthritis-registry/