Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Oligoarticular psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is commonly reported in early disease. Although fewer joints are involved, there may be significant impact on patients’ (pts) quality of life. The ongoing FOREMOST study (NCT03747939) is investigating the efficacy of apremilast vs placebo for treatment of early oligoarticular PsA ( >1 but ≤4 tender and swollen joints involved). The objective of this analysis is to characterize disease burden in pts with early oligoarticular PsA and disease phenotype including location and size of involved joints and presence of certain baseline clinical PsA manifestations in FOREMOST pts.
Methods: Study inclusion criteria include >1 but ≤4 tender and swollen joints involved and meeting the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis at screening. Baseline swollen and tender joint distribution was analyzed. Baseline disease burden was assessed in the overall group and a subgroup with small joint involvement only (for context) using clinical disease activity measures, pt-reported outcomes, and additional PsA manifestations.
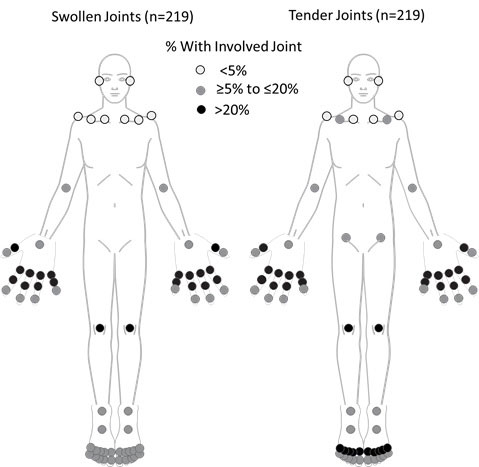
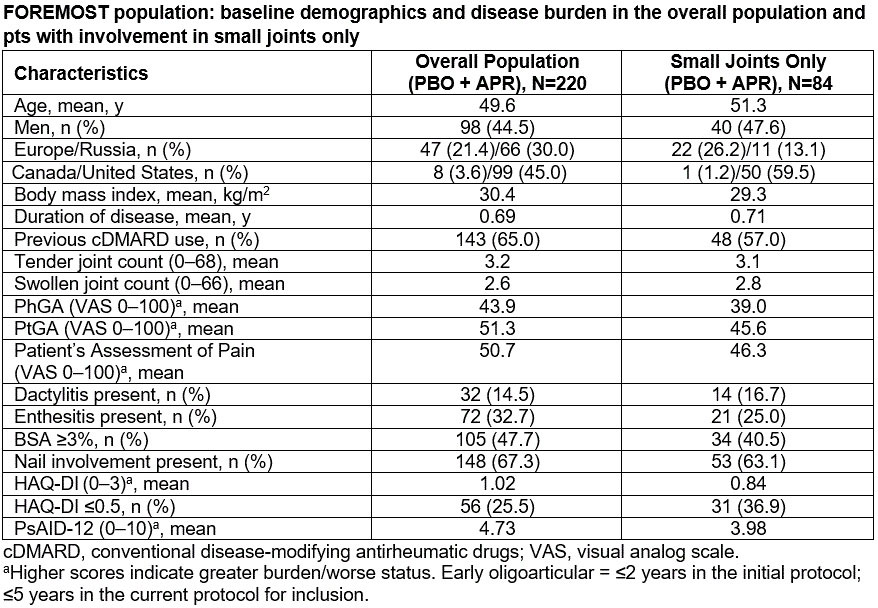
Results: At data cut-off for analysis, 220 pts of 285 planned were enrolled. In the overall group, disease duration was < 1 year and joint distribution for swollen or tender joints involved predominantly small joints, with ~48% of joint involvement observed in finger proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints and < 2% in temporomandibular and clavicular joints across swollen or tender joints (Figure). Mean Physician’s and Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PhGA and PtGA, respectively) scores were 43.9 and 51.3; mean pt pain assessment score was 50.7. Mean Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) functional assessment score was 1.0; 25.5% of pts had HAQ-DI ≤0.5. Pts reported an average PsA Impact of Disease (PsAID-12) domain score of 4.7. Additional manifestations of PsA at baseline included dactylitis (14.5%), enthesitis (32.7%), nail involvement (67.3%), and skin disease (47.7% with body surface area [BSA] ≥3%). Within the overall group, 59% had >1 joint size involved (small [metacarpophalangeal, metatarsophalangeal, distal interphalangeal, PIP, hand carpometacarpal and mid-tarsal]; intermediate [wrist, elbow, ankle, temporomandibular, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular]; large [shoulder, hip, knee]; Figure). Of those with only 1 joint size involved (41% of pts), the majority had small joint involvement predominantly in PIPs (n=84 for small joints; n=1 for intermediate joints; n=5 for large joints). The overall pattern of clinical and disease presentation indicated elevated burden for pts with early oligoarticular PsA, including those pts with only small joints involved (Table).
Conclusion: In FOREMOST, despite few joints involved, pts with early oligoarticular PsA experienced high disease burden and impaired quality of life. Small joint involvement, although less commonly expected in oligoarticular PsA, was the most frequently observed pattern.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gladman D, Coates L, Gossec L, Aelion J, Vasandani J, Cheng S, Tang L, Jardon S, Richter S, Mease P. Characterization of Joint Distribution and Disease Burden in Patients with Early Oligoarticular Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from the Ongoing FOREMOST Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-joint-distribution-and-disease-burden-in-patients-with-early-oligoarticular-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-ongoing-foremost-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-joint-distribution-and-disease-burden-in-patients-with-early-oligoarticular-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-ongoing-foremost-study/