Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The PALACE 1, 2, and 3 trials evaluated the efficacy and safety of apremilast (APR) in subjects with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) despite prior conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and/or biologics. The objective of this analysis is to further characterize the clinical benefits associated with long-term APR exposure in subjects who failed to achieve an ACR20 response at Week 104.
Methods: Subjects were randomized (1:1:1) at baseline to receive placebo (PBO), APR 30 mg BID (APR30), or APR 20 mg BID. Subjects who were randomized to APR30 at baseline and classified as ACR20 non-responders (ACR20NRs) at Week 104 were considered for this analysis. At Weeks 24, 52, and 104, ACR core components were examined as well as the proportions of subjects achieving a low disease activity (LDA) state (Clinical Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis [cDAPSA] score ≤13), PASI-75/PASI-50 response among those with psoriasis involvement >3% of the body surface area at baseline, and dactylitis count and Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis Score (MASES) of 0 among those with dactylitis or enthesitis at baseline. Safety is described for the overall PALACE 1-3 population.
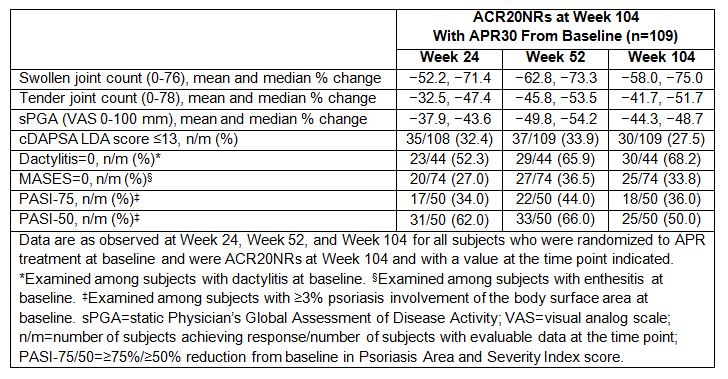
Results: A total of 109 subjects randomized to APR30 treatment at baseline were ACR20NRs at Week 104. Lack of improvement in Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity, patient’s assessment of pain, HAQ-DI, and C-reactive protein outcomes most commonly had an impact on patients’ inability to achieve an ACR20 response. Baseline ACR core components were similar for ACR20NRs and ACR20 responders at Week 104. Among these ACR20NRs, several core components of ACR response, including swollen/tender joint counts and static Physician’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity (visual analog scale) scores, showed sustained improvements from baseline through Week 104 (Table). Importantly, of the 109 ACR20NRs at Week 104, 27.5% achieved cDAPSA LDA state and 50.0% achieved a PASI-50 response after continued treatment with APR30 through Week 104 (Table). Among ACR20NRs with baseline dactylitis (n=44) or enthesitis (n=74), 68.2% achieved a dactylitis count of 0 and 33.8% achieved a MASES of 0 at Week 104. In the overall subject population, no new safety concerns were identified through 104 weeks.
Conclusion: ACR20NRs receiving APR30 demonstrated significant improvements in core PsA domains. The data may explain why subjects who failed to achieve an ACR20 response remained on long-term APR treatment. These findings suggest that some subjects with PsA may experience meaningful clinical improvement that is not completely captured by the assessment of ACR20 response criteria. Outcome measures specifically designed for PsA patients may be more suitable for evaluating treatment response in PsA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease PJ, Gladman DD, Kavanaugh A, Nakasato P, Guerette B, Teng L, Nash P. Characterization of Clinical Benefits in Subjects Classified As ACR20 Non-Responders at Week 104 of Apremilast Treatment: Subanalysis of 3 Long-Term, Phase III Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-clinical-benefits-in-subjects-classified-as-acr20-non-responders-at-week-104-of-apremilast-treatment-subanalysis-of-3-long-term-phase-iii-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-clinical-benefits-in-subjects-classified-as-acr20-non-responders-at-week-104-of-apremilast-treatment-subanalysis-of-3-long-term-phase-iii-trials/