Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1442–1487) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Herpes zoster (HZ) is characterized by a painful dermatomal rash and is associated with increased healthcare costs and reduced quality of life. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is associated with an increased risk of HZ. Data on the clinical and economic impact of HZ among people with SLE in the United States (US) is limited. This study aimed to estimate healthcare resource utilization (HRU) and costs in patients with SLE and HZ in comparison to patients with SLE only.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used US administrative claims data (Optum Research Database) between October 2015 and March 2022 to identify adults (aged ≥18 years) with SLE, based on ≥1 inpatient or ≥2 outpatient claims ≥30 days apart with an International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnosis code for SLE (M32.xx, excluding M32.0). Patients with SLE were either assigned to an SLE+HZ or SLE-only cohort based on ≥1 HZ diagnosis code (ICD-10-CM: B02.xx, excluding B02.2x). Index date was the first observed HZ diagnosis between October 2016 and March 2022 for the SLE+HZ cohort and was assigned for the SLE-only cohort based on the distribution of index dates in the SLE+HZ cohort. All patients were required to have 12 months of continuous enrollment (CE) pre-index (baseline) and ≥1 month of CE post-index (follow-up). Patients with a baseline HZ diagnosis or a HZ vaccine in the up to 5 years pre-index (depending on data availability for patients) were excluded. Clinical and demographic characteristics were measured during baseline. Patients with SLE+HZ were propensity score matched 1:4 to patients with SLE-only with at least as much post-index follow-up time. Propensity scores were calculated using logistic regression with cohort as the outcome and baseline characteristics as predictors. Outcomes included all-cause HRU and costs in the 1-month period post-index and for matched sets with sufficient follow-up time, also in the 3-month period post-index. Outcomes were described overall, and stratified by ambulatory, emergency room, inpatient, and pharmacy HRU and costs.
