Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treat-to-target strategies in PsA recommend aiming for remission or low disease activity (LDA). Several disease activity measures are available including very low/minimal disease activity (VLDA/MDA), cutoffs based on the Disease Activity in PsA (DAPSA) score, and on the Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) score.
We assessed the rates of patients (pts) achieving these criteria at Weeks 12 and 24 using data from the SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2 Phase 3 studies.1,2 Additionally, we assessed the distribution of individual MDA components among pts who did or did not achieve MDA criteria at Week 24.
Methods: This is a post-hoc analysis of 2 randomized controlled trials. In SELECT-PsA 1, pts with PsA and prior inadequate response (IR) or intolerance to ≥1 non-biologic DMARD (N=1705) were randomized to once daily upadacitinib (UPA) 15mg (UPA15), UPA 30mg (UPA30), adalimumab (ADA) 40mg every other week, or placebo (PBO). In SELECT-PsA 2, pts with prior IR or intolerance to ≥1 biologic DMARD (N=642) were randomized to UPA15, UPA30, or PBO. Remission and LDA were assessed using VLDA/MDA, DAPSA scores of ≤4/≤14, and PASDAS scores of ≤1.9/≤3.2, at Weeks 12 and 24 (Table).
For binary outcomes, non-responder imputation (NRI) was used for handling missing data. For MDA and related analyses, NRI was used for handling missing data; pts rescued at Week 16 were considered non-responders. Pairwise comparisons between UPA doses and PBO or ADA were conducted using the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test.
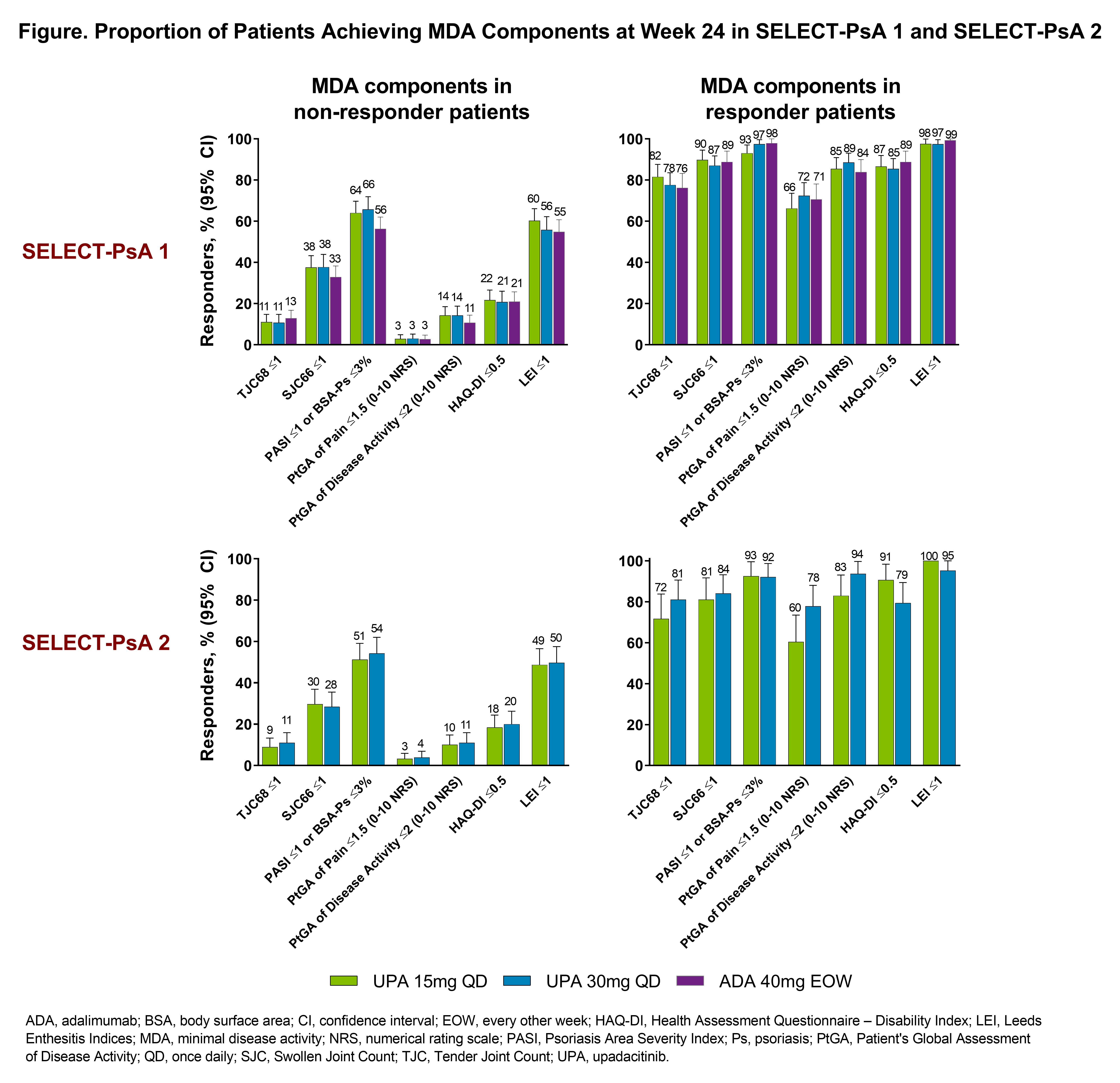
Results: Overall, 2345 pts were analyzed; mean age 51 years, 53% female. In both studies, higher rates of remission and LDA were observed with both UPA doses vs PBO at Weeks 12 and 24 (nominal P-values < 0.05 for both time points; Table). Generally, higher rates of remission and LDA were also observed with UPA30 vs ADA in non-biologic DMARD-IR pts (nominal P-values < 0.05). Greater rates of MDA/VLDA were observed at Weeks 12 and 24 with UPA15 and UPA30 vs PBO in both studies and with UPA30 vs ADA in non-biologic DMARD-IR pts (nominal P-values < 0.05 for all comparisons). The proportion of responder or non-responder pts receiving UPA15 or UPA30 was similar for each of the MDA components in both studies. At Week 24, more responder and non-responder pts in both studies achieved Swollen Joint Count (SJC) 66 ≤1, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) ≤1 or Body Surface Area-Psoriasis (BSA-Ps) ≤3%, and Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) ≤1 (Figure). Conversely, the proportion of pts Achieving Tender Joint Count (TJC) 68 ≤1 and Pt’s Global Assessment of Pain ≤1.5 tended to be lower.
Conclusion: Regardless of previous biologic DMARD failure, pts treated with UPA15 or UPA30 achieved a higher rate of remission or LDA measured by various disease activity measures vs PBO at Weeks 12 and 24; higher rates of response were observed in most of the remission and LDA measures with UPA30 vs ADA in non-biologic DMARD-IR pts. Among pts who did or did not achieve MDA criteria at Week 24, a greater proportion of UPA-treated pts achieved physician derived measures such as SJC ≤1, PASI ≤1 or BSA-Ps ≤3%, and LEI ≤1.
References
1. McInnes IB, et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020; 79:12.
2. Genovese MC, et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020; 79:139.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Kavanaugh A, Gladman D, FitzGerald O, Soriano E, Nash P, Feng D, Lertratanakul A, Douglas K, Lippe R, Gossec L. Characterization of Remission in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Upadacitinib: Post-hoc Analysis from Two Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-remission-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-upadacitinib-post-hoc-analysis-from-two-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-remission-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-upadacitinib-post-hoc-analysis-from-two-phase-3-trials/