Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials of anifrolumab, an anti–type I IFN receptor mAb, enrolled autoantibody-positive (ANA, anti-dsDNA, and/or anti-Smith [anti-Sm]) patients, who fulfilled the ACR 1997 classification criteria for SLE.1–3 The aim of this analysis was to assess how many patients who participated in the TULIP trials also met the updated EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria.4
Methods: TULIP-1 (NCT02446912) and TULIP-2 (NCT02446899) were randomized, placebo-controlled, 52-week trials of intravenously administered anifrolumab in patients with moderate to severe SLE despite standard therapy. Inclusion criteria included fulfilling at least 4 of the ACR 1997 criteria for SLE, positivity for ANA, anti-dsDNA, and/or anti-Sm antibodies, and moderate to severe SLE. Data for investigating classification using EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria were combined from the ACR criteria, BILAG-specific SLE history, and documented medical history.
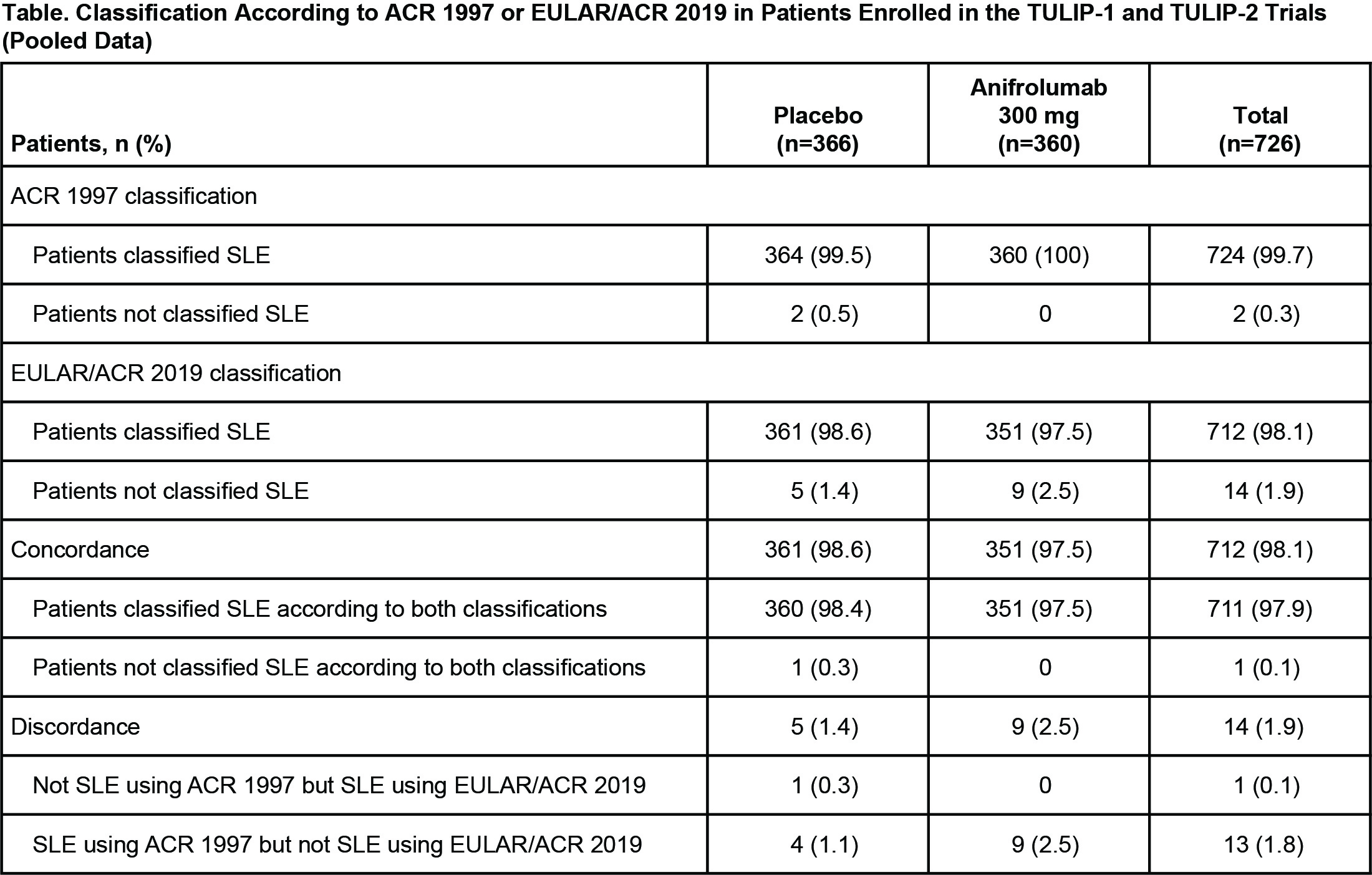
Results: The TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 data pool included 726 patients with SLE. Of these, all but 2 (99.7%) met the ACR 1997 SLE criteria (Table). The EULAR/ACR 2019 classification criteria for SLE were met by 712/726 patients (98.1%). Thus, most patients (97.9% [711/726]) were concordant in meeting both the ACR 1997 and EULAR/ACR 2019 SLE classification criteria. Of the patients classified as having SLE using ACR 1997 criteria, 1.8% (13/726) did not meet the EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria. Of these 13 discordant patients, 8 were ANA negative but either anti-dsDNA or anti-Sm antibody positive, 5 were ANA positive and were discordant mainly due to photosensitivity not being included in the EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria. Two patients did not meet ACR 1997 criteria at baseline; one patient was not classified as having SLE using either ACR 1997 or EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria, and the other patient was classified as having SLE using EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria. This latter discordant patient did not meet ACR 1997 criteria, having just nonerosive arthritis and positive ANA, but met EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria with positive ANA, fever, nonscarring alopecia, and joint involvement. At study baseline, positive ANA (97.2%) and nonerosive arthritis (97.5%) were the 2 most frequent ACR 1997 criteria among all patients.
Conclusion: Nearly all patients enrolled in the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials were classifiable as having SLE using both the ACR 1997 criteria and the EULAR/ACR 2019 criteria. Of the patients not meeting the new criteria, most were ANA negative but had detectable autoantibodies against dsDNA and/or Sm.
1. Furie RA. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019;1:e208–19.
2. Morand EF. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:211–21.
3. Hochberg MC. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1725.
4. Aringer M. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71:1400–12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aringer M, Bruce I, Furie R, Morand E, Maho E, Lindholm C, Tummala R. Classification of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Enrolled in 2 Phase 3 Trials by EULAR/ACR 2019 Criteria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/classification-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-enrolled-in-2-phase-3-trials-by-eular-acr-2019-criteria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/classification-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-enrolled-in-2-phase-3-trials-by-eular-acr-2019-criteria/