Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a severe systemic autoimmune disease in which multiple autoantibodies against nuclear, cytoplasmic and cell surface auto-antigens are produced by antibody secreting cells (ASCs). In the non-disease state, the frequency of circulating ASCs in total B cells is extremely low, and increases in a tightly regulated manner following immunization or infection. However, during active SLE, ASCs are dysregulated and exhibit a dramatic increase in the circulation. Indeed, the frequency of ASCs in the peripheral blood is correlated with disease activity, as measured by the SLEDAI scoring system. Despite their clinical significance, the subsets, morphology, and molecular phenotypes of circulating ASCs in SLE remain largely unknown.
Methods: Healthy subjects received the vaccination against influenza virus were recruited and peripheral blood from healthy controls was obtained at the steady state or at the peak of antibody secreting response after vaccination (day 6-7). Patients with SLE fulfilled four or more criteria of the modified American College of Rheumatology classification were recruited and evaluated by expert rheumatologists for disease status.
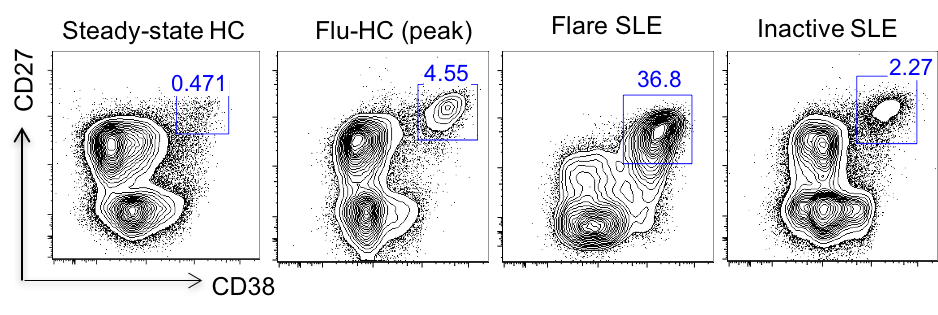
Results: In this study, peripheral ASC were divided into 4 subsets based on the surface expression of the CD19 and CD138: CD19+CD138- (pop2), CD19+CD138+ (pop3), CD19-CD138- (pop4), and CD19-CD138+ (pop5). CD19+ subsets, and to a larger extent, CD19- subsets, were markedly increased in active SLE patients compared to healthy controls post flu-vaccination. Besides, electron microscopy showed ultrastructural changes in the circulating ASCs subsets from active SLE patients relative to those from vaccinated healthy controls, including a condensed nucleus, enhanced endoplasmic reticulum volume, increased numbers of mitochondria, and presence of autophagosomes, features resembling those of bone marrow plasma cells. Interestingly, phenotypic characterization of circulating ASCs suggested that those from active SLE patients had significantly elevated expression of CXCR4, receptors for homing and survival in the bone marrow, compared to healthy controls post vaccination. Furthermore, next generation sequencing was used to analyze the clonality and connectivity between circulating ASC subsets from active SLE patients. In most flare SLE patients, we observed highly polyclonal repertoire and clonal relatedness in all ASC subsets.
Conclusion: Together, these data show that, during flare SLE, ASCs dramatically increase and undergo morphological changes and CXCR4 upregulation, indicating their potential of bone marrow homing and becoming long-lived plasma cells.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen W, Hong S, Tipton C, Hom J, Anam F, Lee E, Sanz I. Characterization of Antibody Secreting Cells in Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-antibody-secreting-cells-in-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-antibody-secreting-cells-in-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/