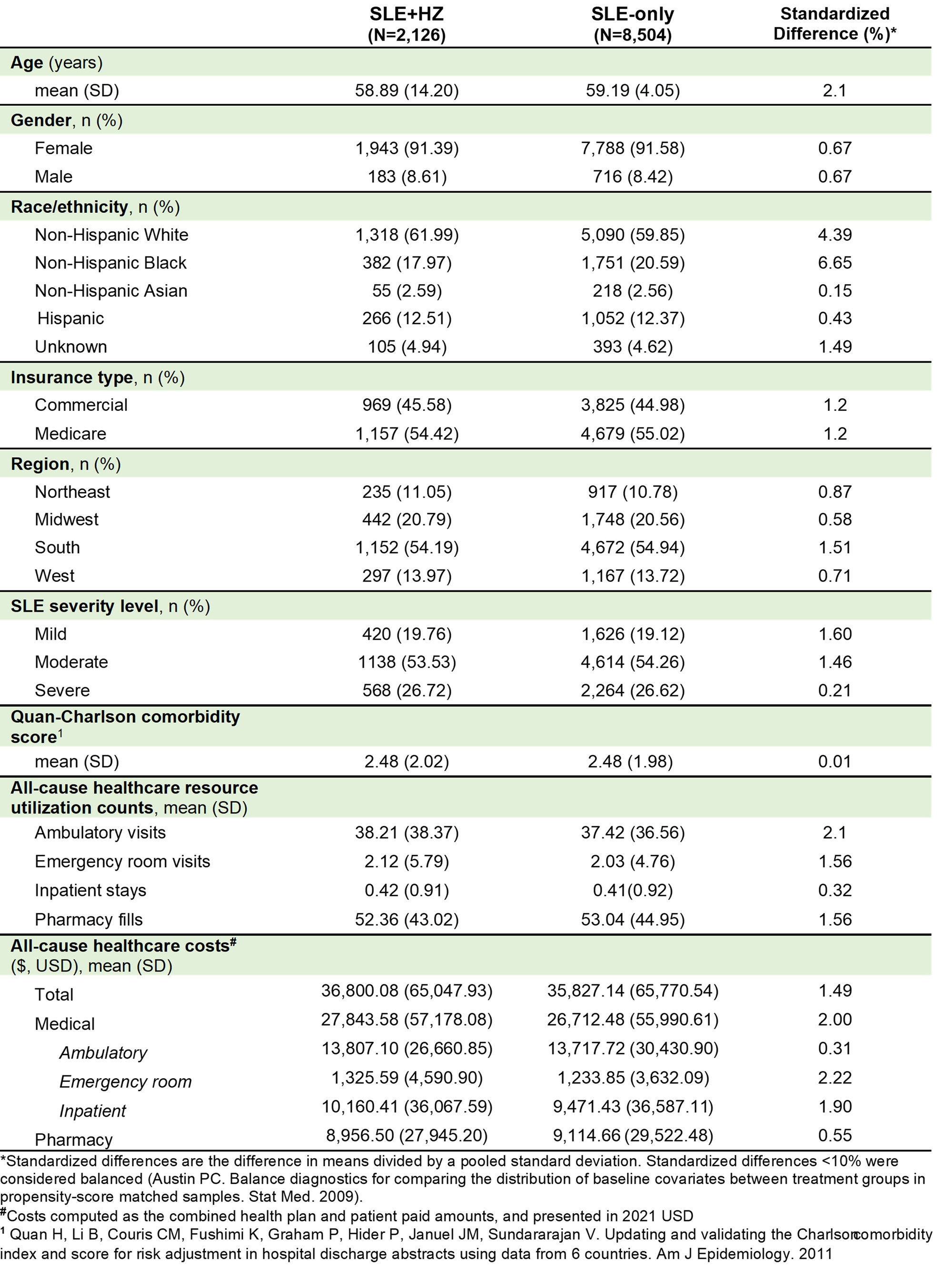
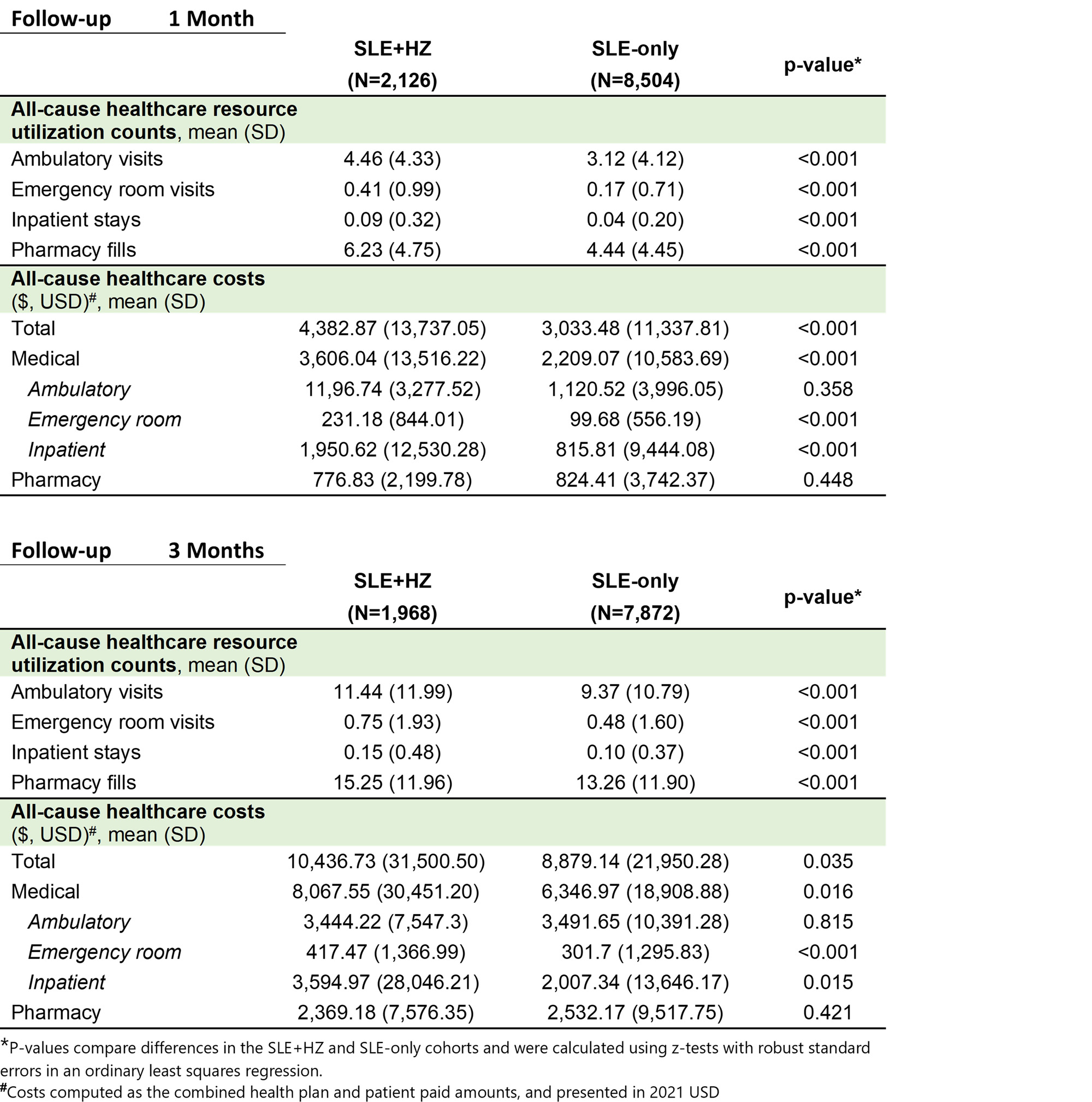
Results: After matching, 2,126 and 8,504 patients were included in the SLE+HZ and SLE-only cohorts, respectively. No significant differences were observed in demographic and clinical characteristics between the matched cohorts, with similar mean (standard deviation [SD]) age (59 [14]), percent female (91-92%), and baseline HRU and costs (table 1). In the 1-month post-index, mean (SD) HRU was higher in the SLE+HZ vs. SLE-only cohort for ambulatory (SLE+HZ: 4.5 [4.3]; SLE-only: 3.1 [4.1]) emergency (SLE+HZ: 0.41 [0.99]; SLE-only: 0.17 [0.71]), inpatient (SLE+HZ: 0.09 [0.32]; SLE-only: 0.04 [0.20]), and pharmacy HRU (SLE+HZ: 6.23 [4.75]; SLE-only: 4.44 [4.45]). Mean (SD) costs 1-month post-index were also higher in the SLE+HZ cohort ($4,383 [$13,737]) vs. SLE-only cohort ($3,033 [$11,337]). Among matched sets with ≥ 3 months of follow-up (93% of overall cohorts), higher HRU and costs in the SLE+HZ vs. SLE-only cohort were also observed in the 3-months post-index (Table 2).
Conclusion: Patients with SLE and HZ had higher HRU and costs than those without HZ, and HZ prevention may be important to consider in this population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stempniewicz N, Steffens A, Kim K, Bell C, DuCharme M, Trenz H, Singer D. Clinical and Economic Burden of Herpes Zoster in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Retrospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-economic-burden-of-herpes-zoster-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-retrospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-economic-burden-of-herpes-zoster-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-retrospective-cohort-study/